Hermes
Hermes

| Hermes | |
|---|---|
Messenger of the gods, god of trade, thieves, travelers, sports, athletes, border crossings, guide to the Underworld | |
| Abode | Mount Olympus |
| Symbol | Talaria, caduceus, tortoise, lyre, rooster, Petasos (Winged helmet) |
| Personal information | |
| Consort | Merope, Aphrodite, Dryope, Peitho |
| Children | Pan, Hermaphroditus, Abderus, Autolycus, Eudorus, Angelia, Myrtilus |
| Parents | Zeus and Maia |
| Siblings | Aeacus, Angelos, Aphrodite, Apollo, Ares, Artemis, Athena, Dionysus, Eileithyia, Enyo, Eris, Ersa, Hebe, Helen of Troy, Hephaestus, Heracles, Minos, Pandia, Persephone, Perseus, Rhadamanthus, the Graces, the Horae, the Litae, the Muses, the Moirai |
| Roman equivalent | Mercury |
Hermes (/ˈhɜːrmiːz/; Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is the god of trade, heralds, merchants, commerce, roads, thieves, trickery, sports, travelers, and athletes in Ancient Greek religion and mythology; the son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia, he was the second youngest of the Olympian gods (Dionysus being the youngest).
Hermes was the emissary and messenger of the gods.[1] Hermes was also "the divine trickster"[2] and "the god of boundaries and the transgression of boundaries, ... the patron of herdsmen, thieves, graves, and heralds."[3] He is described as moving freely between the worlds of the mortal and divine, and was the conductor of souls into the afterlife.[4] He was also viewed as the protector and patron of roads and travelers.[5]
In some myths, he is a trickster and outwits other gods for his own satisfaction or for the sake of humankind. His attributes and symbols include the herma, the rooster, the tortoise, satchel or pouch, winged sandals, and winged cap. His main symbol is the Greek kerykeion or Latin caduceus, which appears in a form of two snakes wrapped around a winged staff with carvings of the other gods.[6]
In the Roman adaptation of the Greek pantheon (see interpretatio romana), Hermes is identified with the Roman god Mercury,[7] who, though inherited from the Etruscans, developed many similar characteristics such as being the patron of commerce.
| Hermes | |
|---|---|
Messenger of the gods, god of trade, thieves, travelers, sports, athletes, border crossings, guide to the Underworld | |
| Abode | Mount Olympus |
| Symbol | Talaria, caduceus, tortoise, lyre, rooster, Petasos (Winged helmet) |
| Personal information | |
| Consort | Merope, Aphrodite, Dryope, Peitho |
| Children | Pan, Hermaphroditus, Abderus, Autolycus, Eudorus, Angelia, Myrtilus |
| Parents | Zeus and Maia |
| Siblings | Aeacus, Angelos, Aphrodite, Apollo, Ares, Artemis, Athena, Dionysus, Eileithyia, Enyo, Eris, Ersa, Hebe, Helen of Troy, Hephaestus, Heracles, Minos, Pandia, Persephone, Perseus, Rhadamanthus, the Graces, the Horae, the Litae, the Muses, the Moirai |
| Roman equivalent | Mercury |
Etymology and origins
The earliest form of the name Hermes is the Mycenaean Greek hermāhās,[8] written 𐀁𐀔𐁀 e-ma-a2 (e-ma-ha) in the Linear B syllabic script.[9] Most scholars derive "Hermes" from Greek ἕρμα herma,[10] "prop,[[11]](http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0057:entry=e(/rma) heap of stones, boundary marker", from which the word hermai ("boundary markers dedicated to Hermes as a god of travelers") also derives.[[12]](http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0057:entry=(ermh=s) The etymology of ἕρμα itself is unknown, but it is probably not a Proto-Indo-European word.[8] However, the stone etymology is also linked to Indo-European *ser- (“to bind, put together”). Scholarly speculation that "Hermes" derives from a more primitive form meaning "one cairn" is disputed.[13] In Greek, a lucky find is a ἕρμαιον hermaion.
