BL 9.2 inch gun Mk IX–X

BL 9.2 inch gun Mk IX–X

| Ordnance BL 9.2-inch gun Mk IX, Mk X | |
|---|---|
| Type | Naval gun Coast defence gun |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1899–1950s |
| Used by | Royal Navy Royal Garrison Artillery, Royal Artillery from 1922Royal Australian Artillery Royal Canadian Artillery South African Artillery Portugal Turkey |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Elswick Ordnance Company Vickers Beardmores[2] |
| Variants | Mk IX, Mk X, Mk XIV |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Mk IX: 27 tons barrel & breech Mk X: 28 tons[3] |
| Barrel length | Mk IX: 35 ft 10 in (10.922 m) Mk X: 35 ft 9 in (10.897 m) bore (46.7 cal)[3] |
| Shell | 380 lb (170 kg)[3] |
| Calibre | 9.2-inch (233.7 mm) |
| Breech | Welin interrupted screw |
| Elevation | 0° to 15° (on Mark V Barbette mount) |
| Traverse | 360° (on Mark V Barbette mount) |
| Muzzle velocity | 2,643 ft/s (806 m/s)[4] |
| Maximum firing range | 29,200 yd (26,700 m)[5] |
The BL 9.2-inch Mk IX and Mk X guns[1] were British breech loading 9.2-inch guns of 46.7 calibre, in service from 1899 to the 1950s as naval and coast defence guns. They had possibly the longest, most varied and successful service history of any British heavy ordnance.
| Ordnance BL 9.2-inch gun Mk IX, Mk X | |
|---|---|
| Type | Naval gun Coast defence gun |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1899–1950s |
| Used by | Royal Navy Royal Garrison Artillery, Royal Artillery from 1922Royal Australian Artillery Royal Canadian Artillery South African Artillery Portugal Turkey |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Elswick Ordnance Company Vickers Beardmores[2] |
| Variants | Mk IX, Mk X, Mk XIV |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Mk IX: 27 tons barrel & breech Mk X: 28 tons[3] |
| Barrel length | Mk IX: 35 ft 10 in (10.922 m) Mk X: 35 ft 9 in (10.897 m) bore (46.7 cal)[3] |
| Shell | 380 lb (170 kg)[3] |
| Calibre | 9.2-inch (233.7 mm) |
| Breech | Welin interrupted screw |
| Elevation | 0° to 15° (on Mark V Barbette mount) |
| Traverse | 360° (on Mark V Barbette mount) |
| Muzzle velocity | 2,643 ft/s (806 m/s)[4] |
| Maximum firing range | 29,200 yd (26,700 m)[5] |
History
These guns succeeded the BL 9.2-inch Mk VIII naval gun and increased the bore length from 40 to 46.7 calibres, increasing the muzzle velocity from 2,347 feet per second (715 m/s) to 2,643 feet per second (806 m/s).
The Mk IX was designed as a coast defence gun, with a three-motion breech. Only fourteen were built and the Mk X, introduced in 1900, incorporated a single-motion breech and changed rifling, succeeded them. As coastal artillery, the Mk X remained in service in Britain until 1956, and in Portugal until 1998. 284 of the Mark X version were built by Vickers, of which 28 examples are known to survive today, all except one fitted on barbette mounts. One in Cape Town is on a disappearing mount.
The 9.2-inch Mk XI gun introduced in 1908 increased the bore length to 50 calibres in an attempt to increase the velocity still further, but proved unsuccessful in service and was phased out by 1920. The Mk X was hence the final Mark of 9.2-inch guns in British Commonwealth service.
