Lung cancer
Lung cancer

| Lung cancer | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Lung carcinoma |
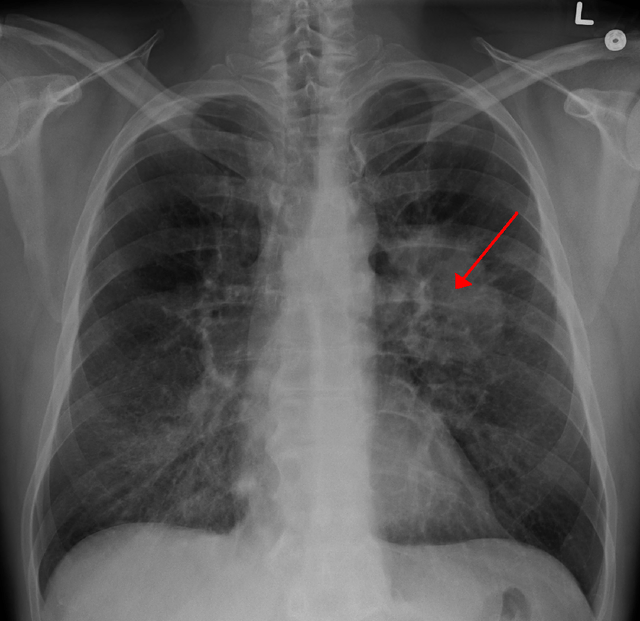
| A chest X-ray showing a tumor in the lung (marked by arrow) | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| Symptoms | Coughing (including coughing up blood), weight loss, shortness of breath, chest pains[1] |
| Usual onset | ~70 years[2] |
| Types | Small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)[3] |
| Risk factors |
|
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging, tissue biopsy[6][7] |
| Treatment | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy[7] |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate 17.4% (US)[2] |
| Frequency | 3.3 million affected as of 2015[8] |
| Deaths | 1.7 million (2015)[9] |
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma,[7] is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung.[10] This growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body.[11] Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas.[12] The two main types are small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).[3] The most common symptoms are coughing (including coughing up blood), weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pains.[1]
The vast majority (85%) of cases of lung cancer are due to long-term tobacco smoking.[4] About 10–15% of cases occur in people who have never smoked.[13] These cases are often caused by a combination of genetic factors and exposure to radon gas, asbestos, second-hand smoke, or other forms of air pollution.[4][5][14][15] Lung cancer may be seen on chest radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans.[7] The diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy which is usually performed by bronchoscopy or CT-guidance.[6][16]
Avoidance of risk factors, including smoking and air pollution, is the primary method of prevention.[17] Treatment and long-term outcomes depend on the type of cancer, the stage (degree of spread), and the person's overall health.[7] Most cases are not curable.[3] Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy.[7] NSCLC is sometimes treated with surgery, whereas SCLC usually responds better to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.[18]
Worldwide in 2012, lung cancer occurred in 1.8 million people and resulted in 1.6 million deaths.[12] This makes it the most common cause of cancer-related death in men and second most common in women after breast cancer.[19] The most common age at diagnosis is 70 years.[2] Overall, 17.4% of people in the United States diagnosed with lung cancer survive five years after the diagnosis,[2] while outcomes on average are worse in the developing world.[20]
| Lung cancer | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Lung carcinoma |
| A chest X-ray showing a tumor in the lung (marked by arrow) | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
| Symptoms | Coughing (including coughing up blood), weight loss, shortness of breath, chest pains[1] |
| Usual onset | ~70 years[2] |
| Types | Small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)[3] |
| Risk factors |
|
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging, tissue biopsy[6][7] |
| Treatment | Surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy[7] |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate 17.4% (US)[2] |
| Frequency | 3.3 million affected as of 2015[8] |
| Deaths | 1.7 million (2015)[9] |
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms which may suggest lung cancer include:[1]
Respiratory symptoms: coughing, coughing up blood, wheezing, or shortness of breath
Systemic symptoms: weight loss, weakness, fever, or clubbing of the fingernails
Symptoms due to the cancer mass pressing on adjacent structures: chest pain, bone pain, superior vena cava obstruction, or difficulty swallowing
Depending on the type of tumor, paraneoplastic phenomena — symptoms not due to the local presence of cancer — may initially attract attention to the disease.[21] In lung cancer, these phenomena may include hypercalcemia, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH, abnormally concentrated urine and diluted blood), ectopic ACTH production, or Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (muscle weakness due to autoantibodies). Tumors in the top of the lung, known as Pancoast tumors, may invade the local part of the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in Horner's syndrome (dropping of the eyelid and a small pupil on that side), as well as damage to the brachial plexus.[1]
Many of the symptoms of lung cancer (poor appetite, weight loss, fever, fatigue) are not specific.[6] In many people, the cancer has already spread beyond the original site by the time they have symptoms and seek medical attention.[22] Symptoms that suggest the presence of metastatic disease include weight loss, bone pain, and neurological symptoms (headaches, fainting, convulsions, or limb weakness).[1] Common sites of spread include the brain, bone, adrenal glands, opposite lung, liver, pericardium, and kidneys.[22] About 10% of people with lung cancer do not have symptoms at diagnosis; these cancers are incidentally found on routine chest radiography.[16]
Causes

Relationship between cigarette consumption per person (blue) and male lung cancer rates (dark yellow) in the US over the century.

