Drupal

Drupal

 Drupal 8 in action. Showing in-context editing and previews (WYSIWYG). | |
| Original author(s) | Dries Buytaert |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Drupal community |
| Initial release | May 18, 2000 (2000-05-18)[1] |
| Stable release | |
| Repository | Drupal Repository [109] |
| Written in | PHP, using Symfony |
| Operating system | Unix-like, Windows |
| Platform | Web platform |
| Size | 80 MB (uncompressed Drupal 8 core)[3] |
| Type | Content management framework, content management system, blog software |
| License | GPLv2+[4] |
| Website | www.drupal.org [110] |
Drupal /ˈdruːpəl/[5] is a free and open-source content management framework written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License.[4][6][7] Drupal provides a back-end framework for at least 2.3% of all websites worldwide[8][9] – ranging from personal blogs to corporate, political, and government sites.[10] Systems also use Drupal for knowledge management and for business collaboration.[11]
As of March 2019, the Drupal community comprised more than 1.37 million members,[12][13] including 114,000 users actively contributing,[14] resulting in more than 42,650 free modules that extend and customize Drupal functionality,[15] over 2,750 free themes that change the look and feel of Drupal,[16] and at least 1,270 free distributions that allow users to quickly and easily set up a complex, use-specific Drupal in fewer steps.[17]
The standard release of Drupal, known as Drupal core, contains basic features common to content-management systems. These include user account registration and maintenance, menu management, RSS feeds, taxonomy, page layout customization, and system administration. The Drupal core installation can serve as a simple website, a single- or multi-user blog, an Internet forum, or a community website providing for user-generated content.
Drupal runs on any computing platform that supports both a web server capable of running PHP and a database to store content and configuration.
 Drupal 8 in action. Showing in-context editing and previews (WYSIWYG). | |
| Original author(s) | Dries Buytaert |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Drupal community |
| Initial release | May 18, 2000 (2000-05-18)[1] |
| Stable release | |
| Repository | Drupal Repository [109] |
| Written in | PHP, using Symfony |
| Operating system | Unix-like, Windows |
| Platform | Web platform |
| Size | 80 MB (uncompressed Drupal 8 core)[3] |
| Type | Content management framework, content management system, blog software |
| License | GPLv2+[4] |
| Website | www.drupal.org [110] |
History
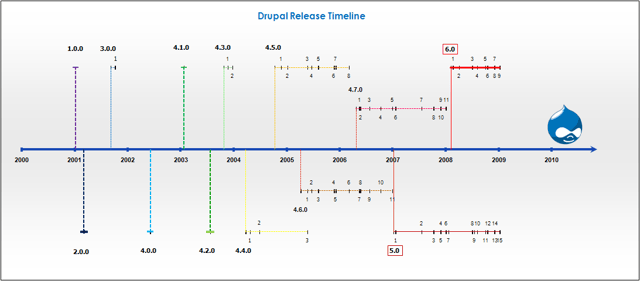
Drupal version 1-6 release history timeline
| Version | Release date | |
|---|---|---|
| Current stable version:8.7.1 | May 8, 2019[3] | |
| Older version, yet still supported:7.67 | May 8, 2019[22] | |
| Old version, no longer supported:6.38 | February 24, 2016[23] | |
| Old version, no longer supported:5.23 | August 11, 2010[24] | |
Legend: Old version Older version, still supported Latest version Latest preview version Future release | ||
Originally written by Dries Buytaert as a message board, Drupal became an open source project in 2001.[25] The name Drupal represents an English rendering of the Dutch word druppel, which means "drop" (as in a water droplet).[26] The name came from the now-defunct Drop.org website, whose code slowly evolved into Drupal. Buytaert wanted to call the site "dorp" (Dutch for "village") for its community aspects, but mistyped it when checking the domain name and thought the error sounded better.[25]
Interest in Drupal got a significant boost in 2003 when it helped build "DeanSpace" for Howard Dean, one of the candidates in the U.S. Democratic Party's primary campaign for the 2004 U.S. presidential election. DeanSpace used open-source sharing of Drupal to support a decentralized network of approximately 50 disparate, unofficial pro-Dean websites that allowed users to communicate directly with one another as well as with the campaign.[27] After Dean ended his campaign, members of his Web team continued to pursue their interest in developing a Web platform that could aid political activism by launching CivicSpace Labs in July 2004, "...the first company with full-time employees that was developing and distributing Drupal technology."[28] Other companies began to also specialize in Drupal development.[29][30] By 2013 the Drupal website listed hundreds of vendors that offered Drupal-related services.[31]
As of January 2017 more than 1,180,000 sites use Drupal.[35] These include hundreds of well-known organizations,[36] including corporations, media and publishing companies, governments, non-profits,[37] schools, and individuals. Drupal has won several Packt Open Source CMS Awards[38] and won the Webware 100 three times in a row.[39][40]
Drupal 6 was released on February 13, 2008,[41] on March 5, 2009 Buytaert announced a code freeze for Drupal 7 for September 1, 2009.[42] Drupal 7 was released on January 5, 2011, with release parties in several countries.[43] After that, maintenance on Drupal 5 stopped, with only Drupal 7 and Drupal 6 maintained.[44] Drupal 7 series maintenance updates are released regularly.[45] Drupal 7 is officially announced to reach end-of-life by 2021, official community support along with support provided by the Drupal Association on Drupal.org will cease by 2021.[46]
On October 7, 2015 Drupal 8 first release candidate (rc1) was announced.[47] Drupal 8 includes new features and improvements for both users and developers, including: a revamped user interface; WYSIWYG and in-place editing; improved mobile support; added and improved key contributed modules including Views, Date, and Entity Reference; introduced a new object-oriented backend leveraging Symfony components; revamped configuration management; and improved multilingual support. Drupal 8 rc1 is the collective work of over 3,200 core contributors.[48]
Drupal 9 is currently in development and is scheduled for release on June 3, 2020[51].
