Fujian

Fujian

Fujian Province 福建省 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Province | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name transcription(s) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Chinese | 福建省(Fújiàn Shěng) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Abbreviation | FJ /闽(pinyin: Mǐn, POJ: Bân) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Hokkien POJ | Hok-kiàn | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Foochow | Hók-gióng | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
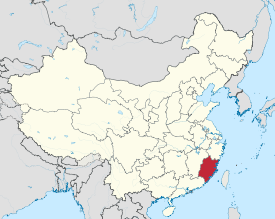 Map showing the location of Fujian Province | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates:25°54′N 118°18′E [74] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Fuzhou | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Largest city | Xiamen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Divisions | ****9 prefectures, 85[9] counties, 1107[9] townships | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Secretary | Yu Weiguo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Governor | Tang Dengjie | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 121,400 km2(46,900 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area rank | 23rd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation | 2,158 m (7,080 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population (2017)[11] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 38,565,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 17th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Density | 320/km2(820/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Density rank | 14th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demographics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Ethnic composition | Han – 98% She – 1% Hui – 0.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Languages and dialects | Min (inc. Hokkien dialects, Fuzhounese), Mandarin, Hakka | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | CN-FJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP(2018) | CN¥3.58 trillion US$540.78 billion[12] (10th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • per capita | CN¥92,830 US$14,022 (6th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HDI(2014) | 0.758[13] (high) (11th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www.Fujian.gov.cn [75] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fujian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
"Fujian" in Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 福建 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Fu(zhou) and Jian(zhou)" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 闽 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 閩 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | [the Min River] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fujian (福建; alternately romanized as Fukien) is a province on the southeast coast of mainland China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou, while its largest city by population is Xiamen, both located near the coast of the Taiwan Strait in the east of the province. The name Fujian came from the combination of Fuzhou and Jianzhou (present Nanping), a city in Fujian, during the Tang dynasty.
While its population is chiefly of Han origin, it is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse provinces in China. Historically the dialects of the language group Min Chinese were most commonly spoken within the province, including the Hokkien dialects of southeastern Fujian. This is reflected in the abbreviation of the province's name (閩). Hakka Chinese is also spoken, by the Hakka people in Fujian. Min and Hakka Chinese are unintelligible with Mandarin Chinese. Due to emigration, a sizable amount of the ethnic Chinese populations of Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and Philippines speak Hokkien.
As a result of the Chinese Civil War, Historical Fujian is now divided between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC, Taiwan), and both territories are named the Fujian province in their respective administration divisions. The majority of the territory of historical Fujian (the mainland territory and a few islands) currently make up the Fujian province of the PRC. The Fujian province of the ROC is made up of the Matsu Islands, the Wuqiu Islands and the Kinmen Islands, the two latter archipelagos constituting Kinmen County.
With a population of 39 million, Fujian ranks 17th in population among Chinese provinces. Its GDP is CN¥3.58 trillion, ranking 10th in GDP. Along with its coastal neighbours Zhejiang and Guangdong, Fujian's GDP per capita is above the national average, at CN¥92,830. It has benefited from its geographical proximity with Taiwan.
Fujian Province 福建省 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Province | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name transcription(s) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Chinese | 福建省(Fújiàn Shěng) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Abbreviation | FJ /闽(pinyin: Mǐn, POJ: Bân) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Hokkien POJ | Hok-kiàn | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Foochow | Hók-gióng | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map showing the location of Fujian Province | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates:25°54′N 118°18′E [74] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Fuzhou | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Largest city | Xiamen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Divisions | ****9 prefectures, 85[9] counties, 1107[9] townships | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Secretary | Yu Weiguo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Governor | Tang Dengjie | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 121,400 km2(46,900 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area rank | 23rd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation | 2,158 m (7,080 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population (2017)[11] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 38,565,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 17th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Density | 320/km2(820/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Density rank | 14th | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demographics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Ethnic composition | Han – 98% She – 1% Hui – 0.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Languages and dialects | Min (inc. Hokkien dialects, Fuzhounese), Mandarin, Hakka | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | CN-FJ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP(2018) | CN¥3.58 trillion US$540.78 billion[12] (10th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • per capita | CN¥92,830 US$14,022 (6th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HDI(2014) | 0.758[13] (high) (11th) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www.Fujian.gov.cn [75] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fujian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
"Fujian" in Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 福建 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Fu(zhou) and Jian(zhou)" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 闽 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 閩 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | [the Min River] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
Prehistoric Fujian
Recent archaeological discoveries in 2011 demonstrate that Fujian had entered the Neolithic Age by the middle of the 6th millennium BC.[14] From the Keqiutou site (7450–5590 BP), an early Neolithic site in Pingtan Island located about 70 kilometres (43 mi) southeast of Fuzhou, numerous tools made of stones, shells, bones, jades, and ceramics (including wheel-made ceramics) have been unearthed, together with spinning wheels, which is definitive evidence of weaving.
The Tanshishan (曇石山) site (5500–4000 BP) in suburban Fuzhou spans the Neolithic and Chalcolithic Age where semi-underground circular buildings were found in the lower level. The Huangtulun (黃土崙) site (ca.1325 BC), also in suburban Fuzhou, was of the Bronze Age in character.
There were four major Neolithic cultures in coastal Fujian, with the earliest Neolithic cultures originating from the north in coastal Zhejiang.[15]
Keqiutou culture 壳丘头文化 (c. 6000–5500 BP, or c. 4050–3550 BC)
Tanshishan culture 昙石山文化 (c. 5000–4300 BP, or c. 3050–2350 BC)
Damaoshan culture 大帽山文化 (c. 5000–4300 BP)
Huangguashan culture 黄瓜山文化 (c. 4300–3500 BP, or c. 2350–1550 BC)
There were two major Neolithic cultures in inland Fujian, which were highly distinct from the coastal Fujian Neolithic cultures.[15] These are the Niubishan culture (牛鼻山文化) from 5000–4000 years ago, and the Hulushan culture (葫芦山文化) from 2050 to 1550 BC.
