Beretta

Beretta

Fabbrica d'Armi Pietro Beretta (Italian pronunciation: [ˈfabbrika ˈdarmi ˈpjɛːtro beˈretta]; "Pietro Beretta Gun Factory") is a privately held Italian firearms manufacturing company operating in several countries. Its firearms are used worldwide for a variety of civilian, law enforcement, and military purposes. Sporting arms account for three-quarters of sales; Beretta is also known for marketing shooting clothes and accessories. Founded in the 16th century, Beretta is the oldest active manufacturer of firearm components in the world.[1] In 1526 its inaugural product was arquebus barrels; by all accounts Beretta-made barrels equipped the Venetian fleet at the Battle of Lepanto in 1571.[2] Beretta has supplied weapons for every major European war since 1650.[3]
History
16th Century map by Giovanni Antonio Magini of the Province of Brescia. Val Trompia is in the center. Map is oriented with West at the top.
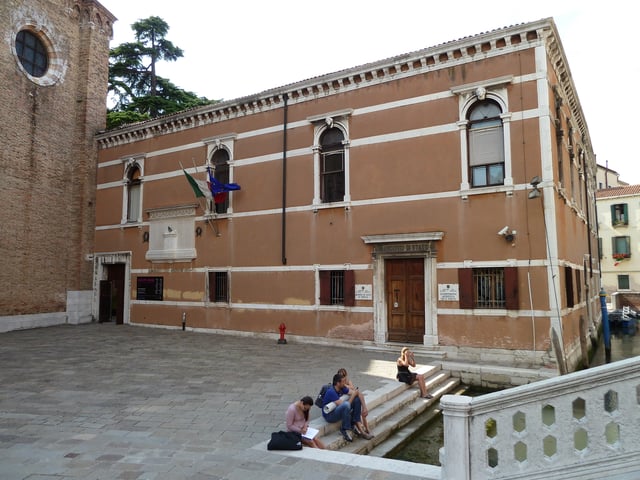

Venetian State Archive building
Val Trompia, a northern Italian river valley in the Province of Brescia, Lombardy, has been mined for iron ore since the time of the Roman Empire. In the Middle Ages, Val Trompia was known for its ironworks; after the Renaissance it came to be a center for the manufacture of weapons.[4] By the mid 16th century Val Trompia had forty ironworks, supplied by fifty mines and eight smelters. The birthplace of Beretta is in the village of Gardone located on the banks of the Mella river, in the middle of Val Trompia (i.e., between the upper valley and lower valley).[1]
The Beretta forge was in operation from about 1500,[5] although the first documented transaction is a contract dated October 3, 1526 for 185 arquebus barrels, for which the Republic of Venice was to pay 296 ducats to Maestro di Canne (master gun-barrel maker) Bartolomeo Beretta (in Italian).[4] The original account document for the order of those barrels is now stored in the Archivio di Stato di Venezia (in Italian) in Venice.[6] By the end of the 17th century, Beretta had become the second largest gun barrel maker in Gardone.[1]
Under the guild system, the knowledge of gun barrel fabrication that was bequeathed to Jacopo (1520/25 – …) from his father Bartolomeo (1490 – 1565/68)[7] was then passed on to his own son Giovannino (1550 – post 1577), and to his grandson Giovan Antonio (1577 – post 1649)[8] and so on until guilds were abolished by Napoleon after his conquest of Venetian Republic in 1797.[1]
In 1918, the Beretta Model 1918, one of the first submachine guns in the world, was fielded by the Italian army. Beretta manufactured rifles and pistols for the Italian military until the 1943 Armistice between Italy and the Allied forces during World War II. With the Wehrmacht's control of northern Italy, the Germans seized Beretta and continued producing arms until the 1945 German surrender in Italy.[4] In that time, the quality of the exterior finish of the weapons diminished and was much more inferior to both the pre-war and mid-war weapons, but their operation remained excellent.[11] The last shipment of Type I Rifles left Venice for Japan in a U-boat in 1942.
After World War II, Beretta was actively involved in repairing the American M1 Garands given to Italy by the U.S. Beretta modified the M1 into the Beretta BM-59 rifle, which is similar to the M14 battle rifle; armourers consider the BM-59 rifle to be superior to the M14 rifle in some ways, because it is more accurate under certain conditions.[12][13]
After the war, Beretta continued to develop firearms for the Italian Army and police, as well as the civilian market.[14]
In the 1980s, Beretta enjoyed a renewal of popularity in North America after its Beretta 92 pistol was selected as the service handgun for the United States Army under the designation of "M9 pistol".[2]
In the 1970s, Beretta also started a manufacturing plant in São Paulo, Brazil. A contract between Beretta and the Brazilian government was signed, under which Beretta produced Beretta 92s for the Brazilian Army until 1980. Later this plant was sold to Taurus, who continues to manufacture the Beretta 92 under the name of PT92 using the same tools and labour which Beretta used, without the need for a license from Beretta, since the design is based on the original Beretta 92, for which the patents are expired.[15]
Beretta acquired several domestic competitors (notably Benelli and Franchi) and some foreign companies (notably in Finland) in the late 1980s.[16]
Overview
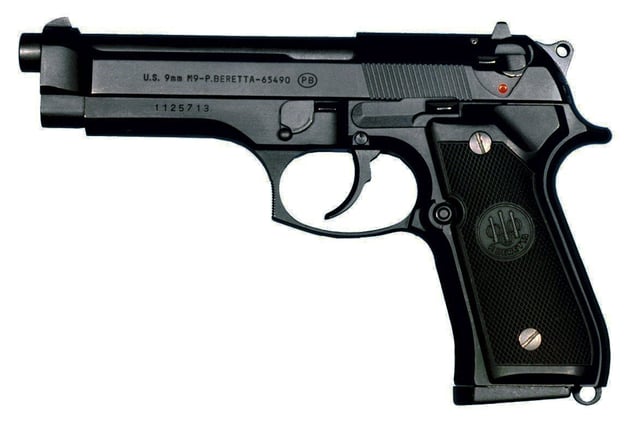