According to a theory that has received considerable scholarly acceptance, Hermes himself originated as a form of the god Pan, who has been identified as a reflex of the Proto-Indo-European pastoral god *Péh2usōn,[14][15] in his aspect as the god of boundary markers. Later, the epithet supplanted the original name itself and Hermes took over the roles as god of messengers, travelers, and boundaries, which had originally belonged to Pan, while Pan himself continued to be venerated by his original name in his more rustic aspect as the god of the wild in the relatively isolated mountainous region of Arcadia. In later myths, after the cult of Pan was reintroduced to Attica, Pan was said to be Hermes's son.[15][16]
Mythology
Early Greek sources
Homer and Hesiod
Homer and Hesiod portrayed Hermes as the author of skilled or deceptive acts and also as a benefactor of mortals. In the Iliad, he is called "the bringer of good luck", "guide and guardian", and "excellent in all the tricks". He was a divine ally of the Greeks against the Trojans. However, he did protect Priam when he went to the Greek camp to retrieve the body of his son Hector and accompanied them back to Troy.[19]
He also rescued Ares from a brazen vessel where he had been imprisoned by Otus and Ephialtes. In the Odyssey, Hermes helps his great-grand son, the protagonist Odysseus, by informing him about the fate of his companions, who were turned into animals by the power of Circe. Hermes instructed Odysseus to protect himself by chewing a magic herb; he also told Calypso of Zeus' order to free Odysseus from her island to allow him to continue his journey back home. When Odysseus killed the suitors of his wife, Hermes led their souls to Hades.[20] In The Works and Days, when Zeus ordered Hephaestus to create Pandora to disgrace humanity by punishing Prometheus's act of giving fire to man, every god gave her a gift, and Hermes' gifts were lies, seductive words, and a dubious character. Hermes was then instructed to take her as wife to Epimetheus.[21]
The Homeric Hymn 4 to Hermes,[22] which tells the story of the god's birth and his subsequent theft of Apollo's sacred cattle, invokes him as the one "of many shifts (polytropos), blandly cunning, a robber, a cattle driver, a bringer of dreams, a watcher by night, a thief at the gates, one who was soon to show forth wonderful deeds among the deathless gods." [23] The word polutropos ("of many shifts, turning many ways, of many devices, ingenious, or much wandering") is also used to describe Odysseus in the first line of the Odyssey. In addition to the chelys lyre,[24] Hermes was believed to have invented many types of racing and the sport of wrestling, and therefore was a patron of athletes.[25]
Athenian tragic playwrights
Aeschylus wrote in The Eumenides that Hermes helped Orestes kill Clytemnestra under a false identity and other stratagems,[26] and also said that he was the god of searches, and those who seek things lost or stolen.[27] In Philoctetes, Sophocles invokes Hermes when Odysseus needs to convince Philoctetes to join the Trojan War on the side of the Greeks, and in Euripides' Rhesus Hermes helps Dolon spy on the Greek navy.[26]
Aesop
Aesop featured him in several of his fables, as ruler of the gate of prophetic dreams, as the god of athletes, of edible roots, and of hospitality. He also said that Hermes had assigned each person his share of intelligence.[28]
Hermes' lovers
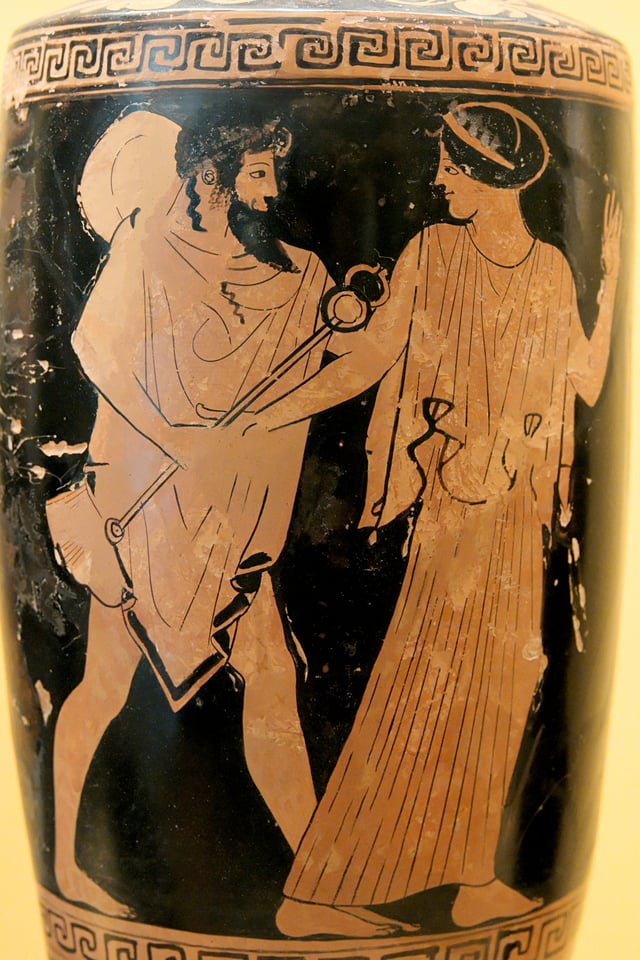

Hermes pursuing a woman, probably Herse. Attic red-figure amphora, ca. 470 BC.
Peitho, the goddess of seduction and persuasion, was said by Nonnus to be the wife of Hermes.[29]
Aphrodite, the goddess of love and beauty, was wooed by Hermes. After she had rejected him, Hermes sought the help of Zeus to seduce her. Zeus, out of pity, sent his eagle to take away Aphrodite's sandal when she was bathing, and gave it to Hermes. When Aphrodite came looking for the sandal, Hermes made love to her. She bore him a son, Hermaphroditus.[30]
Apemosyne, a princess of Crete. One day while travelling, Hermes saw her and fell in love with her. He chased her, but was unable to catch her since she was swifter than him. So he strewed some newly stripped hides along the road, on which she slipped when she was returning after a while. He then made love to her. When she disclosed to her brother, Althaimenes, what had happened, he took her story about the god to be an excuse, and killed her with a kick of his foot.[31]
Chione, a princess of Phokis, attracted the attention of Hermes. He used his wand to put her to sleep and slept with her. To Hermes she bore a son, Autolycus.[32]
Penelopeia, an Arcadian nymph, was loved by Hermes. Their son is said to be the god Pan. She has been confused or conflated with Penelope, the wife of Odysseus.