Minyue kingdom
Fujian was also where the kingdom of Minyue was located. The word "Mǐnyuè" was derived by combining "Mǐn" (simplified Chinese: 闽; traditional Chinese: 閩; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: bân), which is perhaps an ethnic name (simplified Chinese: 蛮; traditional Chinese: 蠻; pinyin: mán; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: bân), and "Yuè", after the State of Yue, a Spring and Autumn period kingdom in Zhejiang to the north. This is because the royal family of Yuè fled to Fujian after its kingdom was annexed by the State of Chu in 306 BC. Mǐn is also the name of the main river in this area, but the ethnonym is probably older.
Han dynasty
Minyue was a de facto kingdom until one of the emperors of the Qin dynasty, the first unified imperial Chinese state, abolished its status. In the aftermath of the Qin dynasty's fall, civil war broke out between two warlords, Xiang Yu and Liu Bang. The Minyue king Wuzhu sent his troops to fight with Liu and his gamble paid off. Liu was victorious and founded the Han dynasty. In 202 BC, he restored Minyue's status as a tributary independent kingdom. Thus Wuzhu was allowed to construct his fortified city in Fuzhou as well as a few locations in the Wuyi Mountains, which have been excavated in recent years. His kingdom extended beyond the borders of contemporary Fujian into eastern Guangdong, eastern Jiangxi, and southern Zhejiang.[16]
After Wuzhu's death, Minyue maintained its militant tradition and launched several expeditions against its neighboring kingdoms in Guangdong, Jiangxi, and Zhejiang, primarily in the 2nd century BC. This was stopped by the Han dynasty as it expanded southward. The Han emperor eventually decided to get rid of the potential threat by launching a military campaign against Minyue. Large forces approached Minyue simultaneously from four directions via land and sea in 111 BC. The rulers in Fuzhou surrendered to avoid a futile fight and destruction and the first kingdom in Fujian history came to an abrupt end.
The Han dynasty collapsed at the end of the 2nd century AD, paving the way for the Three Kingdoms era. Sun Quan, the founder of the Kingdom of Wu, spent nearly 20 years subduing the Shan Yue people, the branch of the Yue living in mountains.
Jin era
The first wave of immigration of the noble class arrived in the province in the early 4th century when the Western Jin dynasty collapsed and the north was torn apart by invasions by nomadic peoples from the north, as well as civil war. These immigrants were primarily from eight families in central China: Lin (林), Huang (黄), Chen (陈), Zheng (郑), Zhan (詹), Qiu (邱), He (何), and Hu (胡). The first four remain as the major surnames of modern Fujian.
Nevertheless, isolation from nearby areas owing to rugged terrain contributed to Fujian's relatively undeveloped economy and level of development, despite major population boosts from northern China during the "barbarian" invasions. Population density in Fujian remained low compared to the rest of China. Only two commanderies and sixteen counties were established by the Western Jin dynasty. Like other southern provinces such as Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, and Yunnan, Fujian often served as a destination for exiled prisoners and dissidents at that time.
During the Southern and Northern Dynasties era, the Southern Dynasties reigned south of the Yangtze River, including Fujian.
Sui and Tang dynasties
The Tang dynasty (618–907) oversaw the next golden age of China, which contributed to a boom in Fujian’s culture and economy. Fuzhou's economic and cultural institutions grew and developed. The later years of the Tang dynasty saw a number of political upheavals in the Chinese heartland, prompting another wave of Chinese to immigrate to Fujian.
Min kingdom
As the Tang dynasty ended, China was torn apart in the period of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms. During this time, a second major wave of immigration arrived in the safe haven of Fujian, led by General Wang, who set up an independent Kingdom of Min with its capital in Fuzhou. After the death of the founding king, however, the kingdom suffered from internal strife, and was soon absorbed by Southern Tang, another southern kingdom.[18]
Quanzhou city was blooming into a seaport under the reign of the Min Kingdom and was the largest seaport in the world. For a long period of time its population was also greater than Fuzhou.[19][20] Due to the Ispah Rebellion, Quanzhou city lost foreign interest of trading and its formerly welcoming international image as the foreigners were all massacred or deported.
Song dynasty
The Lý dynasty monarchs of Vietnam were of Chinese ethnicity.[21] Jinjiang district of Quanzhou prefecture was the origin of Lý Thái Tổ 李公蘊, the ancestor of the Lý dynasty ruling family.[6][22][23][24] China, Fujian was the home of Lý Công Uẩn. The ethnic Chinese background of Lý Công Uẩn has been accepted by Vietnamese historian Trần Quốc Vượng.[25]
The founder of the Trần Dynasty in Vietnam, Emperor Trần Thái Tông, was the great-grandson of a Chinese person who came to Vietnam from Fujian from the Chinese Chen clan. Several members of the family, like the prince Trần Quốc Tuấn, continued to know how to speak Chinese.[26][27] The name of the prince’s great grandfather was Trần Kinh.
People from the Song dynasty of China, like Zhao Zhong and Xu Zongdao, fled to the Trân dynasty after the Mongol invasion of China. The Daoist cleric Xu Zongdaowho, who recorded the Mongol invasion and called them "Northern bandits", also came from Fujian.[28]
Fujian or Guangxi was the origin of the ethnic Chinese Tran who migrated to Vietnam along with a large number of other Chinese, during the Vietnamese Ly dynasty, where they served as officials. Distinctly Chinese last names are found in the Tran and Ly dynasty Imperial exam records.[29] Ethnic Chinese are recorded in Tran and Ly dynasty records of officials.[30] Clothing, food, and language were all Chinese dominated in Van Don where the Tran had moved after leaving their home province of Fujian. The Chinese language could still be spoken by the Tran in Vietnam.[26] The side of Vietnam that borders the ocean was colonized by Chinese migrants from Fujian. This included the Tran among them who settled in the capital's southeastern area.[27][31] The Red River Delta was subjected to migration of people from different provinces all over China through Fujian's major city port. The Tran and Van Don port arose as a result of this interaction.[32] Fujian and Guangdong Chinese moved to the Van Don coastal port during Ly Anh Tong's rule to engage in commerce.[33] The usurpation of the Ly occurred after they married with the fishing Fujianese Tran family.[34]
In 1172 Fujian was attacked by Pi-she-ye pirates from Taiwan.[35]
Ming dynasty
In the early Ming dynasty, Quanzhou was the staging area and supply depot of Zheng He's naval expeditions. Further development was severely hampered by the sea trade ban, and the area was superseded by nearby ports of Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Ningbo and Shanghai despite the lifting of the ban in 1550. Large-scale piracy by Wokou was eventually wiped out by Chinese military and Japanese authority of Toyotomi Hideyoshi.
