António Guterres
António Guterres

His Excellency António Guterres GCC GCL | |
|---|---|
| 9th Secretary-General of the United Nations | |
| Assumed office 1 January 2017 | |
| Deputy | Amina Mohammed |
| Preceded by | Ban Ki-moon |
| United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees | |
| In office 15 June 2005 – 31 December 2015 | |
| Secretary-General | Kofi Annan Ban Ki-moon |
| Preceded by | Ruud Lubbers |
| Succeeded by | Filippo Grandi |
| 114th Prime Minister of Portugal | |
| In office 28 October 1995 – 6 April 2002 | |
| President | Mário Soares Jorge Sampaio |
| Preceded by | Aníbal Cavaco Silva |
| Succeeded by | José Manuel Barroso |
| President of the Socialist International | |
| In office 10 November 1999 – 15 June 2005 | |
| Preceded by | Pierre Mauroy |
| Succeeded by | George Papandreou |
| Secretary-General of the Socialist Party | |
| In office 23 February 1992 – 21 January 2002 | |
| President | António de Almeida Santos |
| Preceded by | Jorge Sampaio |
| Succeeded by | Eduardo Ferro Rodrigues |
| Leader of the Opposition | |
| In office 23 February 1992 – 28 October 1995 | |
| Prime Minister | Aníbal Cavaco Silva |
| Preceded by | Jorge Sampaio |
| Succeeded by | Fernando Nogueira |
| Member of the Assembly of the Republic | |
| In office 3 June 1976 – 4 April 2002 | |
| Constituency | Castelo Branco |
| Personal details | |
| Born | António Manuel de Oliveira Guterres (1949-04-30)30 April 1949 Lisbon, Portugal |
| Nationality | Portuguese |
| Political party | Socialist |
| Spouse(s) | Luísa Guimarães e Melo (m. 1972; died 1998) Catarina Vaz Pinto (m. 2001) |
| Children | 2 |
| Alma mater | Instituto Superior Técnico - University of Lisbon |
| Signature | |
| Website | António Guterres [101] |
António Manuel de Oliveira Guterres GCC GCL (/ɡʊˈtɛrəs/; European Portuguese: [ɐ̃ˈtɔnju ɡuˈtɛʁɨʃ]; born 30 April 1949) is a Portuguese politician and diplomat who is serving as the ninth Secretary-General of the United Nations. Previously, he was the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees between 2005 and 2015.[1]
Guterres was the Prime Minister of Portugal from 1995 to 2002 and was the Secretary-General of the Socialist Party from 1992 to 2002. He served as President of the Socialist International from 1999 to 2005.
His Excellency António Guterres GCC GCL | |
|---|---|
| 9th Secretary-General of the United Nations | |
| Assumed office 1 January 2017 | |
| Deputy | Amina Mohammed |
| Preceded by | Ban Ki-moon |
| United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees | |
| In office 15 June 2005 – 31 December 2015 | |
| Secretary-General | Kofi Annan Ban Ki-moon |
| Preceded by | Ruud Lubbers |
| Succeeded by | Filippo Grandi |
| 114th Prime Minister of Portugal | |
| In office 28 October 1995 – 6 April 2002 | |
| President | Mário Soares Jorge Sampaio |
| Preceded by | Aníbal Cavaco Silva |
| Succeeded by | José Manuel Barroso |
| President of the Socialist International | |
| In office 10 November 1999 – 15 June 2005 | |
| Preceded by | Pierre Mauroy |
| Succeeded by | George Papandreou |
| Secretary-General of the Socialist Party | |
| In office 23 February 1992 – 21 January 2002 | |
| President | António de Almeida Santos |
| Preceded by | Jorge Sampaio |
| Succeeded by | Eduardo Ferro Rodrigues |
| Leader of the Opposition | |
| In office 23 February 1992 – 28 October 1995 | |
| Prime Minister | Aníbal Cavaco Silva |
| Preceded by | Jorge Sampaio |
| Succeeded by | Fernando Nogueira |
| Member of the Assembly of the Republic | |
| In office 3 June 1976 – 4 April 2002 | |
| Constituency | Castelo Branco |
| Personal details | |
| Born | António Manuel de Oliveira Guterres (1949-04-30)30 April 1949 Lisbon, Portugal |
| Nationality | Portuguese |
| Political party | Socialist |
| Spouse(s) | Luísa Guimarães e Melo (m. 1972; died 1998) Catarina Vaz Pinto (m. 2001) |
| Children | 2 |
| Alma mater | Instituto Superior Técnico - University of Lisbon |
| Signature | |
| Website | António Guterres [101] |
Early life
Guterres was born and raised in Lisbon, Portugal, the son of Virgílio Dias Guterres (1913–2009) and Ilda Cândida de Oliveira (born 1923).