The Oreads, the nymphs of the mountains were said to mate with Hermes in the highlands, breeding more of their kind.[33]
Iphthime, a princess of Doros was loved by Hermes and bore him three Satyroi - named Pherespondos, Lykos and Pronomos.
Tanagra was a nymph of for whom the gods Ares and Hermes competed in a boxing match. Hermes won and carried her off to Tanagra in Boeotia.
Hellenistic Greek sources

Sardonyx cameo of a Ptolemaic prince as Hermes, Cabinet des médailles, Paris
Several writers of the Hellenistic period expanded the list of Hermes's achievements. Callimachus said that Hermes disguised himself as a Cyclops to scare the Oceanides and was disobedient to his mother. One of the Orphic Hymns Khthonios is dedicated to Hermes, indicating that he was also a god of the underworld. Aeschylus had called him by this epithet several times.[34] Another is the Orphic Hymn to Hermes, where his association with the athletic games held is mystic in tone.[35]
Phlegon of Tralles said he was invoked to ward off ghosts,[36] and Pseudo-Apollodorus reported several events involving Hermes. He participated in the Gigantomachy in defense of Olympus; was given the task of bringing baby Dionysus to be cared for by Ino and Athamas and later by nymphs of Asia, followed Hera, Athena and Aphrodite in a beauty contest; favored the young Hercules by giving him a sword when he finished his education and lent his sandals to Perseus.[37] The Thracian princes identified him with their god Zalmoxis, considering his ancestor.[38]
I Hermes stand here at the crossroads by the wind beaten orchard, near the hoary grey coast; and I keep a resting place for weary men. And the cool stainless spring gushes out.
Epithets of Hermes
Atlantiades
Kriophoros
Argeiphontes
Hermes's epithet Argeiphontes (Ancient Greek: Ἀργειφόντης; Latin: Argicida), meaning "Argus-slayer",[44][45] recalls his slaying of the hundred-eyed giant Argus Panoptes, who was watching over the heifer-nymph Io in the sanctuary of Queen Hera herself in Argos. Hermes placed a charm on Argus's eyes with the caduceus to cause the giant to sleep; after this he slew the giant.[10] Argus' eyes were then put into the tail of the peacock, a symbol of the goddess Hera.
Messenger and guide
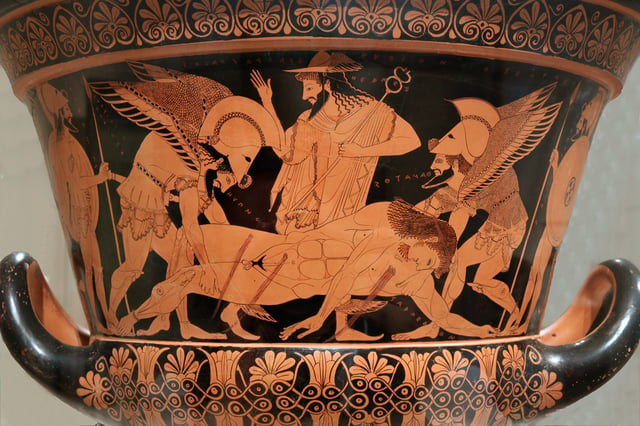

Sarpedon's body carried by Hypnos and Thanatos (Sleep and Death), while Hermes watches. Side A of the so-called "Euphronios krater", Attic red-figured calyx-krater signed by Euxitheos (potter) and Euphronios (painter), c. 515 BC.
The chief office of the god was as messenger.[46] Explicitly, at least in sources of classical writings, of Euripides Electra and Iphigenia in Aulis[47] and in Epictetus Discourses.[48] Hermes (Diactoros, Angelos)[49] the messenger,[50] is in fact only seen in this role, for Zeus, from within the pages of the Odyssey.[26] The messenger divine and herald of the Gods, he wears the gifts from his father, the Petasus and Talaria.[51]
Trade
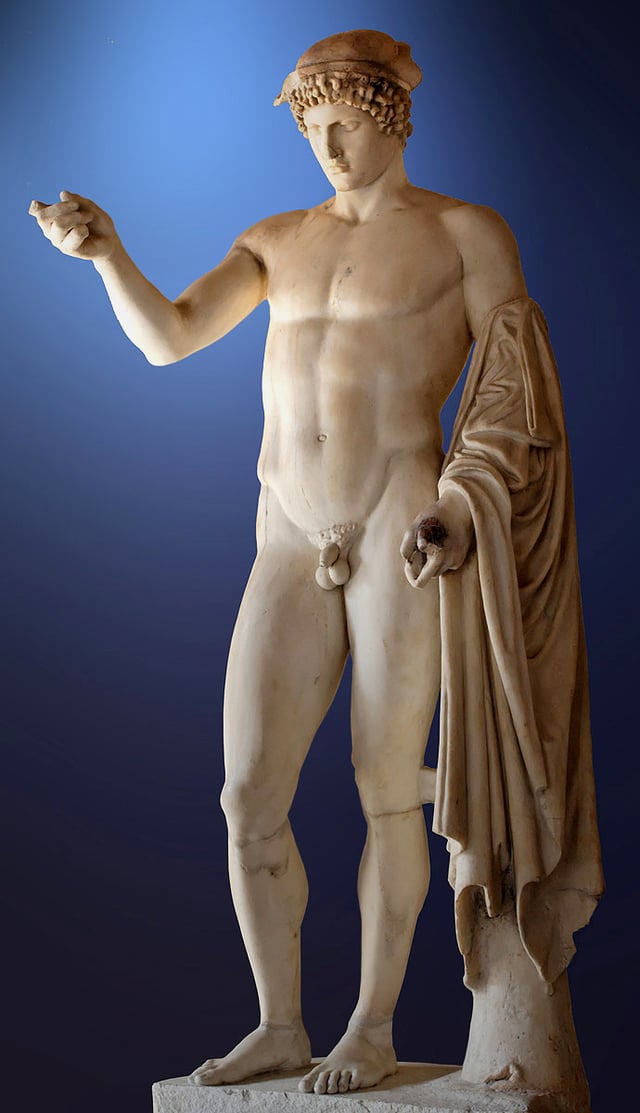

So-called "Logios Hermes" (Hermes Orator). Marble, Roman copy from the late 1st century BC - early 2nd century AD after a Greek original of the 5th century BC.