The Pisheya appear in Quanzhou Ming era records.[38]
Qing dynasty
The late Ming and early Qing dynasty symbolized an era of large influx of refugees and another 20 years of sea trade ban under the Kangxi Emperor, a measure intended to counter the refuge Ming government of Koxinga in the island of Taiwan.
The seaban implented by the Qing forced many people to evacuate the coast in order to deprive Koxinga's Ming loyalists of resources. This has led to the myth that it was because Manchus were "afraid of water".
Incoming refugees did not translate into a major labor force, owing to their re-migration into prosperous regions of Guangdong. In 1683, the Qing dynasty conquered Taiwan and annexed it into the Fujian province, as Taiwan Prefecture. Settlement of Taiwan by Han Chinese followed. Today, most Taiwanese are descendants of Hokkien people from Southern Fujian. Fujian arrived at its present extent after Taiwan was developed into an independent province (Fujian-Taiwan-Province) starting in 1885.[39] Just ten years later, the Qing ceded Taiwan to Japan via the Treaty of Shimonoseki after losing the First Sino-Japanese War.
Republic of China
The Xinhai revolution overthrew the Qing dynasty brought the province into the rule of the Republic of China.
Fujian briefly gained independence from China again under the Fujian People's Government until it was recontrolled by Republic of China.
It came under Japanese sea blockade during World War II.
People's Republic of China
Fujian's slow development in its early days has proved a blessing for the province's ecology; today, the province has the highest forest coverage rate and the most diverse biosphere in China whereas central China suffers from severe overpopulation and displays severe signs of soil erosion, with frequent droughts and floods due to lack of forest coverage.
Development has been accompanied by a large influx of population from the overpopulated areas in the north and west, and much of the farmland and forest, as well as cultural heritage sites such as the temples of king Wuzhu, have given way to ubiquitous high-rise buildings. The government faces challenges at all levels to sustain development while at the same time preserving Fujian's unique and vital natural and cultural heritage.
Geography

Wuyi Mountains

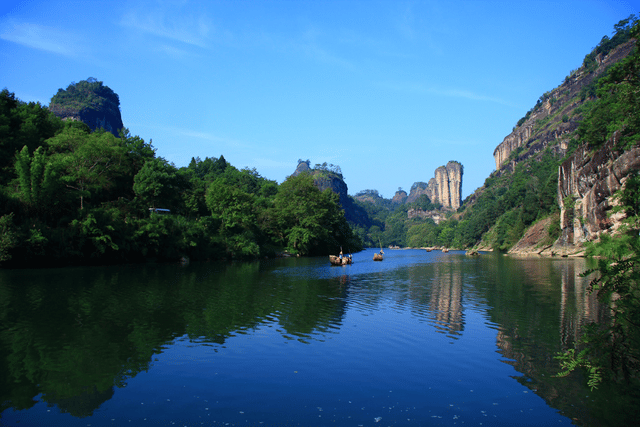
Min River (閩江) in Nanping (南平)
The province is mostly mountainous and is traditionally said to be "Eight parts mountain, one part water, and one part farmland" (八山一水一分田). The northwest is higher in altitude, with the Wuyi Mountains forming the border between Fujian and Jiangxi. It is the most forested provincial-level administrative region in China, with a 62.96% forest coverage rate in 2009.[40] Fujian's highest point is Mount Huanggang in the Wuyi Mountains, with an altitude of 2,157 metres (1.340 mi).
Fujian faces East China Sea to the east, South China Sea to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the southeast. The coastline is rugged and has many bays and islands. Major islands include Quemoy (also known as Kinmen) (controlled by the Republic of China), Haitan Island, and Nanri Island. Meizhou Island occupies a central place in the cult of the goddess Matsu, the patron deity of Chinese sailors.
The Min River and its tributaries cut through much of northern and central Fujian. Other rivers include the Jin and the Jiulong. Due to its uneven topography, Fujian has many cliffs and rapids.
Fujian is separated from Taiwan by the 180 kilometres (110 mi)-wide Taiwan Strait. Some of the small islands in the Taiwan Strait are also part of the province. The islands of Quemoy and Matsu are under the administration of the Republic of China.
Fujian contains several faults, the result of collision between the Asiatic Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate. The Changle-Naoao and Longan-Jinjiang fault zones in this area have annual displacement rates of 3–5 mm. They could cause major earthquakes in the future.[41]
Fujian has a subtropical climate, with mild winters. In January, the coastal regions average around 7–10 °C (45–50 °F) while the hills average 6–8 °C (43–46 °F). In the summer, temperatures are high, and the province is threatened by typhoons coming in from the Pacific. Average annual precipitation is 1,400–2,000 millimetres (55–79 in).