The BL 9.2 also affected the development of radar. Immediately before the second world war, an army team developed a surface-scanning radar to detect enemy ships in the English Channel. By chance, in July 1939 one of these radars was being tested while the 9.2-inch battery at Brackenbury Battery outside Harwich was firing. The radar team noticed odd returns on their displays, and realised that these were due to the waterspouts caused by the shells exploding in the water creating a vertical surface off which the signals reflected. The use of radar to accurately spot the fall of shells was rapidly developed, and was widespread by the war's end.[6]
Design
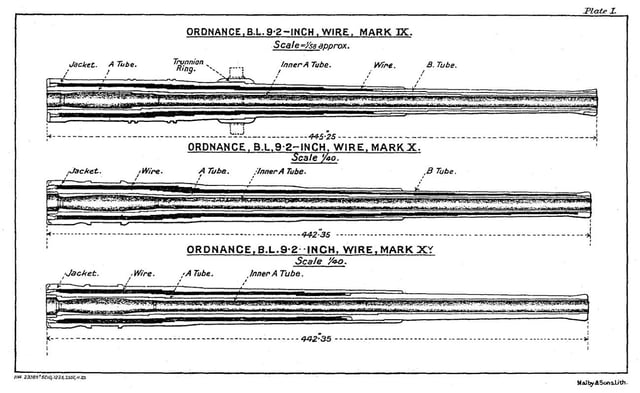
Mk IX & X barrel design
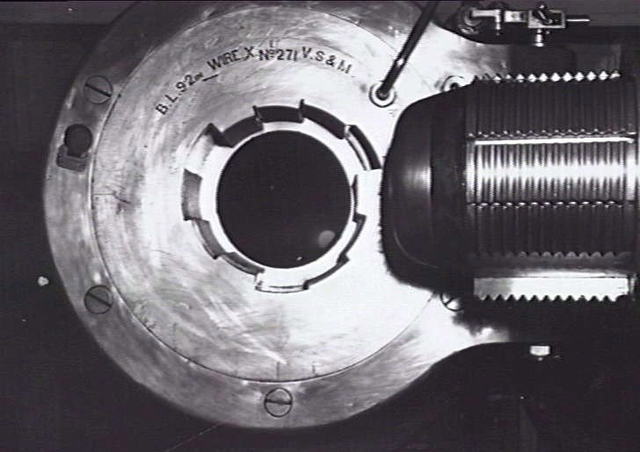
Breech view of a Mk X gun in 1946
These were medium-velocity wire-wound guns with Welin interrupted screw breeches.
Naval service
Royal Navy
Forward gun on HMS Cressy
Mark X guns were mounted on :
Cressy-class armoured cruisers commissioned from 1901
Drake-class armoured cruisers commissioned from 1902
Duke of Edinburgh-class armoured cruisers commissioned from 1906
Warrior-class armoured cruisers commissioned from 1907
King Edward VII-class battleships commissioned from 1905
M15-class monitors M15, M16, M17, M18 from 1915
Greek Navy
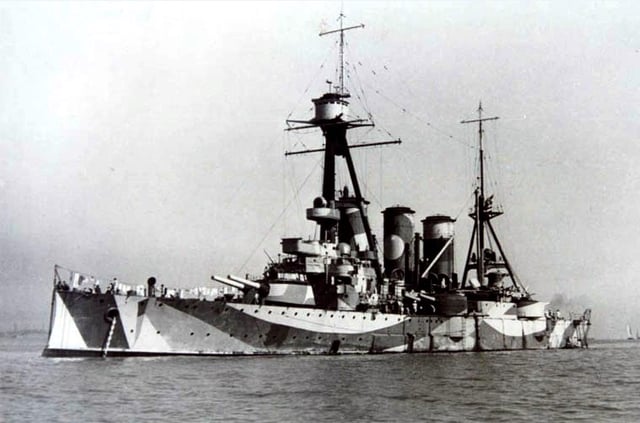

Georgios Averof in camouflage paint, RN Bombay Station, 1942
Four guns of 45 calibres (414 inches) bore produced by Elswick Ordnance Company[7] were mounted in two twin turrets on the Greek cruiser Georgios Averof in 1910, instead of the 10-inch guns mounted on her sisters of the Pisa-class in Italian service. These were similar to the four Vickers 45-calibre export model guns used by Britain as railway artillery on the Western Front in World War I under the designation BL 9.2-inch gun Mark XIV. They fired the same 380-pound shell using the same 120-pound cordite charge as the British service Mk X gun, and it may be assumed that its performance was very similar.