Risk of death from lung cancer is strongly correlated with smoking
Cancer develops after genetic damage to DNA and epigenetic changes. Those changes affect the cell's normal functions, including cell proliferation, programmed cell death (apoptosis), and DNA repair. As more damage accumulates, the risk for cancer increases.[23]
Smoking
Tobacco smoking is by far the main contributor to lung cancer.[4] Cigarette smoke contains at least 73 known carcinogens,[24] including benzo[a]pyrene,[25] NNK, 1,3-butadiene, and a radioactive isotope of polonium – polonium-210.[24] Across the developed world, 90% of lung cancer deaths in men and 70% of those in women during the year 2000 were attributed to smoking.[26] Smoking accounts for about 85% of lung cancer cases.[7]
Passive smoking – the inhalation of smoke from another's smoking – is a cause of lung cancer in nonsmokers. A passive smoker can be defined as someone either living or working with a smoker. Studies from the US,[27][28][29] Europe,[30] and the UK[31] have consistently shown a significantly-increased risk among those exposed to passive smoking.[32] Those who live with someone who smokes have a 20–30% increase in risk while those who work in an environment with secondhand smoke have a 16–19% increase in risk.[33] Investigations of sidestream smoke suggest that it is more dangerous than direct smoke.[34] Passive smoking results in roughly 3,400 lung cancer-related deaths each year in the US.[29]
Marijuana smoke contains many of the same carcinogens as those in tobacco smoke.[35] However, the effect of smoking cannabis on lung cancer risk is not clear.[36][37] A 2013 review did not find an increased risk from light to moderate use.[38] A 2014 review found that smoking cannabis doubled the risk of lung cancer.[39]
Radon gas
Radon is a colorless and odorless gas generated by the breakdown of radioactive radium, which in turn is the decay product of uranium, found in the Earth's crust. The radiation decay products ionize genetic material, causing mutations that sometimes become cancerous. Radon is the second most-common cause of lung cancer in the US,[40] causing about 21,000 deaths each year.[41] The risk increases 8–16% for every 100 Bq/m³ increase in the radon concentration.[42] Radon gas levels vary by locality and the composition of the underlying soil and rocks. About one in 15 homes in the US have radon levels above the recommended guideline of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/l) (148 Bq/m³).[43]
Asbestos
Asbestos can cause a variety of lung diseases such as lung cancer. Tobacco smoking and asbestos both have synergistic effects on the development of lung cancer.[5] In smokers who work with asbestos, the risk of lung cancer is increased 45-fold compared to the general population.[44] Asbestos can also cause cancer of the pleura, called mesothelioma – which actually is different from lung cancer.[45]
Air pollution
Outdoor air pollutants, especially chemicals released from the burning of fossil fuels, increase the risk of lung cancer.[4] Fine particulates (PM2.5) and sulfate aerosols, which may be released in traffic exhaust fumes, are associated with a slightly-increased risk.[4][46] For nitrogen dioxide, an incremental increase of 10 parts per billion increases the risk of lung cancer by 14%.[47] Outdoor air pollution is estimated to cause 1–2% of lung cancers.[4]
Tentative evidence supports an increased risk of lung cancer from indoor air pollution in relation to the burning of wood, charcoal, dung, or crop residue for cooking and heating.[48] Women who are exposed to indoor coal smoke have roughly twice the risk, and many of the by-products of burning biomass are known or suspected carcinogens.[49] This risk affects about 2.4 billion people worldwide,[48] and it is believed to result in 1.5% of lung cancer deaths.[49]
Genetics
About 8% of lung cancer is caused by inherited factors.[50] In relatives of people that are diagnosed with lung cancer, the risk is doubled, likely due to a combination of genes.[51] Polymorphisms on chromosomes 5, 6, and 15 are known to affect the risk of lung cancer.[52] Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the genes encoding the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) – CHRNA5, CHRNA3, and CHRNB4 – are of those associated with an increased risk of lung cancer, as well as RGS17 – a gene regulating G-protein signaling.[52]
Other causes
Numerous other substances, occupations, and environmental exposures have been linked to lung cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) states that there is some "sufficient evidence" to show that the following are carcinogenic in the lungs:[53]
Some metals (aluminium production, cadmium and cadmium compounds, chromium(VI) compounds, beryllium and beryllium compounds, iron and steel founding, nickel compounds, arsenic and inorganic arsenic compounds, and underground hematite mining)
Some products of combustion (incomplete combustion, coal (indoor emissions from household coal burning), coal gasification, coal-tar pitch, coke production, soot, and diesel engine exhaust)
Ionizing radiation (X-ray and gamma)
Some toxic gases (methyl ether (technical grade), and bis-(chloromethyl) ether, sulfur mustard, MOPP (vincristine-prednisone-nitrogen mustard-procarbazine mixture) and fumes from painting)
Rubber production and crystalline silica dust
There is a small increase in the risk of lung cancer in people affected by systemic sclerosis.