Transportation
Roads
As of 2012, there are 54,876 kilometres (34,098 miles) of highways in Fujian, including 3,500 kilometres (2,200 miles) of expressways. The top infrastructure projects in recent years have been the Zhangzhou-Zhaoan Expressway (US$624 million) and the Sanmingshi-Fuzhou expressway (US$1.40 billion). The 12th Five-Year Plan, covering the period from 2011 to 2015, aims to double the length of the province's expressways to 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi).[42]
Railways

Fuzhou train station
Due to Fujian's mountainous terrain and traditional reliance on maritime transportation, railways came to the province comparatively late. The first rail links to neighboring Jiangxi, Guangdong and Zhejiang Province, opened respectively, in 1959, 2000 and 2009. As of October 2013, Fujian has four rail links with Jiangxi to the northwest: the Yingtan–Xiamen Railway (opened 1957), the Hengfeng–Nanping Railway (1998), Ganzhou–Longyan Railway (2005) and the high-speed Xiangtang–Putian Railway (2013). Fujian's lone rail link to Guangdong to the west, the Zhangping–Longchuan Railway (2000), will be joined with the high-speed Xiamen–Shenzhen Railway (Xiashen Line) in late 2013. The Xiashen Line forms the southern-most section of China's Southeast Coast High-Speed Rail Corridor. The Wenzhou–Fuzhou and Fuzhou–Xiamen sections of this corridor entered operation in 2009 and links Fujian with Zhejiang with trains running at speeds of up to 250 km/h (155 mph).
Within Fujian, coastal and interior cities are linked by the Nanping–Fuzhou (1959), Zhangping–Quanzhou–Xiaocuo (2007) and Longyan–Xiamen Railways, (2012). To attract Taiwanese investment, the province intends to increase its rail length by 50 percent to 2,500 km (1,553 mi).[43]
Air
The major airports are Fuzhou Changle International Airport, Xiamen Gaoqi International Airport, Quanzhou Jinjiang International Airport, Nanping Wuyishan Airport, Longyan Guanzhishan Airport and Sanming Shaxian Airport. Xiamen is capable of handling 15.75 million passengers as of 2011. Fuzhou is capable of handling 6.5 million passengers annually with a cargo capacity of more than 200,000 tons. The airport offers direct links to 45 destinations including international routes to Japan, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and Hong Kong.[43]
Administrative divisions
The People's Republic of China controls most of the province and divides it into nine prefecture-level divisions: all prefecture-level cities (including a sub-provincial city):
| Administrative divisions of Fujian | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Prefecture-level city district areasCounty-level cities Prefecture-level city district areasCounty-level cities | ||||||||||
| № | Division code[44] | Division | Area in km2[45] | Population 2010[46] | Seat | Divisions[47] | ||||
| Districts | Counties | CL cities | ||||||||
| 350000 | Fujian Province | 121400.00 | 36,894,217 | Fuzhou city | 29 | 44 | 12 | |||
| 1 | 350100 | Fuzhou city | 12155.46 | 7,115,369 | Gulou District | 6 | 6 | 1 | ||
| 2 | 350200 | Xiamen city | 1699.39 | 3,531,347 | Siming District | 6 | ||||
| 6 | 350300 | Putian city | 4119.02 | 2,778,508 | Chengxiang District | 4 | 1 | |||
| 8 | 350400 | Sanming city | 22928.79 | 2,503,388 | Meilie District | 2 | 9 | 1 | ||
| 7 | 350500 | Quanzhou city | 11245.00 | 8,128,533 | Fengze District | 4 | 5* | 3 | ||
| 9 | 350600 | Zhangzhou city | 12873.33 | 4,809,983 | Longwen District | 2 | 8 | 1 | ||
| 4 | 350700 | Nanping city | 26280.54 | 2,645,548 | Jianyang District | 2 | 5 | 3 | ||
| 3 | 350800 | Longyan city | 19028.26 | 2,559,545 | Xinluo District | 2 | 4 | 1 | ||
| 5 | 350900 | Ningde city | 13452.38 | 2,821,996 | Jiaocheng District | 1 | 6 | 2 | ||
Sub-provincial cities *- including Kinmen County, ROC (Taiwan). Claimed by the PRC. (included in the total Counties' count) | ||||||||||
| Administrative divisions in Chinese and varieties of romanizations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Chinese | Pinyin | Fuzhou BUC | Hokkien POJ |
| Fujian Province | 福建省 | Fújiàn Shěng | Hók-gióng-sēng | Hok-kiàn-séng |
| Fuzhou city | 福州市 | Fúzhōu Shì | Hók-ciŭ-chê | Hok-chiu-chhī |
| Xiamen city | 厦门市 | Xiàmén Shì | Â-muòng-chê | Ē-mn̂g-chhī |
| Putian city | 莆田市 | Pútián Shì | Può-dièng-chê | Phô͘-chhân-chhī |
| Sanming city | 三明市 | Sānmíng Shì | Săng-mìng-chê | Sam-bêng-chhī |
| Quanzhou city | 泉州市 | Quánzhōu Shì | Ciòng-ciŭ-chê | Choân-chiu-chhī |
| Zhangzhou city | 漳州市 | Zhāngzhōu Shì | Ciŏng-ciŭ-chê | Chiang-chiu-chhī |
| Nanping city | 南平市 | Nánpíng Shì | Nàng-bìng-chê | Lâm-pêng-chhī |
| Longyan city | 龙岩市 | Lóngyán Shì | Lṳ̀ng-ngàng-chê | Lêng-nâ-chhī |
| Ningde city | 宁德市 | Níngdé Shì | Nìng-dáik-chê | Lêng-tek-chhī |
All of the prefecture-level cities except Nanping, Sanming, and Longyan are found along the coast.
The nine prefecture-level divisions are subdivided into 85 county-level divisions (28 districts, 13 county-level cities, and 44 counties). Those are in turn divided into 1,107 township-level divisions (605 towns, 328 townships, 18 ethnic townships, and 156 subdistricts).
The PRC claims Wuqiu Township, Kinmen County, Republic of China (Taiwan) as part of Xiuyu District of the prefecture-level city of Putian.
Finally, the PRC claims Matsu Islands (Lienchiang County), Republic of China (Taiwan) as a township of its Lianjiang County, which is part of the prefecture-level city of Fuzhou.
Together, these three groups of islands make up the Republic of China's Fujian Province.