British coastal deployments
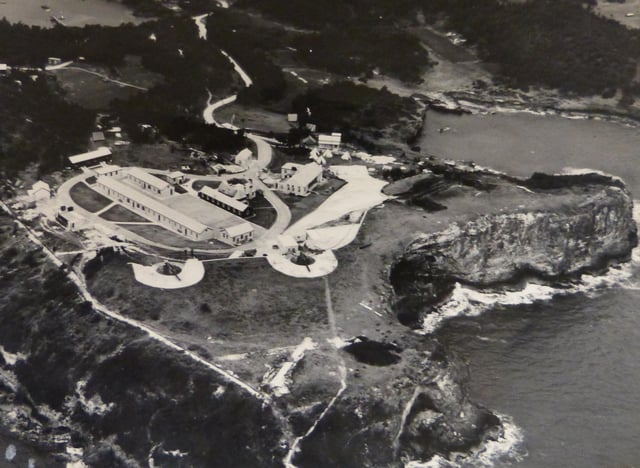

St. David's Battery, Bermuda in 1942, with the two 9.2-inch Mk. X guns in the foreground, and two and two BL 6 inch Mk VII guns at right
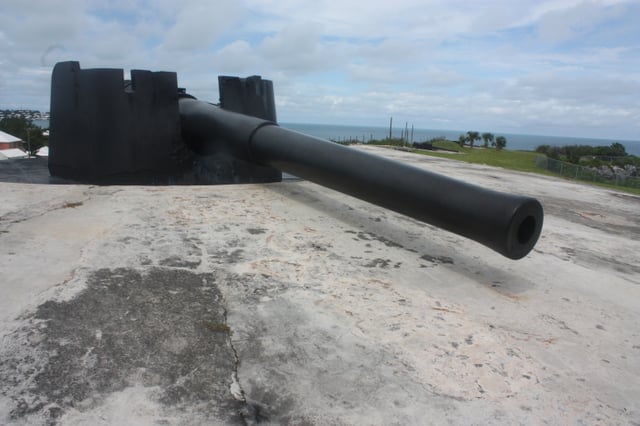

Mk X, on Mark V Barbette mount, one of two surviving at St. David's Battery, Bermuda (a third survived at Fort Victoria, on St. George's Island), which were used by the Bermuda Garrison in guarding the shipping channel through the reefs surrounding the archipelago.

A Mk X (Number 272, built by Vickers) at Fort Victoria on St. George's Island in Bermuda.
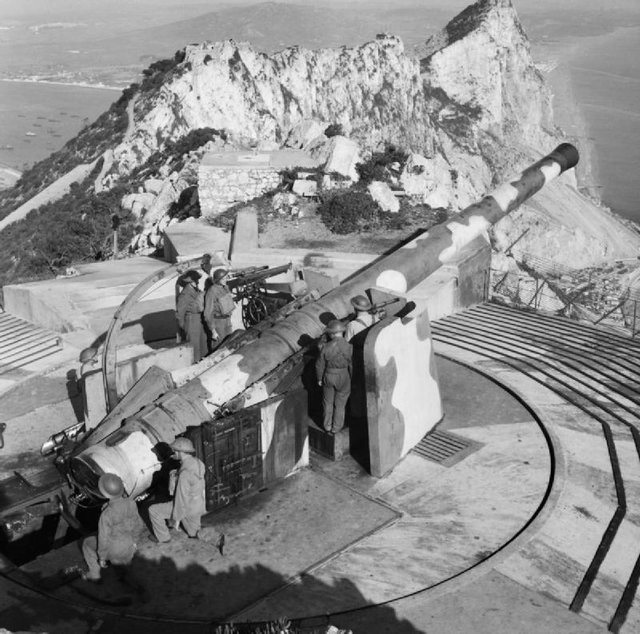
These were 'counter-bombardment' guns designed to defeat ships up to heavy cruisers armed with 8-inch guns. They were deployed in the fixed defences of major defended ports throughout the British Empire until the 1950s.