He attended the Camões Lyceum (now Camões Secondary School) where he graduated in 1965, winning the National Lyceums Award (Prémio Nacional dos Liceus) as the best student in the country. He studied Physics and Electrical Engineering at Instituto Superior Técnico - University of Lisbon in Lisbon. He graduated in 1971 and started an academic career as Assistant Professor teaching Systems Theory and Telecommunications Signals, before leaving academic life to start a political career.[4]
Political career
Guterres' political career began in 1974, when he became a member of the Socialist Party. Shortly thereafter, he quit academic life and became a full-time politician. In the period following the Carnation Revolution of 25 April 1974 that put an end to Caetano's dictatorship, Guterres became involved in Socialist Party leadership and held the following offices:
In 1992, after the Socialists' third consecutive defeat in Parliamentary elections,[9] Guterres became Secretary-General of the Socialist Party and leader of the opposition during Aníbal Cavaco Silva's government.[10] At the time, he was the party's third leader in six years.[11] He was also selected as one of the 25 vice-presidents of the Socialist International in September 1992.[12]
His election represented a break with tradition for the Socialists: not only was Guterres not associated with either the faction around then-President and former Prime Minister Mário Soares or the party's left wing led by Guterres' predecessor Sampaio, but he was also a devout Catholic, running counter to the party's historical secularism. He sought to consult with Portugal's civil society in formulating policy, meeting a range of intellectuals, scientists and entrepreneurs from across the country and the political spectrum in the run-up to the next general election.[9]
Prime Minister of Portugal
Cavaco Silva did not seek a fourth term as prime minister of Portugal (in order to run for the 1996 Presidential election) and the Socialist Party won the 1995 parliamentary election. President Soares appointed Guterres as prime minister[13] and his Cabinet took the oath of office on 28 October that year.
Guterres ran on a platform of keeping a tight hold on budget spending and inflation in a bid to ensure that Portugal met the Euro convergence criteria by the end of the decade, as well as increasing rates of participation in the labor market, especially among women, improving tax collection and cracking down on tax evasion, increased involvement of the mutual and non-profit sectors in providing welfare services, a means-tested guaranteed minimum income (known as the Rendimento Minimo Garantido), and increased investment in education.[9] He was then one of seven Social Democratic prime ministers in the European Union, joining political allies in Spain, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Greece and the Netherlands.[14]
First term (1995–99)
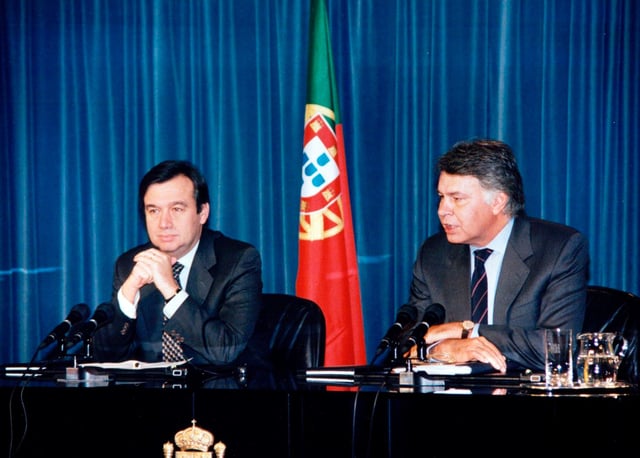

Guterres and Prime Minister of Spain Felipe González, in January 1996.