Agoraeus, of the agora;[56] belonging to the market (Aristophanes)[57]
Empolaios, "engaged in traffic and commerce"[58]
Hermes is sometimes depicted in art works holding a purse.[59]
Dolios
Dolios, "tricky".[60]
The god is ambiguous.[63]
According to prominent folklorist Yeleazar Meletinsky, Hermes is a deified trickster[64] and master of thieves ("a plunderer, a cattle-raider, a night-watching" in Homers' Hymns)[65] and deception (Euripides)[66] and (possibly evil) tricks and trickeries,[58][67][68][69] crafty (from lit. god of craft),[70] the cheat,[71] the god of stealth.[72]
friendliest to man
(As the ways of gain are not always the ways of honesty and straightforwardness, Hermes obtains a bad character and an in-moral (amoral [ed.]) cult as Dolios)[79]
Thief
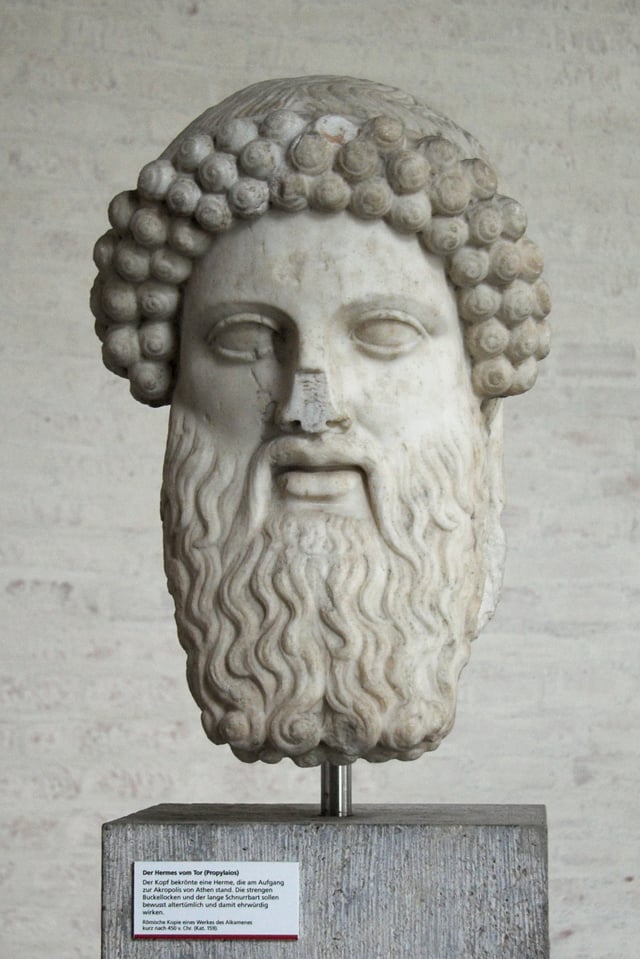

Hermes Propylaeus. Roman copy of the Alcamenes statue from the entrance of the Athenian Acropolis, original shortly after the 450 BC.