Their role was to defeat enemy ships attacking the ships in a port, including warships, alongside or at anchor in the port. However, where guns covered narrows, such as the Dover Straits, the Straits of Gibraltar, or the Narrows of Bermuda, they also had a wider role of engaging enemy ships passing through the straits. Normally deployed in batteries of two or three guns, a few major ports had several batteries positioned miles apart.
There were several marks of mountings and a battery had extensive underground facilities in addition to the guns visible in their individual gun-pits. Together with the 6-inch Mk VII, they provided the main heavy gun defence of the United Kingdom in World War I. 3 Mk IX and 53 Mk X guns were in place as of April 1918.[8]
Mounting
The Mounting Barbette Mark V (the original mounting with Mark IX and X guns) gave a maximum elevation of 15 degrees, and maximum range of 21,000 yards. This and some modified to Mark VI (30 degrees and 29,500 yards) were manually powered, the projectile and propelling charge were manually hoisted to loading level, the projectile manually loaded and rammed, and traverse and elevation were by handwheels. There was an elevated platform around the breech area for the gun detachment commander (No 1) and some detachment members, and a Gun shield to the front. The ordnance and mounting together weighed some 125 tons, they were well balanced and the handwheels needed very little effort to move the gun.[9]
However, the Mark VII mounting appeared in the 1930s and in 1939 a simplified version, Mark IX. Both were hydraulically powered and the platform was enclosed in a roofed gun house with three sides (and rear with Mark IX). The hydraulics meant that both projectile and propelling charge could be hoisted in a single load. With Mark VII and IX the maximum elevation was increased to 35 degrees to give a maximum range of 36,700 yards.[9]
Installation
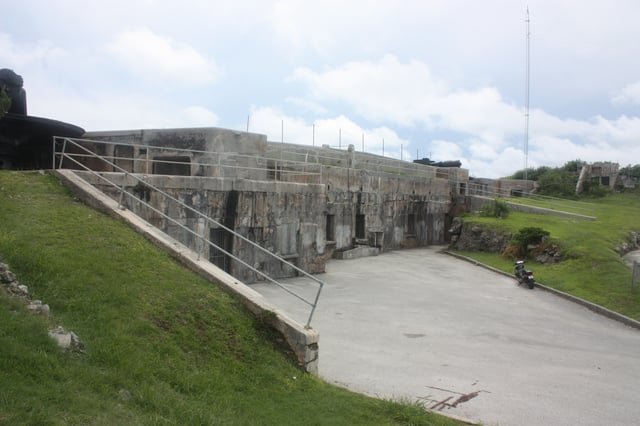

Rear view of the 9.2-inch magazine of St. David's Battery, Bermuda, with the two Mk. X guns visible on top, in 2011
Each gun mounting was installed on a central cast-steel pedestal in an open concrete gunpit 35 feet in diameter and 11 feet deep. The gun and mounting weighed 125 tons. A very narrow gauge rail track was embedded around the gunpit floor. A trolley was manhandled around the track between the two ammunition lifts (one for projectiles, one for propelling charges) and the rear of the gun (this position varied depending on where the gun was pointed).[9]
Below the gun pit were the separate ammunition bunkers for projectiles and shells with direct access to the ammunition lifts. These bunkers had an access road leading to them for ammunition re-supply. The guns presented only a very small target above ground level, guns and gunpits were camouflaged.
Organisation
Two or three guns comprised a named battery position with the guns manned by a Heavy Battery. For example, in 1940 Madalena and Bijemma batteries, both with 9.2 in Malta were manned by 6 Heavy Battery RA of 4 Heavy Regiment RA.[10]
Increasing ranges led to new centralised control arrangements. Fortress observation posts, equipped with rangefinders and directors were sited 4000 – 10,000 yards apart to give observation of all the sea area within range. They reported enemy ship bearings and distances to the ‘fortress plotting centre’ (FPC) where the attackers' positions and courses were plotted, converted to coordinates and then assigned as targets to batteries by the fire commander. The details were telephoned to batteries. The battery plotting room used a coordinate converter to turn the coordinates into bearings and elevations and transmitted them to the guns where pointers were matched by changing the guns’ traverse and elevations.[11]
The observers also reported fall of shot relative to the targets, the FPC used an encoder to convert these into a clock code, which the battery converted to its left/right, add/drop corrections. Various types of radars integrated into the fire command soon became widespread in WW2 and enabled effective night engagements.[11]
Deployments
The following table summarises the deployment of 9.2-inch guns.[12][13][14][15] It is possible that some 1914 guns were still the older marks. * indicates deployment was not completed until after 1940. A third Canadian battery was not completed until after World War II. The three guns in Bermuda remained in battery through the Second World War (and are still in situ), but were not actively utilised.
