Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger | |
|---|---|
| Born | Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (1887-08-12)12 August 1887 Vienna, Austria-Hungary |
| Died | 4 January 1961(1961-01-04)(aged 73) Vienna, Austria |
| Nationality | Austrian |
| Citizenship |
|
| Alma mater | University of Vienna |
| Known for |
|
| Spouse(s) | Annemarie Bertel (1920–1961)[1] |
| Awards | Matteucci Medal (1927) Nobel Prize in Physics (1933) Max Planck Medal (1937) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Physics |
| Institutions |
|
| Thesis | On the conduction of electricity on the surface of insulators in humid air(1910) |
| Doctoral advisor | Friedrich Hasenöhrl[2] |
| Other academic advisors | Franz S. Exner |
| Signature | |

Bust of Schrödinger, in the courtyard arcade of the main building, University of Vienna, Austria
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (UK: /ˈʃrɜːdɪŋər/, US: /ˈʃroʊ-, ˈʃreɪ-/;[3] German: [ˈɛɐ̯viːn ˈʃʁøːdɪŋɐ]; 12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as Erwin Schrodinger or Erwin Schroedinger, was a Nobel Prize-winning Austrian physicist who developed a number of fundamental results in the field of quantum theory: the Schrödinger equation provides a way to calculate the wave function of a system and how it changes dynamically in time.
In addition, he was the author of many works in various fields of physics: statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, physics of dielectrics, colour theory, electrodynamics, general relativity, and cosmology, and he made several attempts to construct a unified field theory. In his book What Is Life? Schrödinger addressed the problems of genetics, looking at the phenomenon of life from the point of view of physics. He paid great attention to the philosophical aspects of science, ancient and oriental philosophical concepts, ethics, and religion.[4] He also wrote on philosophy and theoretical biology. He is also known for his "Schrödinger's cat" thought-experiment.[5][6]
Erwin Schrödinger | |
|---|---|
| Born | Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (1887-08-12)12 August 1887 Vienna, Austria-Hungary |
| Died | 4 January 1961(1961-01-04)(aged 73) Vienna, Austria |
| Nationality | Austrian |
| Citizenship |
|
| Alma mater | University of Vienna |
| Known for |
|
| Spouse(s) | Annemarie Bertel (1920–1961)[1] |
| Awards | Matteucci Medal (1927) Nobel Prize in Physics (1933) Max Planck Medal (1937) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Physics |
| Institutions |
|
| Thesis | On the conduction of electricity on the surface of insulators in humid air(1910) |
| Doctoral advisor | Friedrich Hasenöhrl[2] |
| Other academic advisors | Franz S. Exner |
| Signature | |
Biography
Early years
His mother was of half Austrian and half English descent; his father was Catholic and his mother was Lutheran. Although he was raised in a religious household as a Lutheran, he called himself an atheist.[12] However, he had strong interests in Eastern religions and pantheism, and he used religious symbolism in his works.[13] He also believed his scientific work was an approach to the godhead, albeit in a metaphorical sense.[14]
He was also able to learn English outside school, as his maternal grandmother was British.[15] Between 1906 and 1910 Schrödinger studied in Vienna under Franz S. Exner (1849–1926) and Friedrich Hasenöhrl (1874–1915). He also conducted experimental work with Karl Wilhelm Friedrich "Fritz" Kohlrausch.
In 1911, Schrödinger became an assistant to Exner. At an early age, Schrödinger was strongly influenced by Arthur Schopenhauer. As a result of his extensive reading of Schopenhauer's works, he became deeply interested throughout his life in colour theory and philosophy. In his lecture "Mind and Matter", he said that "The world extended in space and time is but our representation." This is a repetition of the first words of Schopenhauer's main work.
Middle years

Erwin Schrödinger as a young scientist
In 1914 Erwin Schrödinger achieved Habilitation (venia legendi). Between 1914 and 1918 he participated in war work as a commissioned officer in the Austrian fortress artillery (Gorizia, Duino, Sistiana, Prosecco, Vienna). In 1920 he became the assistant to Max Wien, in Jena, and in September 1920 he attained the position of ao. Prof. (ausserordentlicher Professor), roughly equivalent to Reader (UK) or associate professor (US), in Stuttgart. In 1921, he became o. Prof. (ordentlicher Professor, i.e. full professor), in Breslau (now Wrocław, Poland).