Pathogenesis
Epigenetic changes such as alteration of DNA methylation, histone tail modification, or microRNA regulation may result in the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes.[59] Importantly, cancer cells develop resistance to oxidative stress, which enables them to withstand and exacerbate inflammatory conditions that inhibit the activity of the immune system against the tumor.[60][61]
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and tumor invasion.[56] Mutations and amplification of EGFR are common in non-small-cell lung carcinoma, and they provide the basis for treatment with EGFR-inhibitors. Her2/neu is affected less frequently.[56] Other genes that are often mutated or amplified include c-MET, NKX2-1, LKB1, PIK3CA, and BRAF.[56]
The cell lines of origin are not fully understood.[1] The mechanism may involve the abnormal activation of stem cells. In the proximal airways, stem cells that express keratin 5 are more likely to be affected, typically leading to squamous-cell lung carcinoma. In the middle airways, implicated stem cells include club cells and neuroepithelial cells that express club cell secretory protein. Small-cell lung carcinoma may originate from these cell lines[62] or neuroendocrine cells,[1] and it may express CD44.[62]
Metastasis of lung cancer requires transition from epithelial to mesenchymal cell type. This may occur through the activation of signaling pathways such as Akt/GSK3Beta, MEK-ERK, Fas, and Par6.[63]
Diagnosis
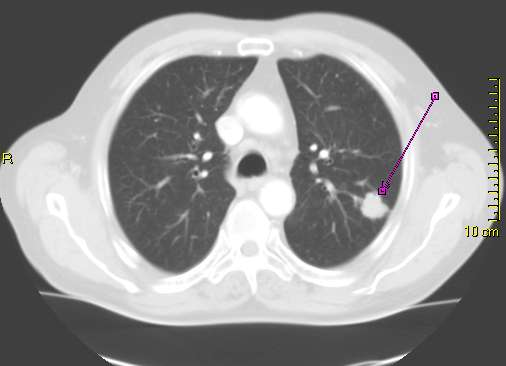
CT scan showing a cancerous tumor in the left lung
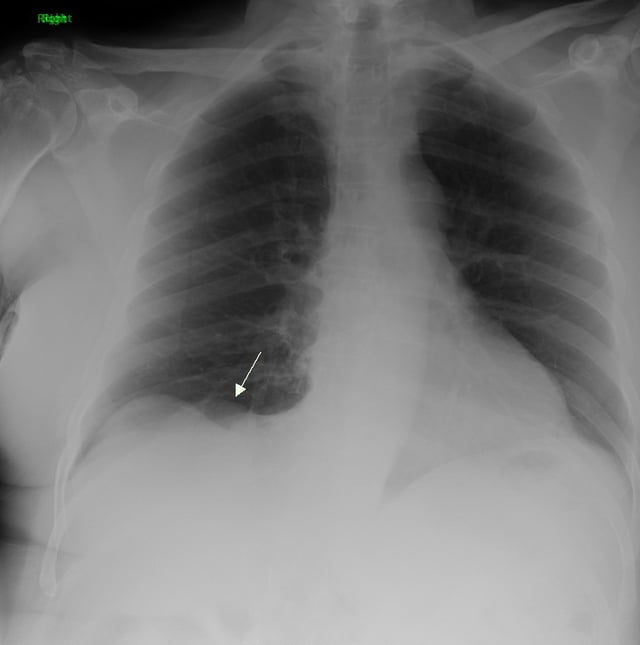
Primary pulmonary sarcoma in an asymptomatic 72-year-old male.
Performing a chest radiograph is one of the first investigative steps if a person reports symptoms that may be suggestive of lung cancer. This may reveal an obvious mass, the widening of the mediastinum (suggestive of spread to lymph nodes there), atelectasis (lung collapse), consolidation (pneumonia), or pleural effusion.[7] CT imaging is typically used to provide more information about the type and extent of disease. Bronchoscopic or CT-guided biopsy is often used to sample the tumor for histopathology.[16]
Lung cancer often appears as a solitary pulmonary nodule on a chest radiograph. However, the differential diagnosis is wide. Many other diseases can also give this appearance, including metastatic cancer, hamartomas, and infectious granulomas caused by tuberculosis, histoplasmosis or coccidioidomycosis.[64] Lung cancer can also be an incidental finding, as a solitary pulmonary nodule on a chest radiograph or CT scan done for an unrelated reason.[65] The definitive diagnosis of lung cancer is based on the histological examination of the suspicious tissue[1] in the context of the clinical and radiological features.[6]
Classification

Pie chart showing incidences of non-small cell lung cancers as compared to small cell carcinoma shown at right, with fractions of smokers versus non-smokers shown for each type.[67]
| Histological type | Incidence per 100,000 per year |
|---|---|
| All types | 66.9 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 22.1 |
| Squamous-cell carcinoma | 14.4 |
| Small-cell carcinoma | 9.8 |
Lung cancers are classified according to histological type.[6] This classification is important for determining both the management and predicting outcomes of the disease. Lung cancers are carcinomas – malignancies that arise from epithelial cells. Lung carcinomas are categorized by the size and appearance of the malignant cells seen by a histopathologist under a microscope. For therapeutic purposes, two broad classes are distinguished: non-small-cell lung carcinoma and small-cell lung carcinoma.[68]
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma
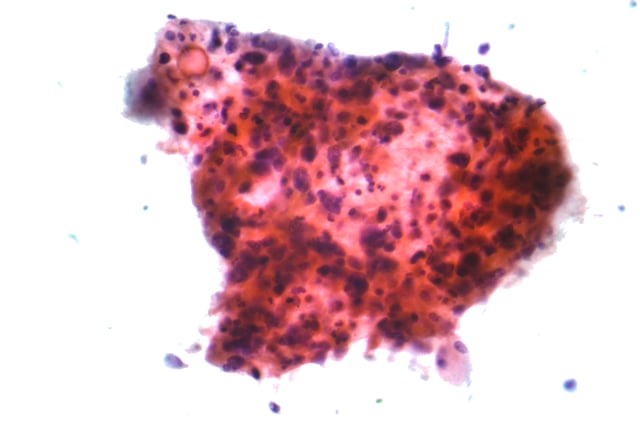
Micrograph of squamous-cell carcinoma, a type of non-small-cell carcinoma, FNA specimen, Pap stain