Urban areas
| Population by urban areas of prefecture & county cities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | Urban area[51] | District area[51] | City proper[51] | Census date | |
| 1 | Xiamen | 3,119,110 | 3,531,347 | 3,531,347 | 2010-11-01 |
| 2 | Fuzhou[1][2] | 2,824,414 | 2,921,762 | 7,115,369 | 2010-11-01 |
| (2) | Fuzhou(new district)[1] | 278,007 | 682,626 | see Fuzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 3 | Jinjiang | 1,172,827 | 1,986,447 | see Quanzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 4 | Quanzhou[3] | 1,154,731 | 1,435,185 | 8,128,533 | 2010-11-01 |
| 5 | Putian | 1,107,199 | 1,953,801 | 2,778,508 | 2010-11-01 |
| 6 | Nan'an | 718,516 | 1,418,451 | see Quanzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 7 | Zhangzhou | 614,700 | 705,649 | 4,809,983 | 2010-11-01 |
| 8 | Fuqing | 470,824 | 1,234,838 | see Fuzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 9 | Shishi | 469,969 | 636,700 | see Quanzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 10 | Longyan[4] | 460,086 | 662,429 | 2,559,545 | 2010-11-01 |
| (10) | Longyan(new district)[4] | 136,496 | 362,658 | see Longyan | 2010-11-01 |
| 11 | Longhai | 422,993 | 877,762 | see Zhangzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 12 | Sanming | 328,766 | 375,497 | 2,503,388 | 2010-11-01 |
| 13 | Fu'an | 326,019 | 563,640 | see Ningde | 2010-11-01 |
| 14 | Nanping[5] | 301,370 | 467,875 | 2,645,548 | 2010-11-01 |
| (14) | Nanping(new district)[5] | 150,756 | 289,362 | see Nanping | 2010-11-01 |
| 15 | Fuding | 266,779 | 276,740 | see Ningde | 2010-11-01 |
| 16 | Ningde | 252,497 | 429,260 | 2,821,996 | 2010-11-01 |
| 17 | Yong'an | 213,732 | 347,042 | see Sanming | 2010-11-01 |
| 18 | Jian'ou | 192,557 | 231,583 | see Nanping | 2010-11-01 |
| 19 | Shaowu | 183,457 | 140,818 | see Nanping | 2010-11-01 |
| 20 | Wuyishan | 122,801 | 121,317 | see Nanping | 2010-11-01 |
| 21 | Zhangping | 113,739 | 126,611 | see Longyan | 2010-11-01 |
Politics
List of the Secretaries of the CPC Fujian Committee
Zhang Dingcheng (张鼎丞): June 1949 – October 1954
Ye Fei (叶飞): October 1954 – June 1958
Jiang Yizhen (江一真): acting 1958–1970
Han Xianchu (韩先楚): April 1971 – December 1973
Liao Zhigao (廖志高): December 1974 – February 1982
Xiang Nan (项南): February 1982 – March 1986
Chen Guangyi (陈光毅); March 1986 – December 1993
Jia Qinglin (贾庆林): December 1993 – October 1996
Chen Mingyi (陈明义): October 1996 – December 2000
Song Defu (宋德福): December 2000 – February 2004
Lu Zhangong (卢展工): February 2004 – November 2009
Sun Chunlan (孙春兰): November 2009 – December 2012
You Quan (尤权): December 2012 – October 2017
Yu Weiguo (于伟国): October 2017 – present
List of Governors
Zhang Dingcheng (张鼎丞): August 1949 – October 1954
Ye Fei (叶飞): October 1954 – January 1959
Jiang Yizhen (江一真): October 1959 – December 1962
Wen Jinshui (魏金水): December 1962 – August 1968
Han Xianchu (韩先楚): August 1968 – December 1973
Liao Zhigao (廖志高): November 1974-December 1979
Ma Xingyuan (马兴元): December 1979 – January 1983
Hu Ping (胡平): January 1983 – September 1987
Wang Zhaoguo (王兆国): September 1987 – November 1990
Jia Qinglin (贾庆林): November 1990 – April 1994
Chen Mingyi (陈明义): April 1994 – October 1996
He Guoqiang (贺国强): October 1996 – August 1999
Xi Jinping (习近平): August 1999 – October 2002
Lu Zhangong (卢展工): October 2002 – December 2004
Huang Xiaojing (黄小晶): December 2004 – April 2011
Su Shulin (苏树林): April 2011 – November 2015
Yu Weiguo (于伟国): November 2015 – January 2018
Tang Dengjie (唐登杰): January 2018 – present
Economy

Fuzhou, the capital and largest city in Fujian province
Fujian is one of the more affluent provinces with many industries spanning tea production, clothing and sports manufacturers such as Anta, 361 Degrees, Xtep, Peak Sport Products and Septwolves. Many foreign firms have operations in Fujian. They include Boeing, Dell, GE, Kodak, Nokia, Siemens, Swire, TDK and Panasonic.[52]
| Historical GDP of Fujian Province for 1952 –present (SNA2008)[53] (purchasing power parity of Chinese Yuan, as Int'l.dollar based on IMF WEO October 2017[54]) | |||||||||
| year | GDP | **GDP per capita (GDPpc) ** based on mid-year population | Reference index | ||||||
| GDP in millions | real growth (%) | GDPpc | exchange rate *1 foreign currency to CNY* | ||||||
| CNY | USD | PPP (Int'l$.) | CNY | USD | PPP (Int'l$.) | USD 1 | Int'l$. 1 (PPP) | ||
| 2016 | 2,881,060 | 433,744 | 822,948 | 8.4 | 74,707 | 11,247 | 21,339 | 6.6423 | 3.5009 |