In 1921, he moved to the University of Zürich. In 1927, he succeeded Max Planck at the Friedrich Wilhelm University in Berlin. In 1934 Schrödinger decided to leave Germany; he disliked the Nazis' anti-semitism. He became a Fellow of Magdalen College at the University of Oxford. Soon after he arrived, he received the Nobel Prize together with Paul Dirac. His position at Oxford did not work out well; his unconventional domestic arrangements, sharing living quarters with two women,[16] were not met with acceptance. In 1934, Schrödinger lectured at Princeton University; he was offered a permanent position there, but did not accept it. Again, his wish to set up house with his wife and his mistress may have created a problem.[17] He had the prospect of a position at the University of Edinburgh but visa delays occurred, and in the end he took up a position at the University of Graz in Austria in 1936. He had also accepted the offer of chair position at Department of Physics, Allahabad University in India.[18]
In the midst of these tenure issues in 1935, after extensive correspondence with Albert Einstein, he proposed what is now called the Schrödinger's cat thought experiment.
Later years
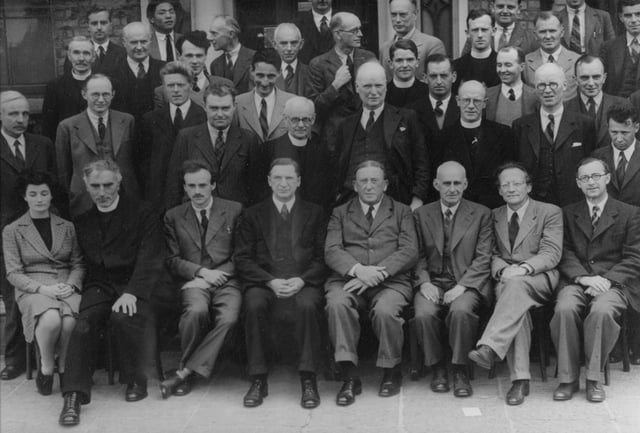

Schrödinger (front row 2nd from right) and Valera (front row 4th from left) at Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies in 1942
In 1938, after the Anschluss, Schrödinger had problems because of his flight from Germany in 1933 and his known opposition to Nazism.[19] He issued a statement recanting this opposition (he later regretted doing so and explained the reason to Einstein).[20] However, this did not fully appease the new dispensation and the University of Graz dismissed him from his job for political unreliability. He suffered harassment and received instructions not to leave the country, but he and his wife fled to Italy. From there, he went to visiting positions in Oxford and Ghent University.[20][19]
In the same year he received a personal invitation from Ireland's Taoiseach, Éamon de Valera – a mathematician himself – to reside in Ireland and agree to help establish an Institute for Advanced Studies in Dublin.[21] He moved to Clontarf, Dublin, became the Director of the School for Theoretical Physics in 1940 and remained there for 17 years. He became a naturalized Irish citizen in 1948, but retained his Austrian citizenship. He wrote around 50 further publications on various topics, including his explorations of unified field theory.
In 1944, he wrote What Is Life?, which contains a discussion of negentropy and the concept of a complex molecule with the genetic code for living organisms. According to James D. Watson's memoir, DNA, the Secret of Life, Schrödinger's book gave Watson the inspiration to research the gene, which led to the discovery of the DNA double helix structure in 1953. Similarly, Francis Crick, in his autobiographical book What Mad Pursuit, described how he was influenced by Schrödinger's speculations about how genetic information might be stored in molecules.
Schrödinger stayed in Dublin until retiring in 1955. He had a lifelong interest in the Vedanta philosophy of Hinduism, which influenced his speculations at the close of What Is Life? about the possibility that individual consciousness is only a manifestation of a unitary consciousness pervading the universe.[22] A manuscript "Fragment from an unpublished dialogue of Galileo"[23] from this time recently resurfaced at The King's Hospital boarding school, Dublin[24] after it was written for the School's 1955 edition of their Blue Coat to celebrate his leaving of Dublin to take up his appointment as Chair of Physics at the University of Vienna.