| Port | Country/territory | World War I | World War II |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dover | United Kingdom | 5 | 6 |
| Medway & Thames | United Kingdom | 4 | 2 |
| Harwich | United Kingdom | 0 | 2 |
| Tyne | United Kingdom | 2 | 1 |
| Tees & Hartlepool | United Kingdom | 0 | 1 |
| Humber | United Kingdom | 0 | 2 |
| Solent | United Kingdom | 14 | 6 |
| Portland | United Kingdom | 6 | 4 |
| Plymouth | United Kingdom | 8 | 6 |
| Milford Haven | United Kingdom | 4 | 2 |
| Forth | United Kingdom | 6 | 3 |
| Cromarty | United Kingdom | 3 | 0 |
| Lough Swilly | Ireland | 2 | 0 |
| Queenstown | Ireland | 4 | 0 |
| Berehaven | Ireland | 2 | 0 |
| Gibraltar | Gibraltar | 14 | 8 |
| Freetown | Sierra Leone | 2 | 2 |
| St. George's | Bermuda | 3 | 0 |
| Kingston | Jamaica | 1 | 0 |
| Valletta | Malta | 16 | 7 |
| Cape Town | South Africa | 2 | 7 |
| Simonstown | South Africa | 3 | 3 |
| Durban | South Africa | 0 | 3* |
| Port Louis | Mauritius | 2 | |
| Colombo | Sri Lanka | 4 | 2 |
| Trincomalee | Sri Lanka | 0 | 2 |
| Singapore | Singapore | 5 | 6 |
| Hong Kong | Hong Kong | 0 | 8 |
| Sydney – North Head | Australia | 0 | 2 |
| Sydney – Cape Banks | Australia | 0 | 2 |
| Port Kembla – Drummond Battery | Australia | 0 | 2 |
| Newcastle | Australia | 0 | 2 |
| Fremantle – Rottnest Island | Australia | 0 | 2 |
| Fremantle – Garden Island[16] | Australia | 0 | 2* |
| Darwin – East Battery | Australia | 0 | 2 |
| Halifax | Canada | 0 | 3* |
| Vancouver Island | Canada | 0 | 2* |
| Auckland – Stony Batter | New Zealand | 0 | 2* |
| Auckland – Whangaparaoa | New Zealand | 0 | 2* |
| Wellington – Wrights Hill Fortress | New Zealand | 0 | 2* |
Portugal has several surviving examples, with live firings as recently as 10 December 1998. The Portuguese refer to these guns as 23.4 cm guns, made by Vickers.[17]
Deployment on railway trucks
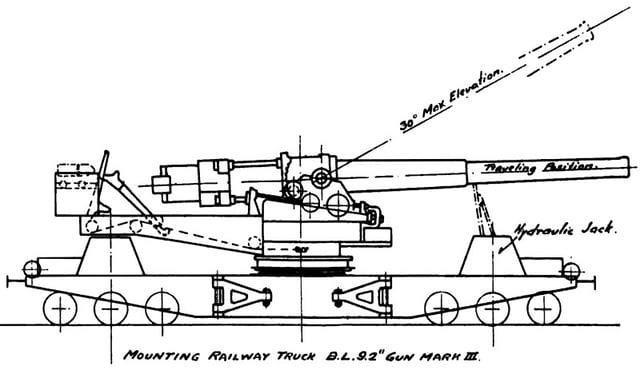
Mk X gun on Mk II "straight-back" truck
In 1916 Elswick adapted a small number of Mk X guns, 2 Mk X variants originally intended for coast defence in Australia, and 4 45-calibre Vickers export guns (under the designation 9.2-inch gun Mk XIV) and mounted them on Mk 3 railway truck mountings for service on the Western Front in France and Belgium.[18]
Belgian coast
From 1917 several Mk X guns were deployed ashore on the section of the Belgian coast still held by the Allies, near Nieuport. They were part of the "Royal Naval siege guns" under the command of Admiral Sir Reginald Bacon, and were used for attacking German heavy gun batteries.