The three main subtypes of NSCLC are adenocarcinoma, squamous-cell carcinoma, and large-cell carcinoma.[1]
Nearly 40% of lung cancers are adenocarcinoma, which usually comes from peripheral lung tissue.[6] Although most cases of adenocarcinoma are associated with smoking, adenocarcinoma is also the most-common form of lung cancer among people who have smoked fewer than 100 cigarettes in their lifetimes ("never-smokers")[1][69] and ex-smokers with a modest smoking history.[1] A subtype of adenocarcinoma, the bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, is more common in female never-smokers, and may have a better long-term survival.[70]
Squamous-cell carcinoma causes about 30% of lung cancers. They typically occur close to large airways. A hollow cavity and associated cell death are commonly found at the center of the tumor.[6]
Nearly 9% of lung cancers are large-cell carcinoma. These are so named because the cancer cells are large, with excess cytoplasm, large nuclei, and conspicuous nucleoli.[6]
Small-cell lung carcinoma
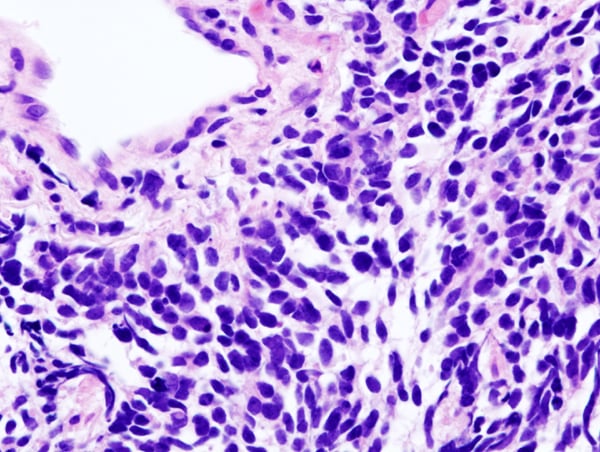
Small-cell lung carcinoma (microscopic view of a core needle biopsy)
In SCLC, the cells contain dense neurosecretory granules (vesicles containing neuroendocrine hormones), which give this tumor an endocrine or paraneoplastic syndrome association.[71] Most cases arise in the larger airways (primary and secondary bronchi).[16] Sixty to seventy percent have extensive disease (which cannot be targeted within a single radiation therapy field) at presentation.[1]
Others
Metastasis
| Histological type | Napsin-A | TTF-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Squamous-cell carcinoma | Negative | Negative |
| Adenocarcinoma | Positive | Positive |
| Small-cell carcinoma | Negative | Positive |
The lungs are a common place for the spread of tumors from other parts of the body. Secondary cancers are classified by the site of origin; for example, breast cancer that has been spread to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer. Metastases often have a characteristic round appearance on chest radiograph.[72]
Primary lung cancers also most commonly metastasize to the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal glands.[6] Immunostaining of a biopsy usually helps determine the original source.[73] The presence of Napsin-A, TTF-1, CK7, and CK20 help confirm the subtype of lung carcinoma. SCLC that originates from neuroendocrine cells may express CD56, neural cell adhesion molecule, synaptophysin, or chromogranin.[1]
Staging
The evaluation of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) staging uses the TNM classification (tumor, node, metastasis). This is based on the size of the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and distant metastasis.[1]
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using the TNM descriptors, a group is assigned, ranging from occult cancer, through stages 0, IA (one-A), IB, IIA, IIB, IIIA, IIIB, and IV (four). This stage group assists with the choice of treatment and estimation of prognosis.[77]
| TNM | Stage group |
|---|---|
| T1a–T1b N0 M0 | IA |
| T2a N0 M0 | IB |
| T1a–T2a N1 M0 | IIA |
| T2b N0 M0 | |
| T2b N1 M0 | IIB |
| T3 N0 M0 | |
| T1a–T3 N2 M0 | IIIA |
| T3 N1 M0 | |
| T4 N0–N1 M0 | |
| N3 M0 | IIIB |
| T4 N2 M0 | |
| M1 | IV |
For both NSCLC and SCLC, the two general types of staging evaluations are clinical staging and surgical staging. Clinical staging is performed before definitive surgery. It is based on the results of imaging studies (such as CT scans and PET scans) and biopsy results. Surgical staging is evaluated either during or after the operation. It is based on the combined results of surgical and clinical findings, including surgical sampling of thoracic lymph nodes.[6]
Prevention

Cross section of a human lung: The white area in the upper lobe is cancer; the black areas are discoloration due to smoking.