In the Lang translation of Homer's Hymn to Hermes, the god after being born is described as a robber, a captain of raiders, and a thief of the gates.[85]
According to the late Jungian psychotherapist López-Pedraza, everything Hermes thieves, he later sacrifices to the gods.[86]
Patron of thieves
Autolycus received his skills as the greatest of thieves due to sacrificing to Hermes as his patron.[87]
Additional
Other epithets included:
chthonius – at the festival Athenia Chytri sacrifices are made to this visage of the god only.[88][89]
cyllenius, born on Mount Kyllini
epimelios, guardian of flocks[44]
koinos[90]
ploutodotes, giver of wealth (as inventor of fire)[91]
proopylaios, "before the gate", "guardian of the gate";[92] Pylaios, "doorkeeper"[93]
Stropheus, "the socket in which the pivot of the door moves" (Kerényi in Edwardson) or "door-hinge". Protector of the door (that is the boundary), to the temple[56][95][96][97][98]
Agoraios, the patron of gymnasia[99]
Worship and cult
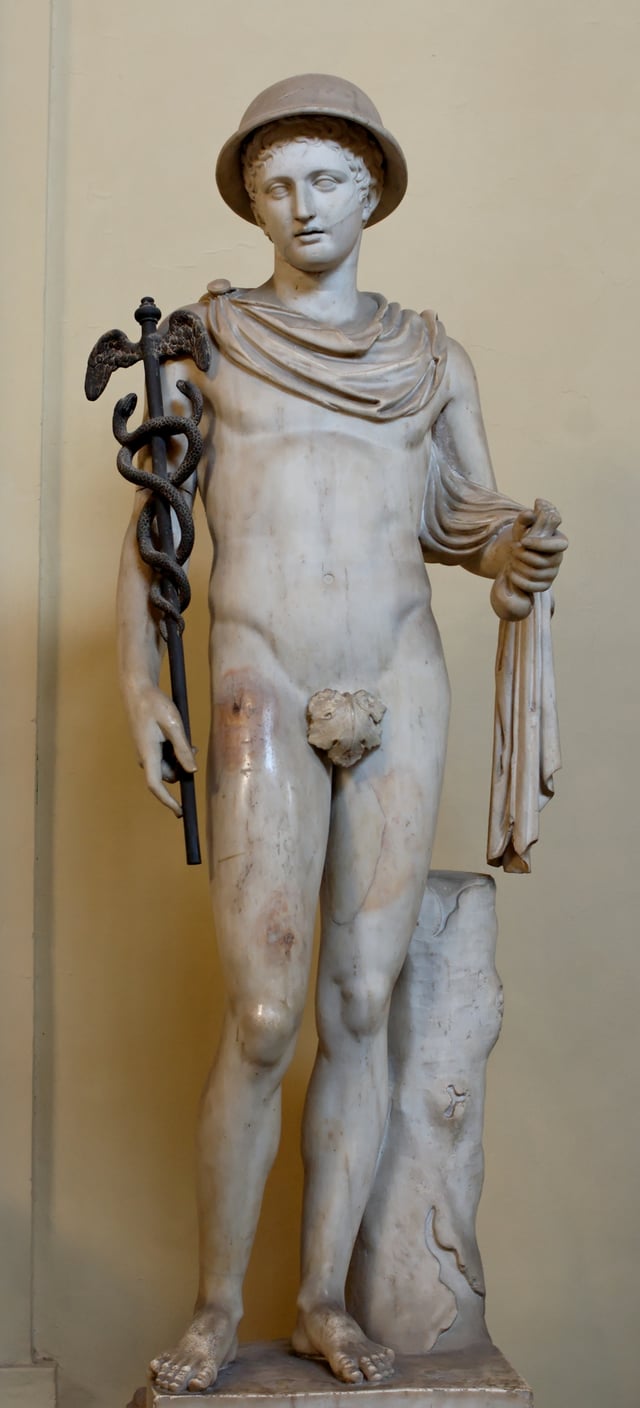

Statue of Hermes wearing the petasos, a voyager's cloak, the caduceus and a purse. Roman copy after a Greek original (Vatican Museums).
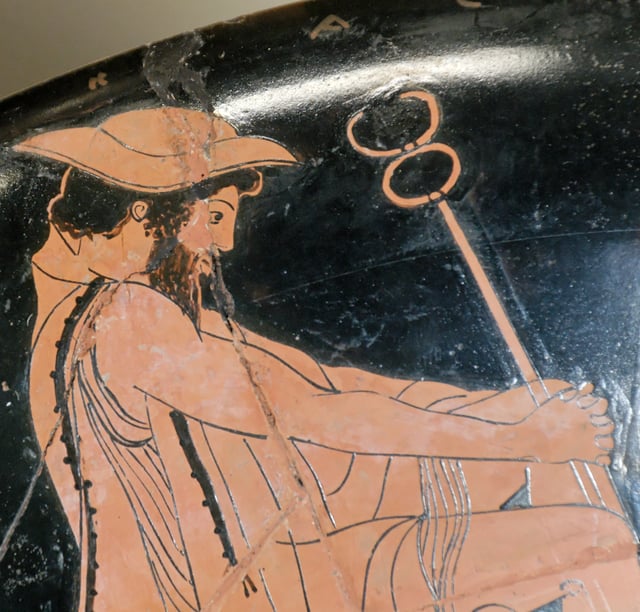

Hermes with a petasus. Attic red-figure cup, ca. 480 BC–470 BC. From Vulci.