| 2015 | 2,623,920 | 421,283 | 739,237 | 9.0 | 68,645 | 11,021 | 19,339 | 6.2284 | 3.5495 |
| 2014 | 2,429,260 | 395,465 | 684,221 | 9.9 | 64,097 | 10,434 | 18,053 | 6.1428 | 3.5504 |
| 2013 | 2,207,780 | 356,485 | 617,233 | 11.0 | 58,702 | 9,478 | 16,411 | 6.1932 | 3.5769 |
| 2012 | 1,988,380 | 314,991 | 559,981 | 11.4 | 53,250 | 8,436 | 14,997 | 6.3125 | 3.5508 |
| 2011 | 1,770,380 | 274,104 | 505,029 | 12.3 | 47,764 | 7,395 | 13,625 | 6.4588 | 3.5055 |
| 2010 | 1,484,580 | 219,304 | 448,432 | 13.9 | 40,320 | 5,956 | 12,179 | 6.7695 | 3.3106 |
| 2009 | 1,232,420 | 180,416 | 390,315 | 12.3 | 33,677 | 4,930 | 10,666 | 6.8310 | 3.1575 |
| 2008 | 1,088,940 | 156,793 | 342,779 | 13.0 | 29,938 | 4,311 | 9,424 | 6.9451 | 3.1768 |
| 2007 | 930,190 | 122,329 | 308,531 | 15.2 | 25,730 | 3,384 | 8,534 | 7.6040 | 3.0149 |
| 2006 | 762,740 | 95,680 | 265,052 | 14.8 | 21,226 | 2,663 | 7,376 | 7.9718 | 2.8777 |
| 2005 | 658,860 | 80,430 | 230,451 | 11.6 | 18,448 | 2,252 | 6,453 | 8.1917 | 2.8590 |
| 2000 | 376,454 | 45,474 | 138,438 | 9.3 | 11,194 | 1,352 | 4,117 | 8.2784 | 2.7193 |
| 1990 | 52,228 | 10,919 | 30,675 | 7.5 | 1,763 | 369 | 1,035 | 4.7832 | 1.7026 |
| 1980 | 8,706 | 5,810 | 5,821 | 18.4 | 348 | 232 | 233 | 1.4984 | 1.4955 |
| 1978 | 6,637 | 4,268 | 17.8 | 273 | 176 | 1.5550 | |||
| 1970 | 3,470 | 1,410 | 9.9 | 173 | 70 | 2.4618 | |||
| 1962 | 2,212 | 899 | 98.6 | 137 | 56 | 2.4618 | |||
| 1957 | 2,203 | 846 | 6.7 | 154 | 59 | 2.6040 | |||
| 1952 | 1,273 | 573 | 23.3 | 102 | 46 | 2.2227 | |||
In terms of agricultural land, Fujian is hilly and farmland is sparse. Rice is the main crop, supplemented by sweet potatoes and wheat and barley.[55] Cash crops include sugar cane and rapeseed. Fujian leads the provinces of China in longan production, and is also a major producer of lychees and tea. Seafood is another important product, with shellfish production especially prominent.
Because of the geographic location with Taiwan, Fujian has been considered the battlefield frontline in a potential war between mainland China and Taiwan. Hence, it received much less investment from Chinese central government and developed much slower than the rest of China before 1978. Since 1978, when China opened to the world, Fujian has received significant investment from overseas Fujianese around the world, Taiwanese and foreign investment. Today, although Fujian is one of the wealthier provinces of China, its GDP per capita is only about the average of China's coastal administrative divisions.[56]
See also List of Chinese administrative divisions by GDP per capita
Minnan Golden Triangle which includes Xiamen, Quanzhou and Zhangzhou accounts for 40 percent of the GDP of Fujian province.
Fujian province will be the major economic beneficiary of the opening up of direct transport with Taiwan which commenced on December 15, 2008. This includes direct flights from Taiwan to major Fujian cities such as Xiamen and Fuzhou. In addition, ports in Xiamen, Quanzhou and Fuzhou will upgrade their port infrastructure for increased economic trade with Taiwan.[57][58]
Fujian is the host of China International Fair for Investment and Trade annually. It is held in Xiamen to promote foreign investment for all of China.
By 2015 Fujian expects to have at least 50 enterprises that have over 10 billion RMB in annual revenues. The government also expects 55 percent of GDP growth to come from the industrial sector.[60]
Economic and Technological Development Zones
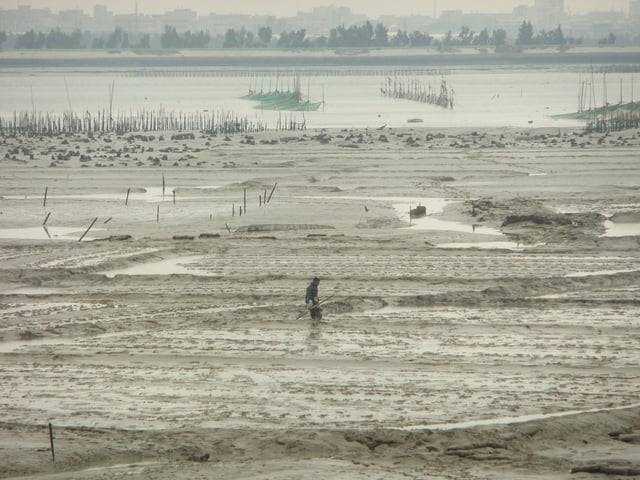

Mud clams, oysters and shrimp are raised in Anhai Bay off Shuitou.[61]
Dongshan Economic and Technology Development Zone
Fuzhou Economic & Technical Development Zone
Fuzhou Free Trade Zone
Fuzhou Hi-Tech Park
Fuzhou Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
Jimei Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
Meizhou Island National Tourist Holiday Resort
Wuyi Mountain National Tourist Holiday Resort
Xiamen Export Processing Zone
Xiamen Free Trade Zone
Xiamen Haicang Economic and Technological Development Zone
Xiamen Torch New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone (Chinese version)
Xinglin Taiwan Merchant Investment Area
Demographics
She ethnic townships in Fujian
As of 1832, the province was described as having an estimated "population of fourteen millions."[62]
Han Chinese make up 98% of the population. Various Fujianese peoples (Min-speaking groups) make up the largest subgroups of Han Chinese in Fujian. This includes the Hoklo people, Fuzhounese people, Teochew people and Putian people.