Other deployments
In the 1950s, Canadian guns were transferred under NATO auspices, to Portugal (Azores) and Turkey. It is unclear if any UK guns were also transferred.
Surviving examples

At Imperial War Museum Duxford
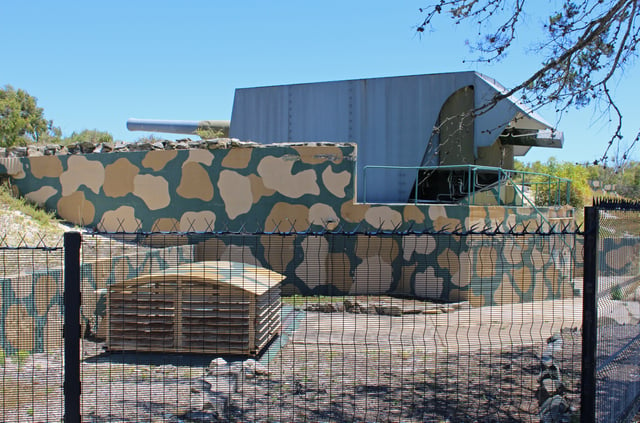

De Waal Battery, Robben Island
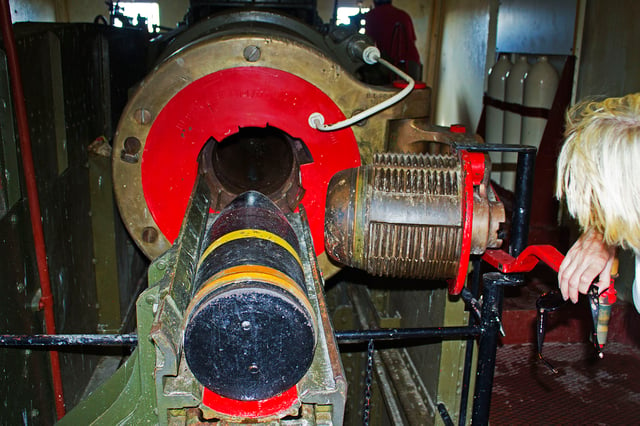
The breech of the Oliver Hill H1 gun
There are ten guns in the surrounds of Cape Town, South Africa :
Near Simon's Town three 9.2-inch guns in the Scala Battery :
Above Llandudno three 9.2-inch guns in the Apostle Battery :
On Robben Island three 9.2-inch guns in the De Waal Battery :
Near central Cape Town one 9.2-inch gun in a unique "disappearing mount" in Fort Wynyard :
33°54.136′S 18°24.807′E [75]
On the Durban Bluff, South Africa, three 9.2-inch guns in the Da Gama Battery :
On Rottnest Island, off Fremantle, Western Australia two 9.2-inch guns in the Oliver Hill Battery :
In Portugal's Bateria da Raposa, near Fonte da Telha, three 9.2-inch guns in good condition :
In Portugal one 9.2-inch gun of the original three of the Alcabideche battery, near Cascais is partly preserved, and accessible (but no entry) to pedestrians, in the centre roundabout of the staff and services parking at the back of the new Cascais Hospital (8/2016):(Personal observation)
38°43.887′N 9°25.137′W [85]
On the Rock of Gibraltar, three 9.2-inch guns :
In Bermuda, two Mk X guns survive on St. David's Island, on Mark V Barbette mounts, at St. David's Battery, overlooking the Narrows Channel that leads to St. George's Harbour, in Bermuda, as well as to the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda, the Great Sound, Hamilton Harbour, and Murray's Anchorage. The battery forms part of Great Head Park, and there is public access.[19] A third Mk X gun, previously at Fort Victoria on St. George's Island, has been relocated to the Bermuda Maritime Museum at the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda to make way for a hotel development, but as of October 2018 has not been remounted.:[20]
The official opening of the restored De Waal Battery on Robben Island, near Cape Town, South Africa, took place on 4 March 2011. The ceremony involved the unveiling and demonstration of the No 3 Gun of the battery of three "Ordnance BL 9.2in Coast Defence Guns". The gun in question, an "Ordnance BL 9.2in Coast Defence Gun on a Mk VII mounting", has been restored as a moving display, with all the hydraulics working, enabling the turret to be fully traversed through 360°, the gun being elevated to 25° and the loading/ramming mechanism fully operational.