Prior to being known as Hermes, Frothingham thought the god to have existed as a snake-god.[100] Angelo (1997) thinks Hermes to be based on the Thoth archetype.[101] The absorbing ("combining") of the attributes of Hermes to Thoth developed after the time of Homer amongst Greek and Roman; Herodotus was the first to identify the Greek god with the Egyptian (Hermopolis), Plutarch and Diodorus also, although Plato thought the gods to be dis-similar (Friedlander 1992).[102][103]
A cult was established in Greece in remote regions, likely making him a god of nature, farmers, and shepherds. It is also possible that since the beginning he has been a deity with shamanic attributes linked to divination, reconciliation, magic, sacrifices, and initiation and contact with other planes of existence, a role of mediator between the worlds of the visible and invisible.[104]
Due to his constant mobility, he was considered the god of commerce and social intercourse, the wealth brought in business, especially sudden or unexpected enrichment, travel, roads and crossroads, borders and boundary conditions or transient, the changes from the threshold, agreements and contracts, friendship, hospitality, sexual intercourse, games, data, the draw, good luck, the sacrifices and the sacrificial animals, flocks and shepherds and the fertility of land and cattle. In addition to serving as messenger to Zeus, Hermes carried the souls of the dead to Hades, and directed the dreams sent by Zeus to mortals.[106][107][108]
Temples
One of the oldest places of worship for Hermes was Mount Cyllene in Arcadia, where the myth says that he was born. Tradition says that his first temple was built by Lycaon. From there the cult would have been taken to Athens, and then radiated to the whole of Greece, according to Smith, and his temples and statues became extremely numerous.[106] Lucian of Samosata said he saw the temples of Hermes everywhere.[109]
In many places, temples were consecrated in conjunction with Aphrodite, as in Attica, Arcadia, Crete, Samos and in Magna Graecia. Several ex-votos found in his temples revealed his role as initiator of young adulthood, among them soldiers and hunters, since war and certain forms of hunting were seen as ceremonial initiatory ordeals. This function of Hermes explains why some images in temples and other vessels show him as a teenager. As a patron of the gym and fighting, Hermes had statues in gyms and he was also worshiped in the sanctuary of the Twelve Gods in Olympia where Greeks celebrated the Olympic Games. His statue was held there on an altar dedicated to him and Apollo together.[110] A temple within the Aventine was consecrated in 495 BC.[111][112]
Symbols of Hermes were the palm tree, turtle, rooster, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish and incense. Sacrifices involved honey, cakes, pigs, goats, and lambs. In the sanctuary of Hermes Promakhos in Tanagra is a strawberry tree under which it was believed he had created,[113] and in the hills Phene ran three sources that were sacred to him, because he believed that they had been bathed at birth.
Festival
Hermes's feast was the special Hermaea which was celebrated with sacrifices to the god and with athletics and gymnastics, possibly having been established in the 6th century BC, but no documentation on the festival before the 4th century BC survives. However, Plato said that Socrates attended a Hermaea. Of all the festivals involving Greek games, these were the most like initiations because participation in them was restricted to young boys and excluded adults.[114]
Hermai/Herms
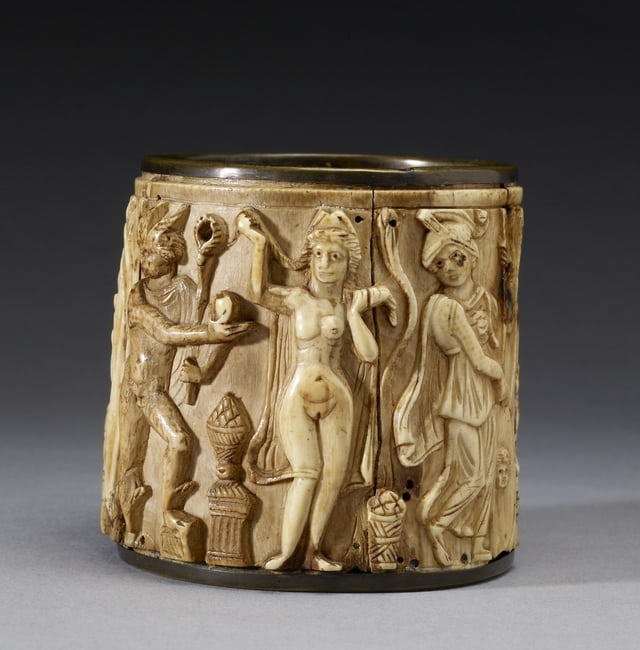

This circular Pyxis or box depicts two scenes. The one shown presents Hermes awarding the golden apple of the Hesperides to Aphrodite, whom Paris has selected as the most beautiful of the goddesses.[115] The Walters Art Museum.