Hakka, a Han Chinese people with its own distinct identity, live in the southwestern parts of the province bordering Guangdong. Hui'an, also a Han branch with their distinct culture and fashion, populate Fujian's southeast coastline near Chongwu in Hui'an County. The She, scattered over mountainous regions in the north, is the largest minority ethnic group of the province.[63]
Many ethnic Chinese around the world, especially in Southeast Asia, trace their ancestries to the Fujianese branches of Hoklo people and Teochew people. Descendants of Southern Min speaking emigrants make up the predominant majority ethnic Chinese populations of Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and Philippines. While Eastern Min speaking people, especially Fuzhounese people, is one of the major sources of China immigrants in the United States, especially since the 1990s.[64]
Religion
The predominant religions in Fujian are Chinese folk religions, Taoist traditions and Chinese Buddhism. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 31.31% of the population believes and is involved in Chinese ancestral religion, while 3.5% of the population identifies as Christian.[65] The reports didn't give figures for other types of religion; 65.19% of the population may be either irreligious or involved in Chinese folk religion, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, folk religious sects, and small minorities of Muslims.
Culture
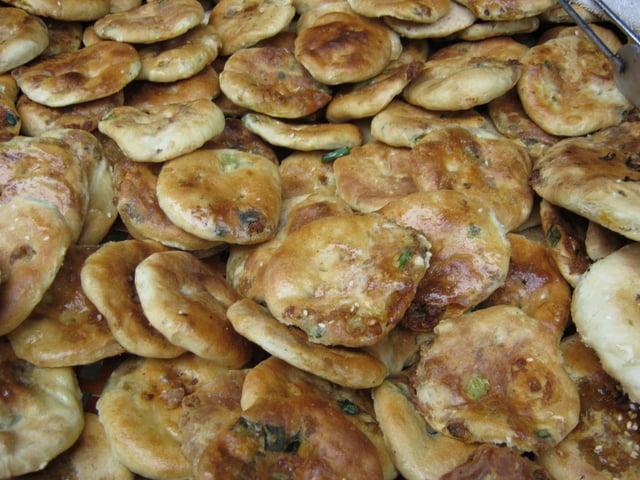

Kompyang (房村光饼) sold on the streets of Fujian cities
Because of its mountainous nature and the numerous waves of migration from north and central China in the course of history, Fujian is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse places in all Han Chinese areas of China. Local dialects can become unintelligible within 10 kilometres (6.2 mi). This is reflected in the expression that "if you drive five miles in Fujian the culture changes, and if you drive ten miles, the language does".[66] Most varieties spoken in Fujian are assigned to a broad Min category. Early classifications, such as those of Li Fang-Kuei in 1937 and Yuan Jiahua in 1960, divided Min into Northern and Southern subgroups. More recent classifications subdivide Min into[67][68]
Southern Min, including the Amoy dialect and Taiwanese
Pu-Xian, spoken in central coastal areas
Eastern Min (the former Northern group), including the Fuzhou dialect
Northern Min, spoken in inland northern areas
Central Min, spoken in the west of the province
Shao-Jiang, spoken in the northwest
(The seventh subdivision of Min, Qiong Wen, is not spoken in Fujian.) Hakka, another subdivision of spoken Chinese, is spoken around Longyan by the Hakka people who live there.
Several regions of Fujian have their own form of Chinese opera. Min opera is popular around Fuzhou; Gaojiaxi around Jinjiang and Quanzhou; Xiangju around Zhangzhou; Fujian Nanqu throughout the south, and Puxianxi around Putian and Xianyou County.
Fujian cuisine, with an emphasis on seafood, is one of the eight great traditions of Chinese cuisine. It is composed of traditions from various regions, including Fuzhou cuisine and Min Nan cuisine. The most prestigious dish is Fotiaoqiang (literally "Buddha jumps over the wall"), a complex dish making use of many ingredients, including shark fin, sea cucumber, abalone and Shaoxing wine (a type of Chinese alcoholic beverage).
Many well-known teas originate from Fujian, including oolong, Wuyi Yancha, Lapsang souchong and Fuzhou jasmine tea. Indeed, the tea processing techniques for three major classes tea, namely, oolong, white tea and black tea were all developed in the province. Fujian tea ceremony is an elaborate way of preparing and serving tea. In fact, the English word "tea" is borrowed from Hokkien of the Min Nan languages. (Mandarin and Cantonese pronounce the word chá.)
Fuzhou bodiless lacquer ware, a noted type of lacquer ware, is noted for using a body of clay and/or plaster to form its shape; the body later removed. Fuzhou is also known for Shoushan stone carvings.
Tourism
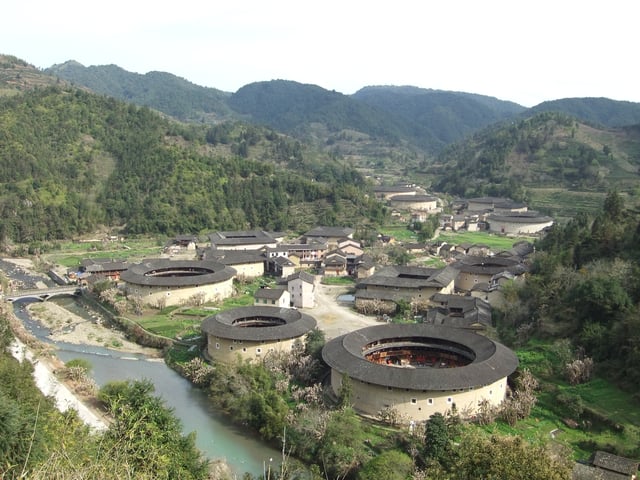

Hekeng village, in Shuyang Town, is one of the many tulou villages of Fujian's Nanjing County.
Fujian is home to a number of tourist attractions, including four UNESCO World Heritage Sites, one of the highest in China.
In the capital of Fuzhou is the Yongquan Temple, a Buddhist temple built during the Tang dynasty.
The Wuyi Mountains was the first location in Fujian to be listed by UNESCO as one of the World Heritage Sites in 1999. They are a mountain range in the prefecture of Nanping and contains the highest peak in Fujian, Mount Huanggang. It is famous as a natural landscape garden and a summer resort in China.
The Fujian Tulou are Chinese rural dwellings unique to the Hakka in southwest Fujian. They were listed by the UNESCO as one of the World Heritage Sites in 2008.