Core
In the Drupal community, "CORE" refers to the collaboratively built codebase that can be extended through contributory modules and – for versions prior to Drupal 8 – is kept outside of the "sites" folder of a Drupal installation.[52] (Starting with version 8, core is kept in its own 'core' sub-directory.) Drupal core is the stock element of Drupal. Bootstrap and Common libraries are defined as Drupal core and all other functionality is defined as Drupal modules including the system module itself.
In a Drupal website's [111] default configuration, authors can contribute content as either registered or anonymous users (at the discretion of the administrator). This content is accessible to web visitors through a variety of selectable criteria. As of Drupal 8, Drupal has adopted some Symfony libraries into Drupal core.
Core modules also includes a hierarchical taxonomy system, which lets developers categorize content or tagged with key words for easier access.[21]
Drupal maintains a detailed changelog of core feature updates by version.[53]
Core modules
Drupal core includes optional modules that can be enabled by the administrator to extend the functionality of the core website.[54]
The core Drupal distribution provides a number of features, including:[54]
Access statistics and logging
Advanced search
Blogs, books, comments, forums, and polls
Caching and feature throttling for improved performance
Descriptive URLs
Multi-level menu system
Multi-site support[55]
Multi-user content creation and editing
OpenID support
RSS feed and feed aggregator
Security and new release update notification
User profiles
Various access control restrictions (user roles, IP addresses, email)
Workflow tools (triggers and actions)
Core themes
Drupal includes core themes, which customize the "look and feel" of Drupal sites,[56] for example, Garland and Bartik.
The Color Module, introduced in Drupal core 5.0, allows administrators to change the color scheme of certain themes via a browser interface.[57]
Localization
Drupal localization is built on top of gettext, the GNU internationalization and localization (i18n) library.
Auto-update notification
Drupal can automatically notify the administrator about new versions of modules, themes, or the Drupal core.[59] It's important to update quickly after security updates are released.
Before updating it is highly recommended to take backup of core, modules, theme, files and database. If there is any error shown after update or if the new update is not compatible with a module, then it can be quickly replaced by backup. There are several backup modules available in Drupal.
On October 15, 2014, a sql injection vulnerability was announced and update released.[60] Two weeks later the Drupal security team released an advisory explaining that everyone should act under the assumption that any site not updated within 7 hours of the announcement are infected.[61] Thus, it can be extremely important to apply these updates quickly and usage of a tool to make this process easier like drush is highly recommended.
Database abstraction
Prior to version 7, Drupal had functions that performed tasks related to databases, such as SQL query cleansing, multi-site table name prefixing, and generating proper SQL queries. In particular, Drupal 6 introduced an abstraction layer that allowed programmers to create SQL queries without writing SQL.
Drupal 9 extends the data abstraction layer so that a programmer no longer needs to write SQL queries as text strings. It uses PHP Data Objects to abstract the database. Microsoft has written a database driver for their SQL Server. Drupal 7 supports the file-based SQLite database engine, which is part of the standard PHP distribution.
Windows development
With Drupal 9's new database abstraction layer, and ability to run on the Windows web server IIS, it is now easier for Windows developers to participate in the Drupal community.
A group on Drupal.org is dedicated to Windows issues.[62]
Accessibility
With the release of Drupal 7, Web accessibility has been greatly improved by the Drupal community.[63] Drupal is a good framework for building sites accessible to people with disabilities, because many of the best practices have been incorporated into the program code Core. The accessibility team is carrying on the work of identifying and resolving accessibility barriers and raising awareness within the community.
Drupal 7 started the adoption of WAI-ARIA support for Rich Internet Applications and this has been carried further in Drupal 8. There have been many improvements to both the visitor and administrator sides of Drupal, especially:
Drag and drop functionality
Improved color contrast and intensity
Adding skip navigation to core themes
Adding labels by default for input forms
Fixing CSS display:none with consistent methods for hiding and exposing text on focus.
The community also added an accessibility gate for core issues in Drupal 8.[64]
Extending the core
Drupal core is modular, defining a system of hooks and callbacks, which are accessed internally via an API.[65] This design allows third-party contributed modules and themes to extend or override Drupal's default behaviors without changing Drupal core's code.