In Ancient Greece, Hermes was a phallic god of boundaries. His name, in the form herma, was applied to a wayside marker pile of stones; each traveler added a stone to the pile. In the 6th century BC, Hipparchos, the son of Pisistratus, replaced the cairns that marked the midway point between each village deme at the central agora of Athens with a square or rectangular pillar of stone or bronze topped by a bust of Hermes with a beard. An erect phallus rose from the base. In the more primitive Mount Kyllini or Cyllenian herms, the standing stone or wooden pillar was simply a carved phallus. In Athens, herms were placed outside houses for good luck. "That a monument of this kind could be transformed into an Olympian god is astounding," Walter Burkert remarked.[116]
In 415 BC, when the Athenian fleet was about to set sail for Syracuse during the Peloponnesian War, all of the Athenian hermai were vandalized one night. The Athenians at the time believed it was the work of saboteurs, either from Syracuse or from the anti-war faction within Athens itself. Socrates' pupil Alcibiades was suspected of involvement, and Socrates indirectly paid for the impiety with his life.[117]
Hermes's possible offspring
Pan
Priapus
Depending on the sources consulted, the god Priapus could be understood as a son of Hermes.[120]
Autolycus
Autolycus, the Prince of Thieves, was a son of Hermes and Chione (mortal) and grandfather of Odysseus.[121]
List of lovers and other children
| Consort | Offspring | Consort | Offspring | Consort | Offspring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acacallis | • Cydon | Chthonophyle | • Polybus | Penelope | • Nomios |
| Aglaurus | • Eumolpus | Daeira | • Eleusis[122] | • Pan (possibly) | |
| Alcidameia of Corinth | • Bounos | Dryope, Arcadian nymph | • Pan (possibly) | Phylodameia | • Pharis |
| Antianeira or Laothoe | • Echion, Argonaut | Erytheia | • Norax[123] | Polymele | • Eudorus |
| • Eurytus, Argonaut | Eupolemeia | • Aethalides | Rhene | • Saon[124] | |
| Apemosyne | no known offspring | Hecate | three daughters[125] | Sicilian nymph | • Daphnis(relation ambiguous) |
| Aphrodite | • Hermaphroditus | Herse | • Cephalus | Sose, nymph | • Agreus |
| • Tyche (possibly) | • Ceryx (possibly) | Tanagra | no known offspring | ||
| Astabe[126] | • Astacus | Hiereia | • Gigas[127] | Thronia | • Arabus |
| Carmentis or a local nymph of the Arcadians, called Themis.[128] | • Evander | Iphthime | • Lycus | Urania | • Linus (possibly) |
| Chione or | • Autolycus | • Pherespondus | Unknown mother | • Abderus | |
| Stilbe[129] or | • Pronomus | Unknown mother | • Angelia | ||
| Telauge[130] | Libye[131] | • Libys[132] | Unknown mother | • Dolops | |
| Cleobule or | • Myrtilus | Ocyrhoe | • Caicus | Unknown mother | • Palaestra |
| Clymene or | Orsinoe, nymph[133] | • Pan (possibly) | Male Lovers | ||
| Clytie or | Palaestra | no known offspring | • Amphion[134] | • Perseus[135] | |
| Myrto or | Pandrosus | • Ceryx (possibly) | • Chryses, priest of Apollo | • Polydeuces[136] | |
| Phaethusa or | Peitho | no known offspring | • Daphnis(relation ambiguous)[137] | • Therses[138] | |
| Theobula | Persephone | unsuccessfully wooed her | • Crocus | • Odrysus[139] | |
Genealogy
Art and iconography
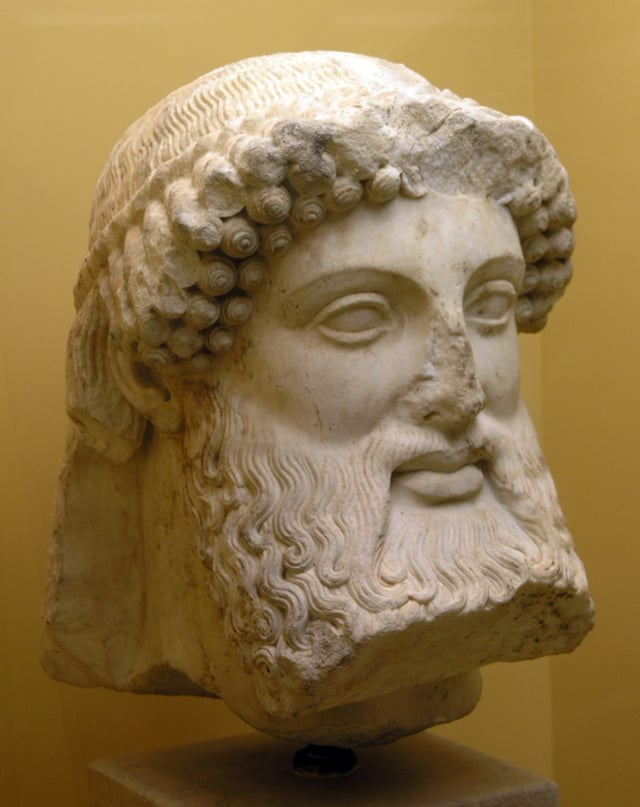

Archaic bearded Hermes from a herm, early 5th century BC.