Smoking prevention and smoking cessation are effective ways of preventing the development of lung cancer.[78]
Smoking ban
While in most countries industrial and domestic carcinogens have been identified and banned, tobacco smoking is still widespread. Eliminating tobacco smoking is a primary goal in the prevention of lung cancer, and smoking cessation is an important preventive tool in this process.[79]
Policy interventions to decrease passive smoking in public areas such as restaurants and workplaces have become more common in many Western countries.[80] Bhutan has had a complete smoking ban since 2005[81] while India introduced a ban on smoking in public in October 2008.[82] The World Health Organization has called for governments to institute a total ban on tobacco advertising to prevent young people from taking up smoking. They assess that such bans have reduced tobacco consumption by 16% where instituted.[83]
Screening
Cancer screening uses medical tests to detect disease in large groups of people who have no symptoms.[84] For individuals with high risk of developing lung cancer, computed tomography (CT) screening can detect cancer and give a person options to respond to it in a way that prolongs life.[66][85] This form of screening reduces the chance of death from lung cancer by an absolute amount of 0.3% (relative amount of 20%).[86][87] High risk people are those age 55–74 who have smoked equivalent amount of a pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years including time within the past 15 years.[66]
CT screening is associated with a high rate of falsely positive tests which may result in unneeded treatment.[88] For each true positive scan there are about 19 falsely positives scans.[89] Other concerns include radiation exposure[88] and the cost of testing along with follow up.[66] Research has not found two other available tests—sputum cytology or chest radiograph (CXR) screening tests—to have any benefit.[85][90]
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends yearly screening using low-dose computed tomography in those who have a total smoking history of 30 pack-years and are between 55 and 80 years old until a person has not been smoking for more than 15 years.[91] Screening should not be done in those with other health problems that would make treatment of lung cancer if found not an option.[91] The English National Health Service was in 2014 re-examining the evidence for screening.[92]
Other prevention strategies
Some studies suggest that people who eat diets with a higher proportion of vegetables and fruit tend to have a lower risk,[29][97] but this may be due to confounding—with the lower risk actually due to the association of a high fruit and vegetables diet with less smoking.[98] Several rigorous studies have not demonstrated a clear association between diet and lung cancer risk,[1][97] although meta-analysis that accounts for smoking status may show benefit from a healthy diet.[99]
Management
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the cancer's specific cell type, how far it has spread, and the person's performance status. Common treatments include palliative care,[100] surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.[1] Targeted therapy of lung cancer is growing in importance for advanced lung cancer.[101] People who have lung cancer should be encouraged to stop smoking.[102] There is no clear evidence which smoking cessation program is most effective for people who have been diagnosed with lung cancer.[102] It is unclear if exercise training is beneficial for people living with advanced lung cancer.[103] Exercise training may benefit people with NSCLC who are recovering from lung surgery.[104]
Surgery
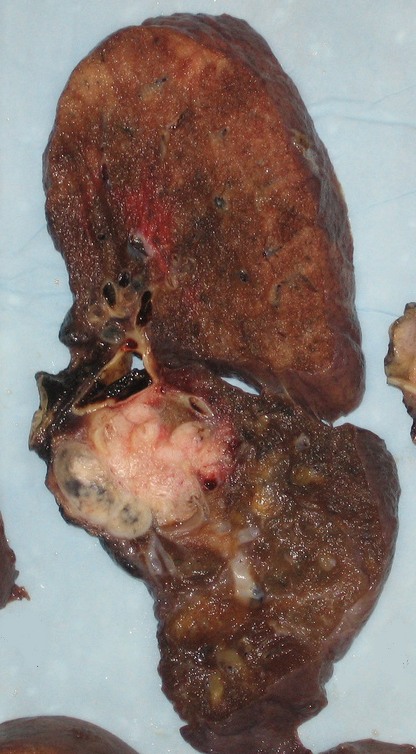
Pneumonectomy specimen containing a squamous-cell carcinoma, seen as a white area near the bronchi
If investigations confirm NSCLC, the stage is assessed to determine whether the disease is localized and amenable to surgery or if it has spread to the point where it cannot be cured surgically. CT scan and positron emission tomography are used for this determination.[1] If mediastinal lymph node involvement is suspected, the nodes may be sampled to assist staging. Techniques used for this include transthoracic needle aspiration, transbronchial needle aspiration (with or without endobronchial ultrasound), endoscopic ultrasound with needle aspiration, mediastinoscopy, and thoracoscopy.[105] Blood tests and pulmonary function testing are used to assess whether a person is well enough for surgery.[16] If pulmonary function tests reveal poor respiratory reserve, surgery may not be possible.[1]
In most cases of early-stage NSCLC, removal of a lobe of lung (lobectomy) is the surgical treatment of choice. In people who are unfit for a full lobectomy, a smaller sublobar excision (wedge resection) may be performed. However, wedge resection has a higher risk of recurrence than lobectomy. Radioactive iodine brachytherapy at the margins of wedge excision may reduce the risk of recurrence. Rarely, removal of a whole lung (pneumonectomy) is performed.[106] Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and VATS lobectomy use a minimally invasive approach to lung cancer surgery.[107] VATS lobectomy is equally effective compared to conventional open lobectomy, with less postoperative illness.[108]
Radiotherapy

Internal radiotherapy for lung cancer given via the airway.