Drupal isolates core files from contributed modules and themes. This increases flexibility and security and allows administrators to cleanly upgrade to new releases without overwriting their site's customizations.[66] The Drupal community has the saying, "Never hack core," a strong recommendation that site developers do not change core files.[52]
Modules
Contributed modules offer such additional or alternate features as image galleries, custom content types and content listings, WYSIWYG editors, private messaging, third-party integration tools,[67] integrating with BPM portals,[68] and more. As of January 2017 the Drupal website lists more than 36,500 free modules.[15]
Some of the most commonly used contributed modules include:[69]
Content Construction Kit (CCK): allows site administrators to dynamically create content types by extending the database schema. "Content type" describes the kind of information. Content types include, but are not limited to, events, invitations, reviews, articles, and products. The CCK Fields API is in Drupal core in Drupal 7.[70][71]
Views: facilitates the retrieval and presentation, through a database abstraction system, of content to site visitors. Basic views functionality has been added to core in Drupal 8.[72]
Panels: drag and drop layout manager that allows site administrators to visually design their site.
Rules: conditionally executed actions based on recurring events.
Features: enables the capture and management of features (entities, views, fields, configuration, etc.) into custom modules.
Context: allows definition of sections of site where Drupal features can be conditionally activated
Media: makes photo uploading and media management easier
Services: provides an API for Drupal.
Organic Groups Mailing List
Themes
As of January 2017, there are more than 2,400[16] free community-contributed themes. Themes adapt or replace a Drupal site's default look and feel.
The inclusion of the PHPTemplate and XTemplate engines in Drupal addressed user concerns about flexibility and complexity.[75] The Drupal theming system utilizes a template engine to further separate HTML/CSS from PHP. A popular Drupal contributed module called 'Devel' provides GUI information to developers and themers about the page build.
Distributions
In the past, those wanting a fully customized installation of Drupal had to download a pre-tailored version separately from the official Drupal core. Today, however, a distribution defines a packaged version of Drupal that upon installation, provides a website or application built for a specific purpose.
The distributions offer the benefit of a new Drupal site without having to manually seek out and install third-party contributed modules or adjust configuration settings.[79] They are collections of modules, themes, and associated configuration settings that prepare Drupal for custom operation. For example, a distribution could configure Drupal as a "brochure" site rather than a news site or online store.
Architecture
Drupal is based on the Presentation Abstraction Control architecture, or PAC.
The menu system [113] acts as the Controller. It accepts input via a single source (HTTP GET and POST), routes requests to the appropriate helper functions, pulls data out of the Abstraction (nodes and, from Drupal 5 onwards, forms), and then pushes it through a filter to get a Presentation of it (the theme system).
It even has multiple, parallel PAC agents in the form of blocks that push data out to a common canvas (page.tpl.php).[80]
Community
Drupal.org has a large community of users and developers who provide active community support by coming up with new updates to help improve the functionality of Drupal,[81] As of January 2017 more than 105,400 users are actively contributing.[14] The semiannual DrupalCon conference alternates between North America, Europe and Asia.[82] Attendance at DrupalCon grew from 500 at Szeged in August 2008, to over 3,700 people at Austin, Texas in June, 2014.
Smaller events, known as "Drupal Camps" or DrupalCamp,[83] occur throughout the year all over the world. The annual Florida DrupalCamp brings users together for Coding for a Cause that benefits a local nonprofit organization, as does the annual GLADCamp (Greater Los Angeles Drupal Camp) event, Coders with a Cause.
The Drupal community also organizes professional and semi-professional gatherings called meetups at a large number of venues around the world. In July, 2013, Droplabs, a co-working space in Los Angeles, California, was recognized as the world's "Top Drupal Location[84]" (with 62 recorded events) when compared with other event venues over a 12-month period.
There are over 30 national communities[89] around drupal.org offering language-specific support.
Security
Administrators of Drupal sites are automatically notified of these new releases via the Update Status module (Drupal 6) or via the Update Manager (Drupal 7).[93]
Downloading and installing an upgrade to Drupal 7.32 fixes the vulnerability, but does not remove any backdoor installed by hackers if the site has already been compromised.[100] Attacks began soon after the vulnerability was announced. According to the Drupal security team, where a site was not patched within hours of the announcement, it should be considered compromised and taken offline by being replaced with a static HTML page while the administrator of its server must be told that other sites on the same server may also have been compromised.
To solve the problem, the site must be restored using backups from before October 15, be patched and manually updated, and anything merged from the site must be audited.[101]
In late March 2018, a patch for vulnerability CVE-2018-7600, also dubbed Drupalgeddon2, was released. The underlying bug allows remote attackers without special roles or permissions to take complete control of Drupal 6, 7, and 8 sites[102]. Starting early April, large scale automated attacks against vulnerable sites were observed,[103] and on April 20, a high level of penetration of unpatched sites was reported.[104]
See also
Comparison of web frameworks
List of applications with iCalendar support
List of content management systems