In 1956, he returned to Vienna (chair ad personam). At an important lecture during the World Energy Conference he refused to speak on nuclear energy because of his skepticism about it and gave a philosophical lecture instead. During this period Schrödinger turned from mainstream quantum mechanics' definition of wave–particle duality and promoted the wave idea alone, causing much controversy.
Personal life
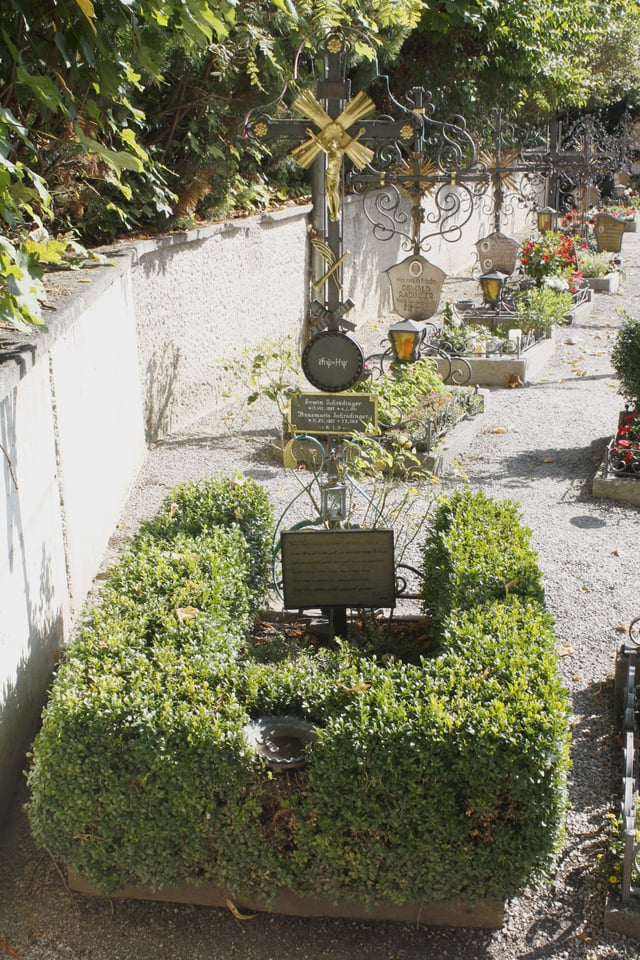

Annemarie and Erwin Schrödinger's gravesite; above the name plate Schrödinger's quantum mechanical wave equation is inscribed:
On 6 April 1920, Schrödinger married Annemarie (Anny) Bertel.[25] Schrödinger suffered from tuberculosis and several times in the 1920s stayed at a sanatorium in Arosa. It was there that he formulated his wave equation.[5] As has been noted above, Schrödinger had an unconventional personal life. When he migrated to Ireland in 1938, he obtained visas for himself, his wife and also another woman, Mrs. Hilde March. March was the wife of an Austrian colleague and Schrödinger had fathered a daughter with her in 1934.[26] Schrödinger wrote personally to the Taoiseach, Éamon de Valera, to obtain the visa for Mrs. March. In October 1939 the ménage à trois duly took up residence in Dublin.[26] Schrödinger fathered two further daughters by two different women during his time in Ireland.[26]
On 4 January 1961, Schrödinger died of tuberculosis, aged 73, in Vienna.[1] He left Anny a widow, and was buried in Alpbach, Austria, in a Catholic cemetery. Although he was not Catholic, the priest in charge of the cemetery permitted the burial after learning Schrödinger was a member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences.[27] His wife, Anny (born 3 December 1896) died on 3 October 1965. Schrödinger's grandson, Professor Terry Rudolph, has followed in his footsteps as a quantum physicist, and teaches at Imperial College London.[28][29]
Scientific activities
Early career
Early in his life, Schrödinger experimented in the fields of electrical engineering, atmospheric electricity, and atmospheric radioactivity, but he usually worked with his former teacher Franz Exner. He also studied vibrational theory, the theory of Brownian movement, and mathematical statistics. In 1912, at the request of the editors of the Handbook of Electricity and Magnetism, Schrödinger wrote an article titled Dieelectrism. That same year, Schrödinger gave a theoretical estimate of the probable height distribution of radioactive substances, which is required to explain the observed radioactivity of the atmosphere, and in August 1913 executed several experiments in Zeehame that confirmed his theoretical estimate and those of Victor Franz Hess. For this work, Schrödinger was awarded the 1920 Haitinger Prize (Haitinger-Preis) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences.[30] Other experimental studies conducted by the young researcher in 1914 were checking formulas for capillary pressure in gas bubbles and the study of the properties of soft beta-radiation appearing in the fall of gamma rays on the surface of metal. The last work he performed together with his friend Fritz Kohlrausch. In 1919, Schrödinger performed his last physical experiment on coherent light and subsequently focused on theoretical studies.