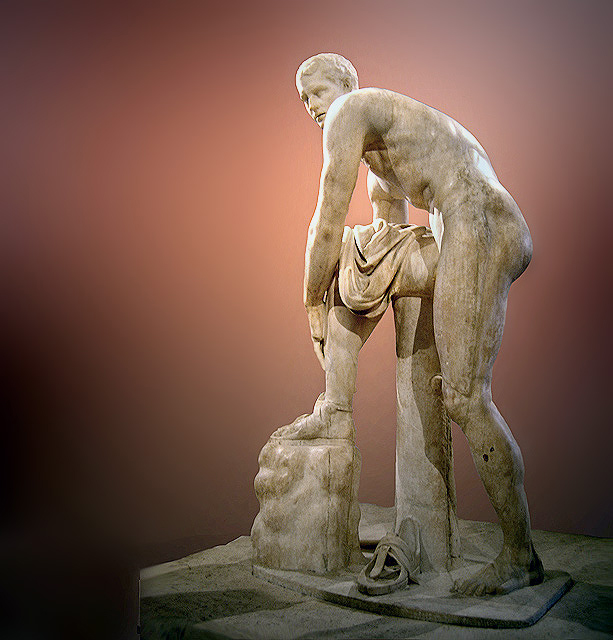

Hermes Fastening his Sandal, early Imperial Roman marble copy of a Lysippan bronze (Louvre Museum)
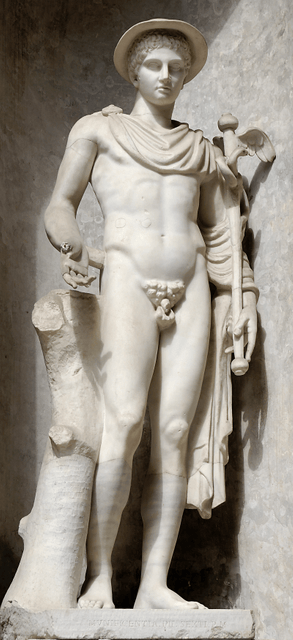
The image of Hermes evolved and varied according to Greek art and culture. During Archaic Greece he was usually depicted as a mature man, bearded, dressed as a traveler, herald, or pastor. During Classical and Hellenistic Greece he is usually depicted young and nude, with athleticism, as befits the god of speech and of the gymnastics, or a robe, a formula is set predominantly through the centuries. When represented as Logios (Greek: Λόγιος, speaker), his attitude is consistent with the attribute. Phidias left a statue of a famous Hermes Logios and Praxiteles another, also well known, showing him with the baby Dionysus in his arms. At all times, however, through the Hellenistic periods, Roman, and throughout Western history into the present day, several of his characteristic objects are present as identification, but not always all together.[106][146]
Among these objects is a wide-brimmed hat, the petasos, widely used by rural people of antiquity to protect themselves from the sun, and that in later times was adorned with a pair of small wings; sometimes the hat is not present, and may have been replaced with wings rising from the hair. Another object is the Porta: a stick, called a skeptron (scepter), which is referred to as a magic wand. Some early sources say that this was the bat he received from Apollo, but others question the merits of this claim. It seems that there may have been two canes, one of a shepherd's staff, as stated in the Homeric Hymn, and the other a magic wand, according to some authors. His bat also came to be called kerykeion, the caduceus, in later times. Early depictions of the staff show it as a baton stick topped by a golden way that resembled the number eight, though sometimes with its top truncated and open. Later the staff had two intertwined snakes and sometimes it was crowned with a pair of wings and a ball, but the old form remained in use even when Hermes was associated with Mercury by the Romans.[106][147]
Hyginus explained the presence of snakes, saying that Hermes was traveling in Arcadia when he saw two snakes intertwined in battle. He put the caduceus between them and parted, and so said his staff would bring peace.[148] The caduceus, historically, appeared with Hermes, and is documented among the Babylonians from about 3500 BC. The two snakes coiled around a stick was a symbol of the god Ningishzida, which served as a mediator between humans and the goddess Ishtar or the supreme Ningirsu. In Greece itself the other gods have been depicted holding a caduceus, but it was mainly associated with Hermes. It was said to have the power to make people fall asleep or wake up, and also made peace between litigants, and is a visible sign of his authority, being used as a sceptre.[106]
He was represented in doorways, possibly as an amulet of good fortune, or as a symbol of purification. The caduceus is not to be confused with the Rod of Asclepius, the patron of medicine and son of Apollo, which bears only one snake. The rod of Asclepius was adopted by most Western doctors as a badge of their profession, but in several medical organizations of the United States, the caduceus took its place since the 18th century, although this use is declining. After the Renaissance the caduceus also appeared in the heraldic crests of several, and currently is a symbol of commerce.[106]
His sandals, called pédila by the Greeks and talaria by the Romans, were made of palm and myrtle branches but were described as beautiful, golden and immortal, made a sublime art, able to take the roads with the speed of wind. Originally, they had no wings, but late in the artistic representations, they are depicted. In certain images, the wings spring directly from the ankles. Hermes has also been depicted with a purse or a bag in his hands, wearing a robe or cloak, which had the power to confer invisibility. His weapon was a sword of gold, which killed Argos; lent to Perseus to kill Medusa.[106]
In other religions
Christianity
According to Acts 14, when Paul the Apostle visited the city of Lystra, the people there mistook him for Hermes and his companion Barnabas for Zeus.[149]
Modern interpretation
Psychology
For Carl Jung Hermes's role as messenger between realms and as guide to the underworld,[150] made him the god of the unconscious,[151] the mediator between the conscious and unconscious parts of the mind, and the guide for inner journeys.[152][153] Jung considered the gods Thoth and Hermes to be counterparts.[154] In Jungian psychology especially,[155] Hermes is seen as relevant to study of the phenomenon of synchronicity[156] (together with Pan and Dionysus):[157][158]
Hermes is ... the archetypal core of Jung's psyche, theories ...— DL Merritt[151]
In the context of abnormal psychology Samuels (1986) states that Jung considers Hermes the archetype for narcissistic disorder; however, he lends the disorder a "positive" (beneficious) aspect, and represents both the good and bad of narcissism.[159]
According to Christopher Booker, all the roles Hermes held in ancient Greek thought all considered reveals Hermes to be a guide or observer of transition.[162]
For Jung, Hermes's role as trickster made him a guide through the psychotherapeutic process.[153]
Hermes series essays
French philosopher Michel Serres wrote a set of essays called the Hermes series.[163]
Hermes in popular culture
See also
Hermes Trismegistus