Beretta M9
Today, Fabbrica d'Armi Pietro Beretta (Beretta S.p.A) is run by Franco Gussalli Beretta, President and CEO.[20]
The traditional father-to-son Beretta dynasty was interrupted when Ugo Gussalli Beretta assumed the firm's control; uncles Carlo and Giuseppe Beretta were childless; Ugo married into the Beretta family and adopted the last name Beretta. His sons are now direct descendants through their mother's side of the family.
Beretta is known for its broad range of firearms: side-by-side shotguns, over-and-under shotguns, semi-automatic shotguns, hunting rifles, express rifles, assault rifles, submachine guns, lever- and bolt-action rifles, single- and double-action revolvers and semi-automatic pistols.[21] The parent company, Beretta Holding, also owns Beretta USA, Benelli, Franchi, SAKO, Stoeger, Tikka, Uberti, and the Burris Optics company.
The model Beretta 92FS was the primary side arm of the United States Army, Marine Corps, Navy and Air Force, designated the M9 pistol.[22] In 1985, Beretta was chosen after a controversial competition to produce the M9, winning a contract for 500,000 pistols.[23][24] A condition of the original agreement was domestic manufacturer of the M9.[25][26] In 2019, the 9mm version of the SIG Sauer P320 was selected to replace the M9 throughout the US Armed Forces.[27]
Product lines
Semi-automatic pistols
Beretta Model 1915
Beretta M1923
Beretta 418
Beretta M951
Beretta M 1934 / Beretta M 1935
Beretta M 1951
Beretta 70 series Beretta 70 Beretta 71 Jaguar Beretta 72 Jaguar Beretta 73, 74, 75 Beretta 76 Beretta 100, 101, 102
Beretta Cheetah Beretta 81 Beretta 84 Beretta 85 Beretta 86 Beretta 87 Beretta 89
Beretta 8000 Beretta 8000 Cougar Beretta 8045 Cougar Beretta Cougar Inox Beretta Mini Cougar
Beretta 90
Beretta 9000 Beretta 9000S
Beretta 92 Beretta 90two Beretta 92F Beretta 92F/FS Beretta 92FS Inox Beretta 92FS Compact Beretta 92FS Centurion Beretta 92FS Brigadier Beretta 92FS Brigadier Inox Beretta 92G Elite 1A Beretta 92G Elite II Beretta 92S Beretta 92SB Beretta 92SB-C Beretta 92A1 M9 pistol
Beretta 96 Beretta 96A1
Beretta Px4 Storm Beretta Px4 Storm Compact Beretta Px4 Storm Subcompact
Beretta U22 Neos
Beretta APX
Beretta 21 Bobcat Beretta 21A Bobcat
Beretta 3032 Tomcat
Beretta 950 Jetfire
Beretta Nano
Beretta Pico
Revolvers
Beretta Stampede
Beretta Laramie
Shotguns
Beretta 1200
Beretta 1200 FP
Beretta 1201
Beretta 1201FP
Beretta AL390
Beretta AL391 Urika and Teknys
Beretta Tx4 Beretta Tx4 Storm
Beretta 1301 Beretta 1301 Comp Beretta 1301 Tactical
Beretta A400 Beretta A400 Xcel Beretta A400 Xtreme Unico Beretta A400 Xplor Action
Beretta A 300 Outlander
Beretta A 350 Outlander
Beretta SO4, SO5 and SO6
Beretta Xtrema
Beretta Xtrema 2
Beretta Model A series
Beretta UGB25 Xcel
Beretta Folder
Beretta Urika
Beretta Urika 2
Beretta RS 202-M2
Beretta LTLX7000
Beretta 470 Silver Hawk
Beretta 682
Berreta 692
Beretta DT-10
Beretta DT-11
Beretta Silver Pigeon
Beretta bellmonte due
Rifles and carbines
Beretta BM-59
Beretta 501 (sporting rifle)
Beretta Rx4 Storm
Beretta AR70/90
Beretta AS70/90
Beretta AR-70/223
Beretta ARX 160
Submachine guns
Beretta Model 1918
Beretta Model 38 Beretta Model 38A Beretta Model 38/42 Beretta Model 38/44
Beretta Model 3 – a postwar modification of the 38/42
Beretta M12 series
Beretta Mx4 Storm
Beretta Cx4 Storm
Beretta PMX
Machine pistols
Beretta M951R
Beretta 93R
Launchers
Beretta GLX-160
See also
Beretta Holding
List of modern armament manufacturers
List of oldest companies