Quantum mechanics
New quantum theory
In the first years of his career Schrödinger became acquainted with the ideas of quantum theory, developed in the works of Max Planck, Albert Einstein, Niels Bohr, Arnold Sommerfeld, and others. This knowledge helped him work on some problems in theoretical physics, but the Austrian scientist at the time was not yet ready to part with the traditional methods of classical physics.
The first publications of Schrödinger about atomic theory and the theory of spectra began to emerge only from the beginning of the 1920s, after his personal acquaintance with Sommerfeld and Wolfgang Pauli and his move to Germany. In January 1921, Schrödinger finished his first article on this subject, about the framework of the Bohr-Sommerfeld effect of the interaction of electrons on some features of the spectra of the alkali metals. Of particular interest to him was the introduction of relativistic considerations in quantum theory. In autumn 1922 he analyzed the electron orbits in an atom from a geometric point of view, using methods developed by the mathematician Hermann Weyl (1885–1955). This work, in which it was shown that quantum orbits are associated with certain geometric properties, was an important step in predicting some of the features of wave mechanics. Earlier in the same year he created the Schrödinger equation of the relativistic Doppler effect for spectral lines, based on the hypothesis of light quanta and considerations of energy and momentum. He liked the idea of his teacher Exner on the statistical nature of the conservation laws, so he enthusiastically embraced the articles of Bohr, Kramers, and Slater, which suggested the possibility of violation of these laws in individual atomic processes (for example, in the process of emission of radiation). Although the experiments of Hans Geiger and Walther Bothe soon cast doubt on this, the idea of energy as a statistical concept was a lifelong attraction for Schrödinger and he discussed it in some reports and publications.[31]
Creation of wave mechanics
In January 1926, Schrödinger published in Annalen der Physik the paper "Quantisierung als Eigenwertproblem" (Quantization as an Eigenvalue Problem)[32] on wave mechanics and presented what is now known as the Schrödinger equation. In this paper, he gave a "derivation" of the wave equation for time-independent systems and showed that it gave the correct energy eigenvalues for a hydrogen-like atom. This paper has been universally celebrated as one of the most important achievements of the twentieth century and created a revolution in most areas of quantum mechanics and indeed of all physics and chemistry. A second paper was submitted just four weeks later that solved the quantum harmonic oscillator, rigid rotor, and diatomic molecule problems and gave a new derivation of the Schrödinger equation. A third paper, published in May, showed the equivalence of his approach to that of Heisenberg and gave the treatment of the Stark effect. A fourth paper in this series showed how to treat problems in which the system changes with time, as in scattering problems. In this paper he introduced a complex solution to the Wave equation in order to prevent the occurrence of fourth and sixth order differential equations. (This was arguably the moment when quantum mechanics switched from real to complex numbers.) When he introduced complex numbers in order to lower the order of the differential equations, something magical happened, and all of wave mechanics was at his feet. (He eventually reduced the order to one.)[33] These papers were his central achievement and were at once recognized as having great significance by the physics community.