Of the original ninety-eight 9.2-inch guns that did service worldwide during WWII, only about twenty-eight remain. Of these twenty-eight, twelve are in South Africa, the De Waal Battery No. 3 gun being the only gun in the world that has been restored as a moving display. Plans are afoot to restore the nearby Scala Battery at Simon's Town as a static display.[21]
On Western Australia's Rottnest Island the H1 gun and associated underground resources are open to visitors as a static display.
On 10 December 1998 the Portuguese Coast Artillery fired the last shots from the 6th Battery of their "Fonte da Telha" 9.2-inch (23.4 cm) guns. The fate of the several Coast Artillery Regiment batteries and their weapons has not yet been determined, but it is known that it is the intent of the Army to conserve one for the future Museum of Coast Artillery.
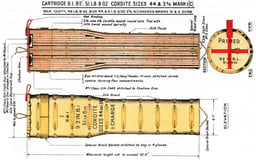
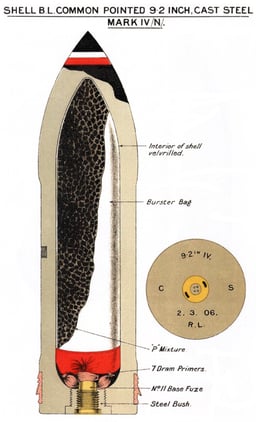
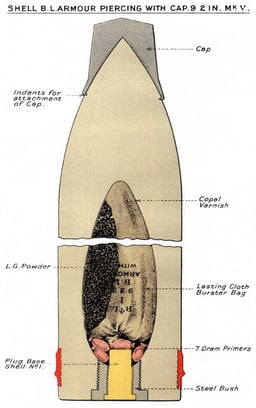
British ammunition up to World War I
Shells up to and including World War I were not streamlined, typically having fairly blunt noses of 2 CRH.
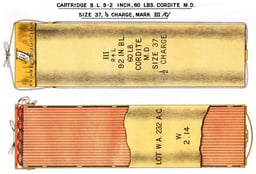
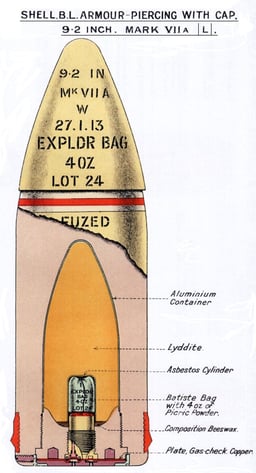
British World War II ammunition
World War II ammunition was somewhat streamlined, typically with ballistic caps of 4 or 5/10 CRH, but still retained square bases rather than the tapered type base typical of projectiles for more modern guns in use in World War II. "Super" charges of 124 pounds cordite SC 205 were available, which boosted the muzzle velocity to 2,872 feet per second (875 m/s)[7]
See also
List of naval guns
List of coastal artillery
Weapons of comparable role, performance and era
10"/40 caliber gun Mark 3 - contemporary US Navy weapon
10-inch gun M1895 - contemporary US Army coast defence weapon
Canon de 240 L Mle 1884 - contemporary French coast defence, siege, and railway weapon