Radiotherapy is often given together with chemotherapy, and may be used with curative intent in people with NSCLC who are not eligible for surgery.[111] This form of high-intensity radiotherapy is called radical radiotherapy.[112] A refinement of this technique is continuous hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy (CHART), in which a high dose of radiotherapy is given in a short time period.[113] Postoperative (adjuvant) thoracic radiotherapy generally should not be used after curative-intent surgery for NSCLC.[114] Some people with mediastinal N2 lymph node involvement might benefit from post-operative radiotherapy.[115]
If cancer growth blocks a short section of bronchus, brachytherapy (localized radiotherapy) may be given directly inside the airway to open the passage. Compared to external beam radiotherapy, brachytherapy allows a reduction in treatment time and reduced radiation exposure to healthcare staff.[117] Evidence for brachytherapy, however, is less than that for external beam radiotherapy.[118]
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a type of radiotherapy to the brain, used to reduce the risk of metastasis. PCI is most useful in SCLC. In limited-stage disease, PCI increases three-year survival from 15% to 20%; in extensive disease, one-year survival increases from 13% to 27%.[119]
Recent improvements in targeting and imaging have led to the development of stereotactic radiation in the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. In this form of radiotherapy, high doses are delivered over a number of sessions using stereotactic targeting techniques. Its use is primarily in patients who are not surgical candidates due to medical comorbidities.[120]
For both NSCLC and SCLC patients, smaller doses of radiation to the chest may be used for symptom control (palliative radiotherapy).[121]
Chemotherapy
The chemotherapy regimen depends on the tumor type.[6] SCLC, even relatively early stage disease, is treated primarily with chemotherapy and radiation.[122] In SCLC, cisplatin and etoposide are most commonly used.[123] Combinations with carboplatin, gemcitabine, paclitaxel, vinorelbine, topotecan, and irinotecan are also used.[124][125] In advanced NSCLC, chemotherapy improves survival and is used as first-line treatment, provided the person is well enough for the treatment.[126] Typically, two drugs are used, of which one is often platinum-based (either cisplatin or carboplatin). Other commonly used drugs are gemcitabine, paclitaxel, docetaxel,[127][128] pemetrexed,[129] etoposide or vinorelbine.[128] Platinum-based drugs and combinations that include platinum therapy may lead to a higher risk of serious adverse effects in people over 70 years old.[130]
Adjuvant chemotherapy refers to the use of chemotherapy after apparently curative surgery to improve the outcome. In NSCLC, samples are taken of nearby lymph nodes during surgery to assist staging. If stage II or III disease is confirmed, adjuvant chemotherapy (including or not including postoperative radiotherapy) improves survival by 4% at five years.[131][132][133] The combination of vinorelbine and cisplatin is more effective than older regimens.[132] Adjuvant chemotherapy for people with stage IB cancer is controversial, as clinical trials have not clearly demonstrated a survival benefit.[134] Chemotherapy before surgery in NSCLC that can be removed surgically may improve outcomes.[135][136]
Chemotherapy may be combined with palliative care in the treatment of the NSCLC.[137] In advanced cases, appropriate chemotherapy improves average survival over supportive care alone, as well as improving quality of life.[138][137] With adequate physical fitness maintaining chemotherapy during lung cancer palliation offers 1.5 to 3 months of prolongation of survival, symptomatic relief, and an improvement in quality of life, with better results seen with modern agents.[139][140] The NSCLC Meta-Analyses Collaborative Group recommends if the recipient wants and can tolerate treatment, then chemotherapy should be considered in advanced NSCLC.[126][141]
Targeted and immunotherapy
Several drugs that target molecular pathways in lung cancer are available, especially for the treatment of advanced disease. Erlotinib, gefitinib and afatinib inhibit tyrosine kinase at the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). These EGFR inhibitors may help delay the spread of cancer cells for people with EGFR M+ lung cancer and may improve a person's quality of life.[142] EGFR inhibitors have not been shown to help people survive longer.[142] For people with EGFR mutations, treatment with gefitinib may result in an improved quality of life compared to treatment with chemotherapy.[143] Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand and may be useful in the treatment of bone metastases.[144]
Bronchoscopy
Several treatments can be provided via bronchoscopy for the management of airway obstruction or bleeding. If an airway becomes obstructed by cancer growth, options include rigid bronchoscopy, balloon bronchoplasty, stenting, and microdebridement.[148] Laser photosection involves the delivery of laser light inside the airway via a bronchoscope to remove the obstructing tumor.[149]
Palliative care
Palliative care when added to usual cancer care benefits people even when they are still receiving chemotherapy.[150] These approaches allow additional discussion of treatment options and provide opportunities to arrive at well-considered decisions.[151][152] Palliative care may avoid unhelpful but expensive care not only at the end of life, but also throughout the course of the illness. For individuals who have more advanced disease, hospice care may also be appropriate.[16][152]
Prognosis
| Clinical stage | Five-year survival (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-small-cell lung carcinoma | Small-cell lung carcinoma | |
| IA | 50 | 38 |
| IB | 47 | 21 |
| IIA | 36 | 38 |
| IIB | 26 | 18 |
| IIIA | 19 | 13 |
| IIIB | 7 | 9 |
| IV | 2 | 1 |
Of all people with lung cancer in the US, 16.8% survive for at least five years after diagnosis.[2][153] In England and Wales, between 2010 and 2011, overall five-year survival for lung cancer was estimated at 9.5%.[154] Outcomes are generally worse in the developing world.[20] Stage is often advanced at the time of diagnosis. At presentation, 30–40% of cases of NSCLC are stage IV, and 60% of SCLC are stage IV.[6] Survival for lung cancer falls as the stage at diagnosis becomes more advanced: the English data suggest that around 70% of patients survive at least a year when diagnosed at the earliest stage, but this falls to just 14% for those diagnosed with the most advanced disease (stage IV).[155]
Prognostic factors in NSCLC include presence of pulmonary symptoms, large tumor size (>3 cm), non-squamous cell type (histology), degree of spread (stage) and metastases to multiple lymph nodes, and vascular invasion. For people with inoperable disease, outcomes are worse in those with poor performance status and weight loss of more than 10%.[156] Prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer include performance status, biological sex, stage of disease, and involvement of the central nervous system or liver at the time of diagnosis.[157]
For NSCLC, the best prognosis is achieved with complete surgical resection of stage IA disease, with up to 70% five-year survival.[158] People with extensive-stage SCLC have an average five-year survival rate of less than 1%. The average survival time for limited-stage disease is 20 months, with a five-year survival rate of 20%.[7]
According to data provided by the National Cancer Institute, the median age at diagnosis of lung cancer in the US is 70 years,[159] and the median age at death is 72 years.[160] In the US, people with medical insurance are more likely to have a better outcome.[161]
Epidemiology

Trachea, bronchus, and lung cancers deaths per million person in 2012 0–7 8–12 13–32 33–53 54–81 82–125 126–286 287–398 399–527 528–889
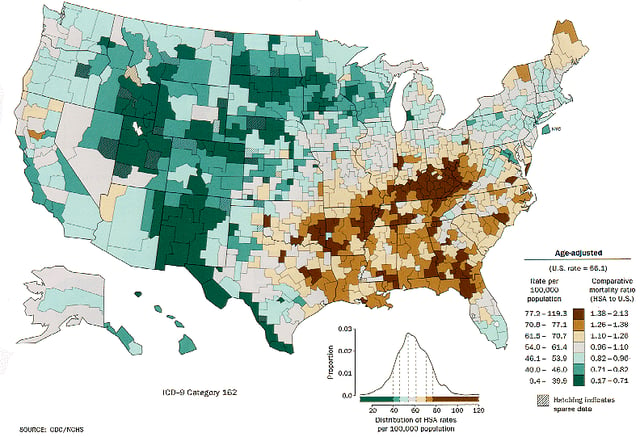
Lung cancer distribution for white males in the United States
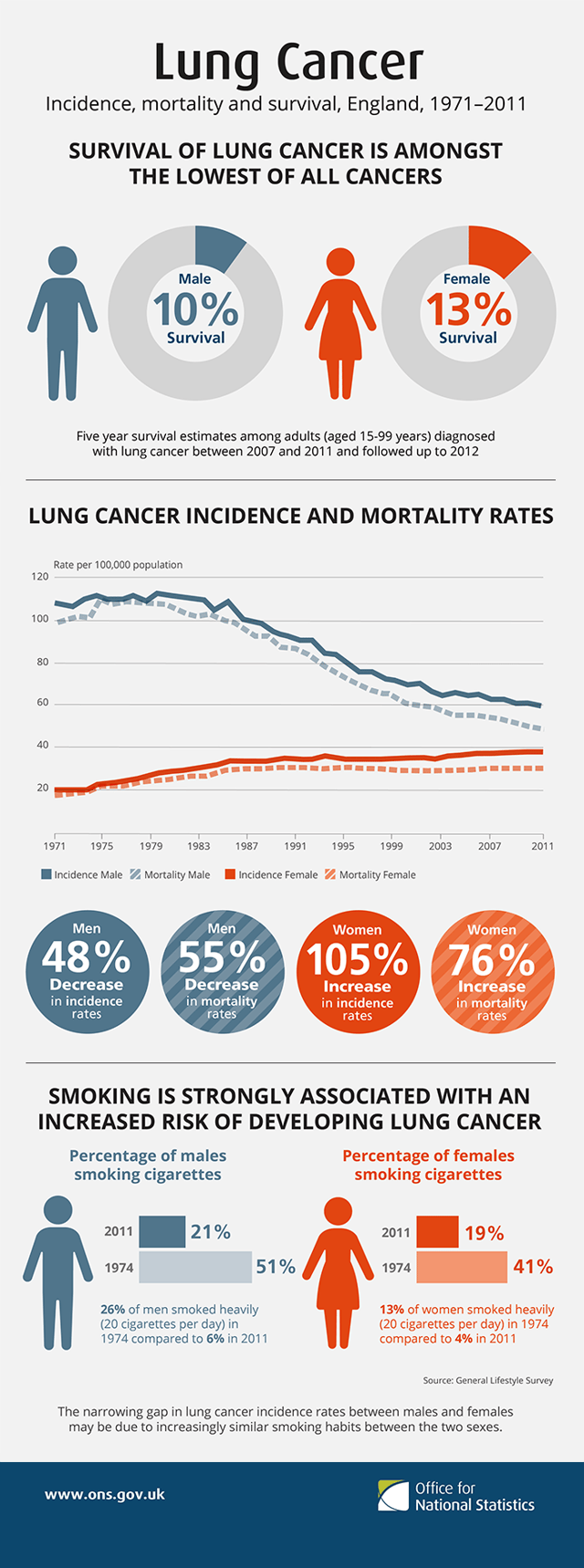
Lung cancer, incidence, mortality and survival, England 1971–2011
Worldwide, lung cancer is the most-common cancer among men in terms of both incidence and mortality, and among women has the third-highest incidence, and is second after breast cancer in mortality. In 2012, there were 1.82 million new cases worldwide, and 1.56 million deaths due to lung cancer, representing 19.4% of all deaths from cancer.[19] The highest rates are in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with over a third of new cases in China that year. Rates in Africa and South Asia are much lower.[162]
The population segment that is most likely to develop lung cancer is people aged over 50 who have a history of smoking. Unlike the mortality rate in men – which began declining more than 20 years ago, women's lung cancer mortality rates have risen over the last decades, and are just recently beginning to stabilize.[163] In the US, the lifetime risk of developing lung cancer is 8% in men and 6% in women.[1]
For every 3–4 million cigarettes smoked, one lung cancer death can occur.[164] The influence of "Big Tobacco" plays a significant role in smoking.[165] Young nonsmokers who see tobacco advertisements are more likely to smoke.[166] The role of passive smoking is increasingly being recognized as a risk factor for lung cancer,[32] resulting in policy interventions to decrease the undesired exposure of nonsmokers to others' tobacco smoke.[167]
Also in the US, military veterans have a 25–50% higher rate of lung cancer primarily due to higher rates of smoking.[172] During World War II and the Korean War, asbestos also played a role, and Agent Orange may have caused some problems during the Vietnam War.[173]
From the 1960s, the rates of lung adenocarcinoma started to rise in relation to other kinds of lung cancer, partially due to the introduction of filter cigarettes. The use of filters removes larger particles from tobacco smoke, thus reducing deposition in larger airways. However, the smoker has to inhale more deeply to receive the same amount of nicotine, increasing particle deposition in small airways where adenocarcinoma tends to arise.[176] The incidence of lung adenocarcinoma continue to rise.[177]
History
Lung cancer was uncommon before the advent of cigarette smoking; it was not even recognized as a distinct disease until 1761.[178] Different aspects of lung cancer were described further in 1810.[179] Malignant lung tumors made up only 1% of all cancers seen at autopsy in 1878, but had risen to 10–15% by the early 1900s.[180] Case reports in the medical literature numbered only 374 worldwide in 1912,[181] but a review of autopsies showed the incidence of lung cancer had increased from 0.3% in 1852 to 5.66% in 1952.[182] In Germany in 1929, physician Fritz Lickint recognized the link between smoking and lung cancer,[180] which led to an aggressive antismoking campaign.[183] The British Doctors' Study, published in the 1950s, was the first solid epidemiological evidence of the link between lung cancer and smoking.[184] As a result, in 1964 the Surgeon General of the United States recommended smokers should stop smoking.[185]
The connection with radon gas was first recognized among miners in the Ore Mountains near Schneeberg, Saxony. Silver has been mined there since 1470, and these mines are rich in uranium, with its accompanying radium and radon gas.[186] Miners developed a disproportionate amount of lung disease, eventually recognized as lung cancer in the 1870s.[187] Despite this discovery, mining continued into the 1950s, due to the USSR's demand for uranium.[186] Radon was confirmed as a cause of lung cancer in the 1960s.[188]
The first successful pneumonectomy for lung cancer was performed in 1933.[189] Palliative radiotherapy has been used since the 1940s.[190] Radical radiotherapy, initially used in the 1950s, was an attempt to use larger radiation doses in patients with relatively early-stage lung cancer, but who were otherwise unfit for surgery.[191] In 1997, CHART was seen as an improvement over conventional radical radiotherapy.[192] With SCLC, initial attempts in the 1960s at surgical resection[193] and radical radiotherapy[194] were unsuccessful. In the 1970s, successful chemotherapy regimens were developed.[195]
Research directions
Current research directions for lung cancer treatment include immunotherapy,[196][197] which encourages the body's immune system to attack the tumor cells, epigenetics, and new combinations of chemotherapy and radiotherapy, both on their own and together. Many of these new treatments work through immune checkpoint blockade, disrupting cancer's ability to evade the immune system.[196][197]
Ipilimumab blocks signaling through a receptor on T cells known as CTLA-4 which dampens down the immune system. It has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of melanoma and is undergoing clinical trials for both NSCLC and SCLC.[196]
Other immunotherapy treatments interfere with the binding of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) protein with its ligand PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), and have been approved as first- and subsequent-line treatments for various subsets of lung cancers.[197] Signaling through PD-1 inactivates T cells. Some cancer cells appear to exploit this by expressing PD-L1 in order to switch off T cells that might recognise them as a threat. Monoclonal antibodies targeting both PD-1 and PD-L1, such as pembrolizumab, nivolumab,[63] atezolizumab, and durvalumab[197] are currently in clinical trials for treatment for lung cancer.[196][197]
Epigenetics is the study of small, usually heritable, molecular modifications—or "tags"—that bind to DNA and modify gene expression levels. Targeting these tags with drugs can kill cancer cells. Early-stage research in NSCLC using drugs aimed at epigenetic modifications shows that blocking more than one of these tags can kill cancer cells with fewer side effects.[198] Studies also show that giving patients these drugs before standard treatment can improve its effectiveness. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate how well these drugs kill lung cancer cells in humans.[198] Several drugs that target epigenetic mechanisms are in development. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in development include valproic acid, vorinostat, belinostat, panobinostat, entinostat, and romidepsin. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in development include decitabine, azacytidine, and hydralazine.[59]
The TRACERx project is looking at how NSCLC develops and evolves, and how these tumors become resistant to treatment.[199] The project will look at tumor samples from 850 NSCLC patients at various stages including diagnosis, after first treatment, post-treatment, and relapse.[200] By studying samples at different points of tumor development, the researchers hope to identify the changes that drive tumor growth and resistance to treatment. The results of this project will help scientists and doctors gain a better understanding of NSCLC and potentially lead to the development of new treatments for the disease.[199]
For lung cancer cases that develop resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitors, new drugs are in development. EGFR inhibitors include afatinib and dacomitinib.[142] An alternative signaling pathway, c-Met, can be inhibited by tivantinib and onartuzumab. New ALK inhibitors include crizotinib and ceritinib.[201] If the MAPK/ERK pathway is involved, the BRAF kinase inhibitor dabrafenib and the MAPK/MEK inhibitor trametinib may be beneficial.[202]
Lung cancer stem cells are often resistant to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This may lead to relapse after treatment. New approaches target protein or glycoprotein markers that are specific to the stem cells. Such markers include CD133, CD90, ALDH1A1, CD44 and ABCG2. Signaling pathways such as Hedgehog, Wnt and Notch are often implicated in the self-renewal of stem cell lines. Thus treatments targeting these pathways may help to prevent relapse.[203]