Schrödinger was not entirely comfortable with the implications of quantum theory. He wrote about the probability interpretation of quantum mechanics, saying: "I don't like it, and I'm sorry I ever had anything to do with it." (Just in order to ridicule the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics he contrived the famous thought-experiment called Schrödinger's cat paradox.)[34]
Work on a unified field theory
Following his work on quantum mechanics, Schrödinger devoted considerable effort to working on a unified field theory that would unite gravity, electromagnetism, and nuclear forces within the basic framework of General Relativity, doing the work with an extended correspondence with Albert Einstein.[35] In 1947, he announced a result, "Affine Field Theory,"[36] in a talk at the Royal Irish Academy, but the announcement was criticized by Einstein as "preliminary" and failed to lead to the desired unified theory.[35] Following the failure of his attempt at unification, Schrödinger gave up his work on unification and turned to other topics.
Colour
Schrödinger had a strong interest in psychology, in particular colour perception and colorimetry (German: Farbenmetrik). He spent quite a few years of his life working on these questions and published a series of papers in this area:
"Theorie der Pigmente von größter Leuchtkraft", Annalen der Physik, (4), 62, (1920), 603–22 (Theory of Pigments with Highest Luminosity)
"Grundlinien einer Theorie der Farbenmetrik im Tagessehen", Annalen der Physik, (4), 63, (1920), 397–456; 481–520 (Outline of a theory of colour measurement for daylight vision)
"Farbenmetrik", Zeitschrift für Physik, 1, (1920), 459–66 (Colour measurement).
"Über das Verhältnis der Vierfarben- zur Dreifarben-theorie", Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, 134, 471, (On The Relationship of Four-Color Theory to Three-Color Theory).
"Lehre von der strahlenden Energie", Müller-Pouillets Lehrbuch der Physik und Meteorologie, Vol 2, Part 1 (1926) (Thresholds of Color Differences).
His work on the psychology of colour perception follows the step of Newton, Maxwell and von Helmholtz in the same area. Some of these papers have been translated into English and can be found in: Sources of Colour Science, Ed. David L. MacAdam, MIT Press (1970).
Legacy
The philosophical issues raised by Schrödinger's cat are still debated today and remain his most enduring legacy in popular science, while Schrödinger's equation is his most enduring legacy at a more technical level. Schrödinger is one of several individuals who have been called "the father of quantum mechanics". The large crater Schrödinger, on the far side of the Moon, is named after him. The Erwin Schrödinger International Institute for Mathematical Physics was established in Vienna in 1993.
Schrödinger's portrait was the main feature of the design of the 1983–97 Austrian 1000-schilling banknote, the second-highest denomination.
Schrödinger's 126th birthday anniversary in 2013 was celebrated with a Google Doodle.[39][40]
Honors and awards
Nobel Prize in Physics (1933) for the formulation of the Schrödinger equation
Max Planck Medal (1937)
Elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1949[4]
Erwin Schrödinger Prize of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (1956)
Austrian Decoration for Science and Art (1957)
Schrödinger's cat is named in his honour, see also: List of things named after Erwin Schrödinger.
Published works
The List of Erwin Schrödinger's publications [57] , compiled by Auguste Dick, Gabriele Kerber, Wolfgang Kerber and Karl von Meyenn
Science and the human temperament Allen & Unwin (1935), translated and introduced by James Murphy, with a foreword by Ernest Rutherford
Nature and the Greeks and Science and Humanism Cambridge University Press (1996) ISBN 0-521-57550-8.
The interpretation of Quantum Mechanics Ox Bow Press (1995) ISBN 1-881987-09-4.
Statistical Thermodynamics Dover Publications (1989) ISBN 0-486-66101-6.
Collected papers Friedr. Vieweg & Sohn (1984) ISBN 3-7001-0573-8.
My View of the World Ox Bow Press (1983) ISBN 0-918024-30-7.
Expanding Universes Cambridge University Press (1956).
Space-Time Structure [58] Cambridge University Press (1950) ISBN 0-521-31520-4.[41]
What Is Life? Macmillan (1944).
What Is Life? & Mind and Matter Cambridge University Press (1974) ISBN 0-521-09397-X.