Gulangyu Island, Xiamen, is notable for its beaches, winding lanes and rich architecture. The island is on China's list of National Scenic Spots and is classified as a 5A tourist attraction by the China National Tourism Administration (CNTA). It was listed by the UNESCO as one of the World Heritage Site in 2017. Also in Xiamen is the South Putuo Temple.
The Guanghua Temple is a Buddhist temple in Putian. It was built in the penultimate year of the Southern Chen Dynasty. Located in the northern half of the mouth of Meizhou Bay, it is about 1.8 nautical miles from the mainland and faces the Strait of Taiwan to the southeast. Covering an area of six square miles, the island is swathed in luxuriant green foliage. The coastline is indented with over 12 miles of beach area. Another buddhist temple, Nanshan Temple is located in Zhangzhou.
Around Meizhou Islands is the Matsu pilgrimage
The Kaiyuan Temple, is a Buddhist temple in West Street, Quanzhou, China, the largest in Fujian province with an area of 78,000 square metres.[69] Although it is known as a both a Hindu and Buddhist temple, on account of added Tamil-Hindu influences, the main statue in the most important hall is that of Vairocana Buddha, the main Buddha according to Huayan Buddhism.
Mount Taimu is a mountain and a scenic resort in Fuding. It offers a grand view of mountain and sea, and is famous for its natural scenery including granite caves, odd-shaped stones, steep cliffs, clear streams, cascading waterfalls, and cultural attractions such as ancient temples and cliff Inscriptions.
The Danxia landform in Taining was listed by the UNESCO as one of the World Heritage Sites in 2010. It is a unique type of petrographic geomorphologyfound in China. Danxia landform is formed from red-coloured sandstones and conglomerates of largely Cretaceous age. The landforms look very much like karst topography that forms in areas underlain by limestones, but since the rocks that form danxia are sandstones and conglomerates, they have been called "pseudo-karst" landforms. They were formed by endogenous forces (including uplift) and exogenous forces (including weathering and erosion)
Notable individuals
The province and its diaspora abroad also has a tradition of educational achievement and has produced many important scholars, statesmen and other notable people since the time of the Song dynasty, such as:
Cai Jing (1047–1126), government official and calligrapher who lived during the Northern Song dynasty
Li Gang (1083–1140), a politician and general serving during the transition from the Northern Song to the Southern Song dynasty
Zhu Xi (1130–1200), Confucian philosopher
Ong Sum Ping (14th–15th century), royal son-in-law of Sultan Muhammad Shah of Brunei
Yu Dayou (1503–1579), Ming dynasty general and martial artist
Ingen (1592–1673), well known Buddhist monk, poet and calligrapher who lived during Ming Dynasty
Hong Chengchou (1593–1665), Ming dynasty official
Shi Lang (1621–1696), Qing dynasty admiral
Koxinga (1624–1662), Ming dynasty general who expelled the Dutch from Taiwan
Lin Zexu (1785–1850), Qing dynasty scholar and official
Zhan Shi Chai (1840s–1893), entertainer as "Chang the Chinese giant"
Wong Nai Siong (1849–1924), scholar, revolutionary, discovered the town of Sibu in Sarawak, east Malaysia in 1901
Lin Shu (1852–1924), translator
Yan Fu (1854–1921), scholar and translator
Sa Zhenbing (1859–1952), high-ranking naval officer of Mongolian origin
Zheng Xiaoxu (1860–1938), statesman, diplomat and calligrapher
Lin Changmin(zh:林長民) (1876—1925), a high-rank governor in the Beiyang Government
Lin Juemin (1887–1911), one of 72 Revolutionary Martyrs at Huanghuagang, Guangzhou
Lin Yutang (1894–1976), writer
Zheng Zhenduo (1898–1958), literary historian
Ong Schan Tchow (Chinese: 翁占秋) (1900–1945), artist well known for the painting of the “Book of Chrysanthemums”
José Rizal (1861–1896), National Hero of the Philippines whose lineage is from Fujian
Lin Huiyin (1904–1955), architect and writer
Tsai Chi-Kun (1912–2004), "father of the Taiwan Symphony"
Go Seigen (1914–2014), pseudonym of Go champion Wú Qīngyuán
Lin Dan (born 1983), professional badminton player
Jeremy Lin (born 1988), professional basketball player
Sports
Fujian includes professional sports teams in both the Chinese Basketball Association and the Chinese League One.
The representative of the province in the Chinese Basketball Association are the Fujian Sturgeons, who are based in Jinjiang, Quanzhou. The Fujian Sturgeons made their debut in the 2004–2005 season, and finished in seventh and last place in the South Division, out of the playoffs. In the 2005–2006 season, they tied for fifth, just one win away from making the playoffs.
The Xiamen Lanshi F.C represent Xiamen in the Chinese League One. Other football teams include Fujian Broncos F.C. and Fujian Tianxin F.C.
Education
High schools
Fuzhou Gezhi High School
Fuzhou No.1 Middle School
Fuzhou No.3 Middle School
Quanzhou No.5 Middle School
Xiamen Shuangshi High School
Xiamen No.1 Middle School
Xiamen Foreign Language School
Colleges and universities
National
Xiamen University (founded 1921, also known as University of Amoy, "985 project", "211 project") (Xiamen)
Huaqiao University (Quanzhou, Xiamen)
Provincial
Fuzhou University (founded 1958, one of "211 project" key Universities)u(Fuzhou)
Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Fuzhou)
Fujian College of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Fuzhou)
Fujian Medical University (Fuzhou)
Fujian Normal University (founded 1907) (Fuzhou)
Fujian University of Technology (Fuzhou)
Xiamen University (Xiamen)
Jimei University (Xiamen)
Xiamen University of Technology (Xiamen)
Longyan University (Longyan)
Minnan Normal University (Zhangzhou)
Minjiang University (Fuzhou)
Putian University (Putian)
Quanzhou Normal College (Quanzhou)
Wuyi University (Wuyishan)
Private
Yang-en University (Quanzhou)
See also
Major national historical and cultural sites in Fujian





