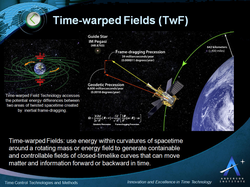
Space-Time Warp

Space-Time Warp
A space time warp (or spacetime warp) is the bending or curving by gravity of the 3D space and time around a mass or body.
Phrased differently, mass indicates to spacetime how to bend and bended spacetime directs mass how to move.
Popularly misunderstood as merely science fiction, spacetime warping has been confirmed by satellite, probe [0]and Hubble telescope observations.
Space time warping was originally predicted by Albert Einstein in his Theory of General Relativity.
Time runs more slowly (relative time stretching/dilation) where gravity, hence mass, is greater or more dense; conversely time runs relatively more quickly/faster (relative time compression) where mass is less dense or outside the spacetime warp.
Time would approach zero in a black hole where gravity-mass approaches but does not quite reach infinity; similar time stretching occurs, albeit less absolute, for a neutron star.
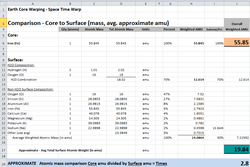
Scientists estimate earth's core is two and a half years younger than its surface - since earth's core is more dense than its surface, again due to spacetime warping.
The earth is roughly 4.55 billion years old [7], a comparatively long time - so it's core's time dilation has taken eons to evolve.
Earth has an iron core (symbol Fe, 26 protons, 30 neutrons, 26 electrons, atomic mass 55.85 amu or atomic mass units).
[9]Earth's surface is 70% water[H2O, (2 x 1.01 amu) + (1 x 16.00 amu) = 18.02 amu] [-1] [11]and 30% other elements (approx avg 24.09 amu), yielding an approximate overall surface atomic mass average of 19.84 amu.
Earth's iron core is very roughly 2.8 times more dense than it's surface average (see attached table and calculations at end of article).
Earth's denser and rotating iron core generates the space time warp vs. its surface.
[8]Phrased differently, earth's surface, outside its core - has aged two and a half years more than its core.
Astronomers and astrophysicists were originally confused when observations by the Hubble Telescope showed galaxies were moving away from Earth at greater than the speed of light.
[1]The speed of light is postulated to be a constant, a maximum relative speed measured at ~300,000 km/sec.
Objects moving faster than the speed of light therefore seemed impossible yet telescopic images over time showed what appeared to be faster than speed-of-light galaxy progressions away from Earth.
The galaxies may not actually be moving away hyper-light through space.
Space itself appears to be expanding or 3D bending away, and galaxies are being carried along with that warping of spacetime.
No physical laws are being broken even though to a casual observer such appears to be the case.
It is also important to note that light is not merely being bent by gravity such that something appears farther away.
An actual warping of space-time occurs.
Imagine [5]you have a friend just inside a machine that can turn on and off black hole-like impossibly dense matter simulation.
Before turning on his machine you measured the distance to the machine, say it was 5 meters away, 5 feet, whatever.
Your friend waves at you and revs/starts up his black-hole or neutron star machine for some short period of time, say a very small fraction of a nano-second.
He and his machine immediately appear to move incomprehensibly fast to you.
You physically walk up five units of measurement, trying to touch his machine, but it really is not there.
Light is not just visibly bent, but an actual warping of space-time occurs.
A warp in spacetime caused a pulsar to just vanish entirely [2]and astronomers were able to actually measure a space-time warp in the gravity of a binary star and determined the mass of a neutron star—just before it disappeared completely from view.
[-1]A distant spacetime warp may be holding evidence to dark matter's composition.
Einstein's theory of spacetime warping has been confirmed; mass tells spacetime how to bend and yet bended spacetime tells mass how it should move.
Paradox redux in relativity terms: matter actually can (appear to) travel faster than the speed of light and time being relative may be bent or folded.
See also: Gravitational wave
Exhibits and Videos: