Heckler & Koch G36

Heckler & Koch G36

| Heckler & Koch G36 | |
|---|---|
| Type | Assault rifle Carbine Light machine gun Squad automatic weapon |
| Place of origin | Germany |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1997–present |
| Used by | 40+ countries (see Users) |
| Wars |
|
| Production history | |
| Designer | Heckler & Koch |
| Designed | 1990–1995 |
| Manufacturer | Heckler & Koch Santa Bárbara Sistemas Military Industries Corporation |
| Produced | G36: 1996–present G36K: 1997–present G36C: 2001–present |
| No. built | 176,000[3] |
| Variants | See Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | G36: 3.63 kg (8.00 lb) G36V: 3.33 kg (7.3 lb) G36K: 3.30 kg (7.3 lb) G36KV: 3.0 kg (6.6 lb) G36C: 2.82 kg (6.2 lb) MG36: 3.83 kg (8.4 lb) MG36E: 3.50 kg (7.7 lb) |
| Length | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 999 mm (39.3 in) stock extended / 758 mm (29.8 in) stock folded G36K, G36KV: 860 mm (33.9 in) stock extended / 615 mm (24.2 in) stock folded G36C: 720 mm (28.3 in) stock extended / 500 mm (19.7 in) stock folded |
| Barrel length | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 480 mm (18.9 in) G36K, G36KV: 318 mm (12.5 in) G36C: 228 mm (9.0 in) |
| Width | 64 mm (2.5 in) |
| Height | G36, G36K, MG36: 320 mm (12.6 in) G36V, G36KV, MG36E: 285 mm (11.2 in) G36C: 278 mm (10.9 in) |
| Cartridge | 5.56×45mm NATO |
| Action | Short-stroke piston, rotating bolt |
| Rate of fire | 750 rounds/min cyclic |
| Muzzle velocity | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 920 m/s (3,018 ft/s) G36K, G36KV: 850 m/s (2,788.7 ft/s) G36C, G36CV: 722 m/s (2,368.8 ft/s) |
| Effective firing range | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 800 metres (870 yd) G36K, G36KV: 500 metres (550 yd) G36C, G36CV: 200 metres (220 yd) |
| Maximum firing range | 2,860 metres (3,130 yd) |
| Feed system | 30-round detachable box magazine or 100-round C-Mag drum magazine |
| Sights | Reflex sight with 1× magnification, telescopic sight with 3× magnification (export version has a 1.5× magnified sight) and back-up fixed notch sight |
The G36 is a 5.56×45mm assault rifle, designed in the early 1990s by Heckler & Koch in Germany as a replacement for the heavier 7.62mm G3 battle rifle.[4] It was accepted into service with the Bundeswehr in 1997, replacing the G3.[5] The G36 is gas-operated and feeds from a 30-round detachable box magazine or 100-round C-Mag drum magazine.[4]
| Heckler & Koch G36 | |
|---|---|
| Type | Assault rifle Carbine Light machine gun Squad automatic weapon |
| Place of origin | Germany |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1997–present |
| Used by | 40+ countries (see Users) |
| Wars |
|
| Production history | |
| Designer | Heckler & Koch |
| Designed | 1990–1995 |
| Manufacturer | Heckler & Koch Santa Bárbara Sistemas Military Industries Corporation |
| Produced | G36: 1996–present G36K: 1997–present G36C: 2001–present |
| No. built | 176,000[3] |
| Variants | See Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | G36: 3.63 kg (8.00 lb) G36V: 3.33 kg (7.3 lb) G36K: 3.30 kg (7.3 lb) G36KV: 3.0 kg (6.6 lb) G36C: 2.82 kg (6.2 lb) MG36: 3.83 kg (8.4 lb) MG36E: 3.50 kg (7.7 lb) |
| Length | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 999 mm (39.3 in) stock extended / 758 mm (29.8 in) stock folded G36K, G36KV: 860 mm (33.9 in) stock extended / 615 mm (24.2 in) stock folded G36C: 720 mm (28.3 in) stock extended / 500 mm (19.7 in) stock folded |
| Barrel length | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 480 mm (18.9 in) G36K, G36KV: 318 mm (12.5 in) G36C: 228 mm (9.0 in) |
| Width | 64 mm (2.5 in) |
| Height | G36, G36K, MG36: 320 mm (12.6 in) G36V, G36KV, MG36E: 285 mm (11.2 in) G36C: 278 mm (10.9 in) |
| Cartridge | 5.56×45mm NATO |
| Action | Short-stroke piston, rotating bolt |
| Rate of fire | 750 rounds/min cyclic |
| Muzzle velocity | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 920 m/s (3,018 ft/s) G36K, G36KV: 850 m/s (2,788.7 ft/s) G36C, G36CV: 722 m/s (2,368.8 ft/s) |
| Effective firing range | G36, G36V, MG36, MG36E: 800 metres (870 yd) G36K, G36KV: 500 metres (550 yd) G36C, G36CV: 200 metres (220 yd) |
| Maximum firing range | 2,860 metres (3,130 yd) |
| Feed system | 30-round detachable box magazine or 100-round C-Mag drum magazine |
| Sights | Reflex sight with 1× magnification, telescopic sight with 3× magnification (export version has a 1.5× magnified sight) and back-up fixed notch sight |
History
Development
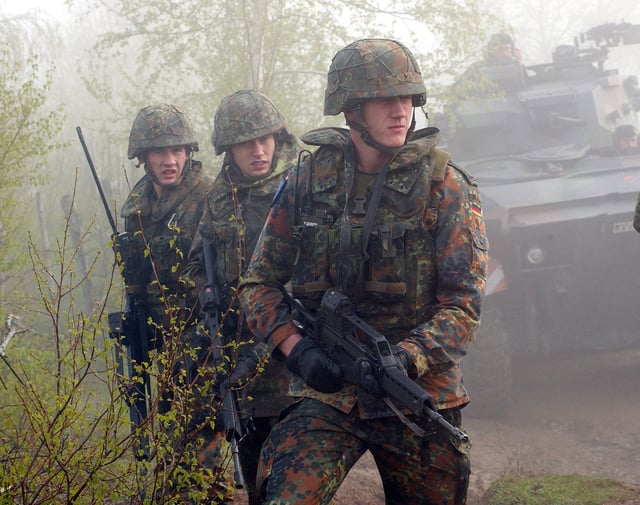

German Bundeswehr land force soldiers deployed with G36s
Work on a successor for the venerable G3 rifle had been ongoing in Germany since the second half of the 1970s. These efforts resulted in the innovative 4.73mm G11 assault rifle (developed jointly by a group of companies led by H&K), that used caseless ammunition (designed by the Dynamit Nobel company). It had been predicted that this weapon would eventually replace the G3, therefore further development of H&K's series of firearms chambered for the 5.56×45mm NATO cartridge had been halted. Heckler & Koch, having no incentive to pursue a new 5.56 mm weapon system, was content with the export-oriented HK33 and G41 rifles. However, the G11 program came to an abrupt end when the Bundeswehr cancelled its procurement due to defence budget cuts after the unification of East and West Germany and H&K was acquired in 1991 by British Aerospace's Royal Ordnance division (known today as BAE Systems).
Increasing interest in Germany for a modern service rifle chambered for the NATO-standard 5.56 mm cartridge led H&K to offer the German armed forces the G41 rifle, which, too, was rejected. Design work was then initiated from the ground up on a modern 5.56 mm assault rifle designated "Project 50" or HK50.[5] The prototype was then trialed, where it was rated higher than the rival Austrian Steyr AUG system.[5] The final version of the G36 was completed in 1995. Production of the G36 began in 1996.
On 22 April 2015, the German Minister of Defence announced that the G36 would be phased out of the German army due to concerns about overheating.
Production
The HK50 rifle was selected for service and an initial order was placed for 33,000 rifles under the Bundeswehr designation Gewehr G36. The order also involved an option for a further 17,000 rifles. Deliveries were first made to the *Bundeswehr'*s NATO Quick Reaction Force during the fourth quarter of 1997. The G36's production line began in early 1996.
In July 1998, it was announced that the G36 had been selected as the standard rifle for the Spanish Armed Forces, replacing the 5.56 mm CETME Model L and LC rifles.[6] Deliveries first took place at the end of 1999. These rifles are manufactured in Spain under license by General Dynamics Santa Bárbara Sistemas at the FACOR (Fábrica de Armas de la Coruña) facility, in Coruña, Galicia.
In addition, the rifle has been licensed for local production in Saudi Arabia.[7] The manufacturer in the country is the Military Industries Corporation.[8] Technology transfer was granted by Germany to Saudi Arabia on 30 June 2008[9][10] The first Saudi-made G36 was produced at MIC's factory on 30 June 2009.[10] However, some components of their own G36s are supplied by Heckler & Koch.[9]
Design details
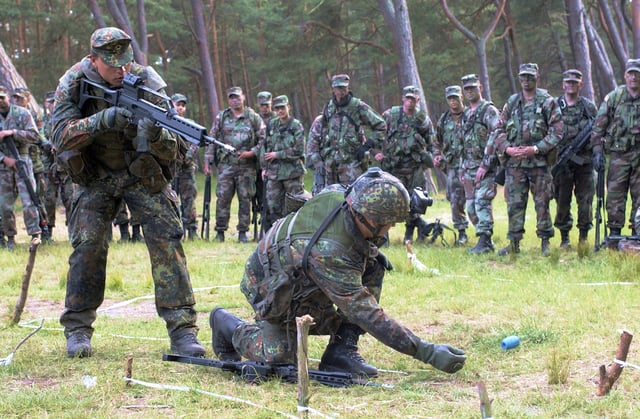

A German infantryman stands at the ready with his G36 during a practice exercise with US troops
The G36 is a selective-fire 5.56 mm assault rifle, firing from a closed rotary bolt. The G36 has a conventional layout and a modular component design. Common to all variants of the G36 family are: the receiver and buttstock assembly, bolt carrier group with bolt and the return mechanism and guide rod. The receiver contains the barrel, carry handle with integrated sights, trigger group with pistol grip, handguard and magazine socket.
The G36 employs a free-floating barrel (the barrel does not contact the handguard). The barrel is fastened to the receiver with a special nut, which can be removed with a wrench. The barrel is produced using a cold hammer forging process and features a chrome-lined bore with 6 right-hand grooves and a 1 in 178 mm (1:7 in) rifling twist rate. The barrel assembly consists of the gas block, a collar with a bayonet lug that is also used to launch rifle grenades and a slotted flash suppressor.
The weapon can be stripped and re-assembled without tools through a system of cross-pins similar to that used on earlier HK designs. For cleaning purposes, the G36 dismantles into the following groups: receiver housing, return mechanism, bolt carrier group and trigger group.
Features
Fire selector
The fire and safety selector is ambidextrous and has controls on both sides of the receiver which took upon the design of the original G3 selector. Selector settings are described with letters: "S"—safe ("Sicher"), "E"—semi-automatic fire ("Einzelfeuer") and "F"—continuous fire ("Feuerstoß").[5] HK also offers several other trigger options, including the so-called Navy trigger group, with settings analogous to the standard trigger, but the selector positions have been illustrated with pictograms. A semi-automatic only trigger unit (lacks the "F" setting) is also available.
Magazine
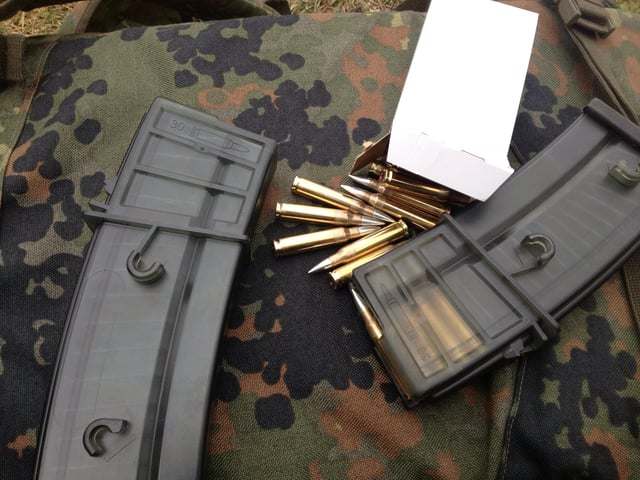

30-round G36 magazines, which insert and release like AK magazines and are not interchangeable with NATO STANAG magazines. Side inter-connect studs are visible.
In the box magazine is room for 30 cartridges staggered (or double-stacked) on top of one another. The magazines are molded with shock resistant plastic, and are translucent allowing the user to see the ammunition. On the sides are studs which allow the magazines to be attached next to each other, this way the operator can reload more easily. An empty G36 magazine weighs 127 grams (4.5 oz) and filled with 30 rounds 483 grams (17.0 oz). STANAG magazines cannot be normally used, but the G36 can use an adapter that will accept the STANAG. Certain types of Beta C-Mags can also be used and are employed with the MG36 support variant.
Stock
The stock too is multifunctional; it has the ability to fold to one side, shortening the overall length of the weapon for use in tight areas or vehicles. The rifle can also still fire with the stock collapsed. Also, it incorporates holes where assembly pins can be placed during weapon cleaning and maintenance.[5]
Material
The G36 employs a large number of lightweight, corrosion-resistant synthetic materials in its design; the receiver housing, stock, trigger group (including the fire control selector and firing mechanism parts), magazine well, handguard and carry handle are all made of a carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide. The receiver has an integrated steel barrel trunnion (with locking recesses) and a nylon 66 steel reinforced receiver.[11]
Sights

Optical sight reticle pattern

Dual combat sighting system ZF 3×4° as used on German G36A1 assault rifles
The standard German Army versions of the G36 are equipped with a ZF 3×4° dual optical sight that combines a 3× magnified telescopic sight (with the main reticle designed for firing at 200 m and bullet drop compensation markings for: 200, 400, 600 and 800 m crosshairs and a range-finding scale) and an unmagnified reflex sight (calibrated for firing at 100 m) mounted on top of the telescopic sight.[5] The reflex sight is illuminated by ambient light during the day and uses battery powered illumination for use at night. Electric illumination is activated automatically by a built in photo sensor and can be manually activated to boost the brightness of the reticle in daytime low contrast situations.[12]
The export versions have a single telescopic sight with a 1.5× magnification and an aiming reticle fixed at 300 m. All rifles are adapted to use the Hensoldt NSA 80 third-generation night sight, which clamps into the G36 carry handle adapter in front of the optical sight housing and mates with the rifle's standard optical sight.[13] The sighting bridge also functions as a carrying handle and features auxiliary open sights molded on top of the handle that consist of a forward blade and rear notch, but these can only be used with the reflex sight removed, as in the G36V. The optical sight system is produced by Hensoldt AG (a subsidiary of Carl Zeiss AG).
Operating mechanism

H&K G36 Variants from top to bottom: G36C, G36K, G36E, G36, MG-36 and SL8.
The G36 uses a short-stroke piston system[5] from which HK later developed the HK-416's impingement system. Unlike direct impingement, this system takes gas trailing the bullet to operate a piston instead of pushing directly on the bolt. The G36's bolt is operated by a cam that guides the bolt carrier by its respective cutout. Then when fully pushed forward 7 radial locking lugs fully enclose the chamber.
HK included several design features that are essential in modern military firearms. For example, the bolt locks back after the last round is spent (this can be deactivated), and at the front end of the trigger guard there is a bolt catch button. The cocking handle can be switched from either end, folds in, and unfolds from a spring[14][15] so the shooter need not unfold it by hand before firing. Another feature of it is that it doubles as the forward assist, which is used in the instance that the spent cartridge is ejected but the next round does not properly feed. In addition, the ejection port has a brass deflector to mitigate the amount of casings that may strike the face of left-handed operators. Instead of a dust cover which has the need to be flipped back up when the gun isn't in use, the bolt acts as the seal from dirt.
Accessories
The rifle can be fitted with a 40 mm AG36 (AG—Anbau-Granatwerfer) under-barrel grenade launcher, which is a breech-loaded break-action weapon with a side-tilting barrel.
Standard equipment supplied with the G36 includes: spare magazines, a cleaning and maintenance kit, sling, speed-loading device and sometimes modified AKM type II blade bayonets (many of which are left over in Germany from stocks of the former National People's Army).
Overheating
In April 2012, reports surfaced that G36 rifles used in Afghanistan would overheat during prolonged firefights after several hundred rounds were fired. Overheating affected the accuracy of the G36, making it difficult to hit targets past 100 meters, ineffective past 200 meters, and incapable of effective fire past 300 meters. The G36 has been called unsuitable for long battles. H&K said the rifle was not designed for sustained, continuous fire. German soldiers gave no negative feedback. Operational commanders advised allowing the weapon to cool between periods of rapid shooting.[16] [17] [18]
In February 2014, the German Federal Ministry of Defence announced that the overheating deficiencies of the G36 were not a result of weapon design, but of the ammunition. A report by the Bundeswehr on 21 February 2014, revealed that the issues were not the fault of the rifle, but that one manufacturer of ammunition was making bullets with copper plated jackets that were too thin.[19] [20] The manufacturer of the ammunition confirmed this,[21] although experts disagreed, and also said the accuracy problems were already known to the defence ministry by 2010.[22]
On 22 June 2014, it was reported that Germany's defense ministry had temporarily halted new orders worth €34 million ($45 million) over accuracy concerns for the rifle. The Bundeswehr consulted the Fraunhofer Institute for High-Speed Dynamics (Ernst Mach Institut) and the Federal Criminal Police Office.[23] On 30 March 2015, Minister of Defence Ursula von der Leyen told the Associated Press that the weight-saving design is the root of the issues.[24] This is based on a letter from Inspector General Volker Wieker advising the Stewards of Defence and Budget Committee of the Bundestag and the troops in advance of publication of the report.[25] [26] The report was released by the Fraunhofer Ernst Mach Institut (EMI) and Wehrtechnische Dienststelle 91 (WTD91) on 19 April 2015. According to their 372-page report, the observed hit rate of the predominantly plastic weapon with the unsupported free-floating barrel drops down to a mere 7% at 100 meters when the temperature increases by 30 °C (86 °F) or more, whereas the Bundeswehr required a hit rate of 90% at that distance.[27] [28]
On 22 April 2015, the German Minister of Defence announced that the G36 would be phased out of the German army due to these concerns. Defense Minister von der Leyen considers the weapon to be useless.[29] She stated that the German military will stop using a plastic assault rifle that cannot shoot straight when temperatures increase by 30 °C (86 °F) or the rifle heats up during a firefight.[30]
In 2016, the German Defence Ministry lost its lawsuit filed against Heckler & Koch on the ministry's claim for compensation or warranty work on the subpar G36 rifles, because the Bundeswehr did not make its specifications for the weapon clear enough in the beginning of the procurement process.[31] The District Court of Koblenz rejected claims from the Bundeswehr procurement office, and ruled that weapon manufacturer Heckler & Koch did not have to pay damages on the 167,000 rifles still in use out of more than 176,000 G36 rifles Germany had originally purchased.[32]
Variants
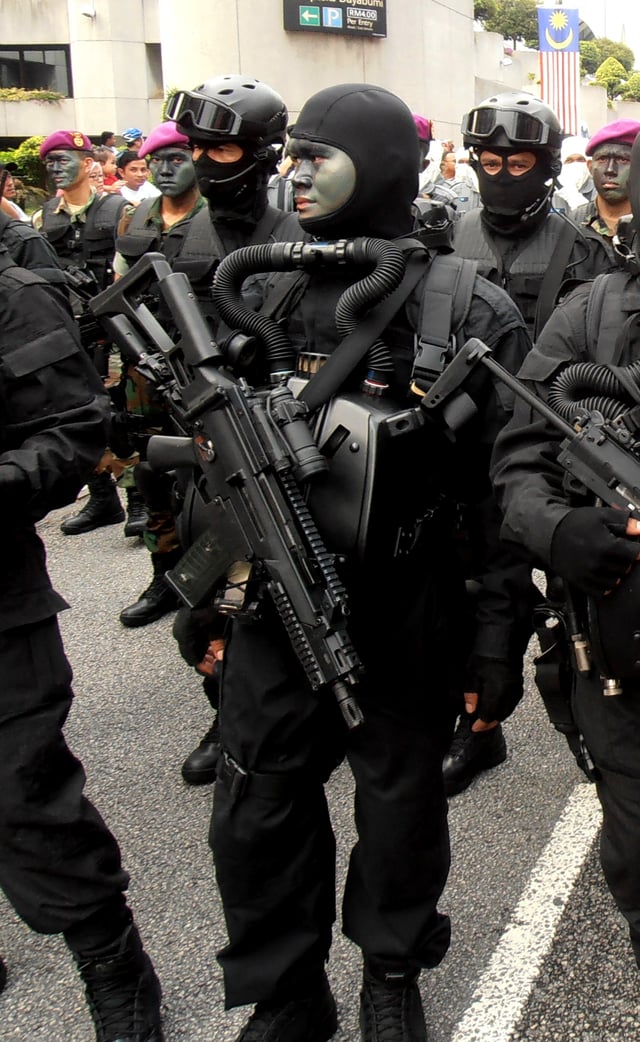

A Malaysian Navy diver from PASKAL armed with a G36C in 57th Malaysian National Day. It is configured with birdcage flash suppressor and a buttstock short with cheek rest.
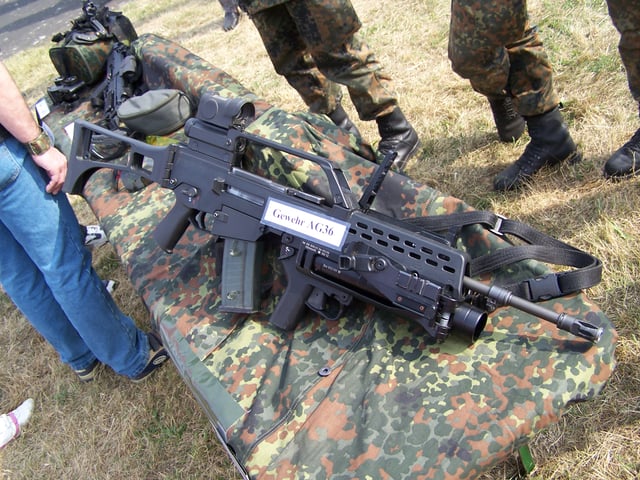

G36A2 with a Zeiss RSA reflex sight and an AG36 grenade launcher on display as part of Germany's IdZ modernization program
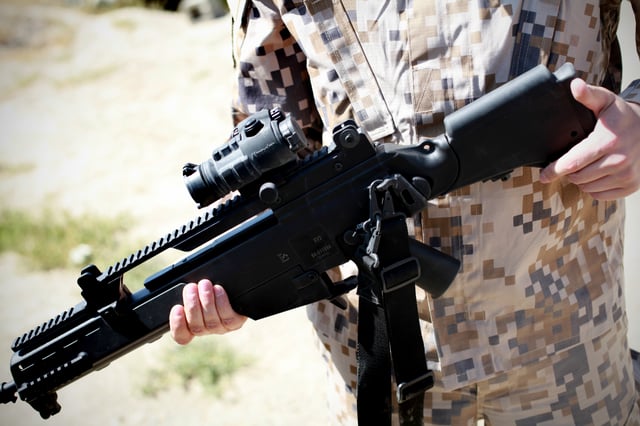

A G36KV as delivered to the Latvian Army. It is configured with a telescopic stock and a Picatinny sight rail
G36V (V—Variante "variant"): Previously known as the G36E (E—Export), it is the export version of the standard G36. The G36V has all of the characteristics of the standard rifle with the exception of the sight setup and bayonet mount. It is fitted with a x1.5 or x3 sight and lacks the integrated reflector sight; the bayonet mount is a standard NATO type. This version was first produced for Spain and Latvia.
MG36 (MG—Maschinengewehr "machine gun"): Squad automatic weapon version of the G36 equipped with a heavier barrel for increased heat and cook-off resistance.[5] The MG36 and MG36E are no longer offered by H&K.
G36K (K—kurz "short"): carbine variant with a shorter barrel (fitted with an open-type flash suppressor) and a shorter forend, which includes a bottom rail that can be used to attach tactical accessories, such as a UTL flashlight from the USP pistol. The carbine's barrel lacks the ability to launch rifle grenades and it will not support a bayonet. The weapon retained the ability to be used with the AG36 grenade launcher. G36Ks in service with German special forces are issued with a 100-round C-Mag drum. There are two variants of the G36K. The first and most commonly known has x3 scope/carry handle attached to the top, while the second is equipped with iron sights and a rail (no scope included).
G36KV (formerly G36KE): export version of carbine variant G36K, with sights like G36V.
G36C (C="Compact", commonly mistaken for "Commando", a term trademarked by Colt Firearms for the CAR-15): This subcarbine model is a further development of the G36K. It has a shorter barrel than the G36K, and a four-prong open-type flash hider or a birdcage type flash hider. The extremely short barrel forced designers to move the gas block closer to the muzzle end and reduce the length of the gas piston operating rod. The handguard and stock were also shortened and the fixed carry handle (with optics) was replaced with a carrying handle with an integrated MIL-STD-1913 Picatinny rail. The dual optical sight found on the standard G36 and G36K models was replaced with a set of rail-mounted detachable iron sights that consist of a semi-shrouded front post and a flip-up rear sight with two apertures of different diameter. The short handguard has four accessory attachment points, one of which could be used for a vertical grip. The G36C was developed and produced in January 2001.
G36A2: This is an ordnance designation allocated to an upgraded variant of the G36 used by the German Army. The G36A2 is equipped with a quick-detachable Zeiss RSA reflex red dot sight[33] mounted on a Picatinny rail that replaces the original red dot sight of the dual combat sighting system. The G36A2 upgrade kit also consists of the shorter G36C stock (Designed for better handling with use of body armor and load bearing equipment), new handguard made of aluminium (provides better heat resistance during long periods of firing) with an optional 4 Picatinny rails and a vertical foregrip with an integrated switch for operating an Oerlikon Contraves LLM01 laser light module.[34]
Sporting models
Based on the G36, Heckler & Koch also created the semi-automatic SL8 rifle and the straight-pull, bolt-action R8, which are offered to the civilian sport shooting markets. The SL8 is substantially different from the G36, it has a modified receiver and a thumbhole stock with a cheek rest, which is integral with the trigger group. The SL8 has a heavy profile, extended, 510 mm (20.1 in) barrel that does not have a flash hider or bayonet lug. The rifle uses a 10-round single-stack magazine and an extended top rail used to mount a wide variety of Picatinny-standard optics. Mounted to the rail are a set of iron sights with a hooded foresight and adjustable flip rear aperture. The SL8 can also mount the G36 carry handle and integrated sight assembly, after removing the mechanical iron sights. The SL8 has an unloaded weight of 4.3 kg, overall length of 980–1030 mm and a trigger rated at 20 N (4.5 lbf).
In November 2013, Heckler & Koch applied for permission from the German Government to sell a new civilian-legal version of the G36. Called the HK243 in Europe and the HK293 in America, it is more similar to the G36 assault rifle than previous civilian models. The main difference is the bolt is redesigned to not allow a conversion to fully automatic fire. It has quad picatinny rails and accepts STANAG magazines. Four different barrel lengths from 230 mm (9.1 in) to 480 mm (19 in) and four stock models (short fixed, long fixed and two adjustable) will be offered.[35]
Users
| Country | Organization name | Model | Quantity | Date | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Special Operations Battalion (Albania) | G36C | 350 | 2007 | ||
| Airport Security Police (Argentina) | G36K | ||||
| Australian Federal Police Specialist Response Group | _ | _ | [36][37] | ||
| Antwerp local police special squad BBT (Bijzondere Bijstandsteam) | _ | _ | _ | [38] | |
| Brazilian Federal Police | G36K, G36C | _ | _ | [39] | |
| Victoria Police Department | G36 | ~100 | 2004 | [40] | |
| Croatian police special units | _ | 300 | 2004 | [41][42] | |
| Croatian Armed Forces contingents in international operations | _ | 550 | 2007 | ||
Police of the Czech republic:
| G36C, G36K | _ | _ | [43] | |
| Politiets Aktionsstyrke | G36C | _ | _ | [44][45] | |
| Policia Nacional de Timor-Leste | G36K | _ | _ | [46] | |
| Used by special forces and police, Some later to Libyan Jamahiriya, see below | _ | 608+ | 2003 | [47] | |
| Estonian Special Operations Force | G36K | _ | _ | [48][49] | |
| Finnish Border Guard | G36C | _ | _ | [50] | |
| Finnish Police | _ | _ | |||
| French Army | G36E | _ | _ | [51] | |
| Groupes d'Intervention de la Police Nationale | G36C | _ | _ | [52][53] | |
| Brigade Anti-criminalité (BAC) | G36C, G36K | 204 | 2016 | [54][55][56] | |
| Standard service rifle of the Bundeswehr | G36A1, G36A2 G36K, G36C | 176,544 delivered, 166,619 in use | _ | [57][58][59] | |
| Bundespolizei | _ | _ | _ | [60] | |
| Police special forces: Central Anti Crime Division, Special Crisis Unit, Special Operations Department, Coast Guard Anti piracy Unit | G36K/C/E/A | _ | _ | [61] | |
| Hellenic Army ETA | |||||
| Special Duties Unit of the Hong Kong Police Force | G36KV | _ | 2001 | [62] | |
| National Police of Iceland and its special forces unit Víkingasveitin | _ | _ | _ | [63] | |
| Peshmerga | _ | 8,000 supplied by Germany | 2014 | [64] | |
| Komando Pasukan Khusus (Kopassus) special forces group of the Indonesian Army | G36C | _ | _ | [65] | |
| Detasemen Jala Mangkara (Denjaka) tactical diver group of the Indonesian Navy | G36V, G36C | _ | _ | [66] | |
| NOCS team of the Italian Police | G36C | _ | _ | [67] | |
| Jordanian special forces 71st Special Battalion | G36C | _ | _ | [68][69] | |
| Kosovo Security Force | G36V | 3500 | 2010 | [70][71] | |
| Latvian Army, National Guard, State Border Guard | G36KV | _ | 2006 | [72][73][74] | |
| Lebanese Armed Forces, Internal Security Forces | G36C3 | 250 | 2008 | [75] | |
| Unclear (unit based in Tripoli; special forces/Khamis Brigade?). Weapons are from a batch legally sold to Egypt in 2003. | G36KV, G36E | "numerous" Probably <600 | 2003–2005? | [47][76][77] [78][79] | |
| Tripoli Brigade (looted from Bab al-Azizia arms store) | 2011 | [76][80] | |||
| Lithuanian Armed Forces | G36KA4, G36KV1 G36C, G36KA4M1 | _ | 2017 (G36KA4M1) | [81][82][83][84] | |
| Pasukan Khas Laut (PASKAL) Maritime Counter-Terrorism Forces of the Royal Malaysian Navy | G36C, G36E G36KE | _ | 2006 | [85][86][87][88] | |
| Pasukan Gerakan Khas (PGK) Counter-Revolutionary Warfare of the Royal Malaysia Police | G36C | _ | _ | [85] | |
| Standard service rifle of the Military of Mauritius | G36A2, G36K G36C | _ | _ | ||
| Various Mexican law enforcement agencies use the G36, namely the Mexican Federal Police and many state and city police forces | G36 Family | _ | _ | [89] | |
| Mongolian Armed Forces | _ | _ | _ | [90] | |
| Military of Montenegro | _ | _ | _ | [91] | |
| Norwegian Navy Kystjegerkommandoen | G36KV2 | _ | 2001–2007 | [72] | |
| Armed Forces of the PhilippinesPresidential Security Group | G36K, G36C | _ | _ | [92] | |
| BOA/SPAP special units of the Policja | G36V, G36K G36C | _ | _ | [93] | |
| Biuro Ochrony Rządu (BOR) Government Protection Bureau | G36C | _ | _ | [94] | |
| Jednostka Wojskowa Formoza naval unit of the Polish Special Forces | G36KV3, G36C | _ | 2006 | [95] | |
| Portuguese Army | G36KV, G36KV3 | _ | _ | [96] | |
| Portuguese Marines | _ | _ | _ | [72] | |
| Portuguese Air Force | |||||
| Guarda Nacional Republicana (GNR) | G36C | 200 | _ | [97] | |
| Grupo de Operações Especiais (GOE) of the Polícia de Segurança Pública | _ | _ | _ | [98] | |
| Korea Coast Guard SSAT (Special Sea Attack Team) | _ | _ | 2007 | [99] | |
| 1st Special Operations Regiment (Romania) of the Romanian Army | G36K, G36C | _ | _ | [100] | |
| Saudi Arabian Army, Police, Border Guards, Special Forces | G36C, G36E G36KE | _ | _ | [101] | |
| Special Brigade of the Serbian Army | G36C | _ | 2010 | [102] | |
| Sierra Leone Police force | G36K | 112+ | 2001 | [103] | |
| 5th Special Forces Regiment of the Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic | G36 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Spanish Armed ForcesGuardia Civil | G36E, G36KE G36CE | _ | _ | [72][104][105] | |
| Unidad de Operaciones Especiales special group of Spanish Navy and Spanish Marines | _ | _ | [106] | ||
| National Task Force | G36C | _ | _ | [107] | |
| Piketen | _ | _ | [107] | ||
| Särskilda operationsgruppen | G36K, G36C | _ | _ | [108] | |
| Will soon replace the Galil in use by the Trinidad and Tobago Regiment and become the primary service rifle. | G36 | ||||
| Naresuan 261 Counter-Terrorism Unit Special Operations Unit of the Royal Thai Police | G36C, G36K SL8 | _ | 2007 | [109][110] | |
| Royal Thai Army Infantry. | G36K, G36KE G36E, MG36 | _ | _ | [111][112][113] | |
| Underwater Demolition Assault Unit (UDAU) tactical diver group of the Royal Thai Navy | G36KV | _ | 2004 | [114][115] | |
| Royal Thai Marine Corps Amphibious Reconnaissance battalion Special operations forces (RECON) Royal Thai Navy | G36C | _ | 2004 | [116][117][118][119] | |
| Avon and Somerset Police | G36 | _ | _ | [120] | |
| City of London Police | _ | _ | |||
| Civil Nuclear Constabulary | _ | _ | [121] | ||
| Greater Manchester Police | _ | _ | [121] | ||
| Kent Police | _ | _ | |||
| Lancashire Constabulary | _ | _ | [121] | ||
| Norfolk Constabulary | _ | _ | |||
| Northumbria Police | _ | _ | |||
| Nottinghamshire Police | _ | _ | |||
| Police Scotland | _ | _ | [122] | ||
| Police Service of Northern Ireland | _ | _ | [121] | ||
| Specialist Firearms Command, Metropolitan Police Service | _ | _ | [123] | ||
| West Yorkshire Police | _ | Until 2017 | |||
| Special Air Service | _ | _ | _ | [124] | |
| United States Capitol Police | _ | _ | _ | _ | |
| Baltimore City Police Department | _ | _ | _ | [125] | |
| United Nations Department for Safety and Security | G36V, G36KV G36CV, MG36 | _ | _ | _ | |
| Department of Peacekeeping Operations | _ | _ | [126] | ||
| Uruguayan Army | G36, G36K, G36C | _ | _ | ||
| Uruguayan Navy | G36E, G36V, AG G36 40 mm | _ | _ |
|India[Macros]