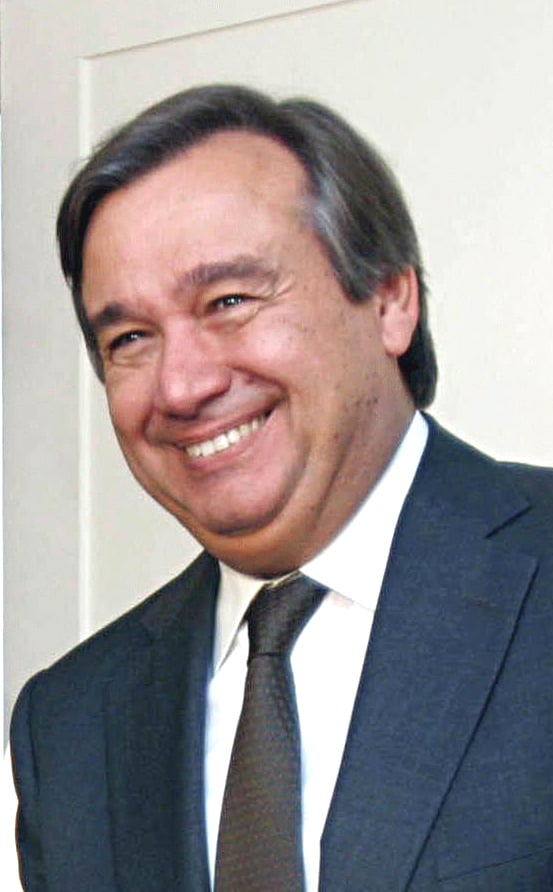

António Guterres in 2003
With a style markedly different from that of his predecessor, and based on dialogue and discussion with all sections of society, Guterres was a popular prime minister in the first years of his office. Portugal was enjoying a solid economic expansion which allowed the Socialists to reduce budget deficits while increasing welfare spending and creating new conditional cash transfer programs.[15] His government also accelerated the program of privatizations which had been undertaken by Cavaco Silva's government: a total of 29 companies were privatized between 1996 and 1999, with proceeds from privatizations in 1996-7 being greater than those of the previous six years, and the public sector's share of GDP being halved from 11 percent in 1994 to 5.5 percent five years later. Share ownership was also widened, with 800,000 people investing in Portugal Telecom upon its privatization in 1996 and 750,000 applying for shares in Electricidade de Portugal.[9]
In 1998, Guterres presided over Expo 98 in Lisbon, commemorating the 500th anniversary of the voyage of Vasco da Gama.[16] Also in 1998, two nationwide referenda were held. The first one was held in June, and asked the voters whether abortion rules should be liberalized. The Socialist Party split over the issue of liberalization, and Guterres himself led the pro-life side, which eventually won the referendum.[15] A second referendum was held in November, this time over the regionalization of the mainland. In this referendum, both Guterres and his party supported the approval of such an administrative reform. In this second referendum, Guterres suffered a political defeat, as the proposal was rejected by the voters.
Contrary to his party stance and following the removal of homosexuality from the list of mental illnesses by the World Health Organization in 1990, Guterres said, in 1995, that "he did not like homosexuality" and that he considered it "something that bothered him".[17]
On foreign policy, Guterres campaigned for United Nations intervention in East Timor in 1999, after the former Portuguese colony was virtually destroyed by Indonesian-backed militias when it voted for independence.[8] He also finalized the 12-year-long negotiations on the transfer of sovereignty over Macau, which had been a Portuguese colony, to Chinese control in 1999.[18]
Second term (1999–2002)
In the 1999 parliamentary election the Socialist Party and the opposition won exactly the same number of MPs (115). Guterres was re-appointed for the office and from January to July 2000, occupied the six-month rotating presidency of the European Council. This second term in government was not as successful, however. Internal party conflicts along with a slowdown in economic growth and the Hintze Ribeiro Bridge disaster damaged his authority and popularity. Nevertheless, some long-lasting measures were taken during his second term: in October 2000, the Parliament approved the decriminalization of drug use (effective from 1 July 2001)[19] and in March 2001, same-sex civil unions were legalized.[18][20]
In December 2001, following a disastrous defeat for the Socialist Party in local elections, Guterres resigned[13] to "prevent the country from falling into a political swamp".[21] President Jorge Sampaio dissolved Parliament and called for elections. Eduardo Ferro Rodrigues, until then Minister for Social Security, assumed the Socialist Party leadership, but the general election was lost to the Social Democratic Party of José Manuel Durão Barroso, who would later become President of the European Commission.
President of Socialist International
Diplomatic career
In 2005, following Guterres' proposal, George Papandreou was elected Vice President of the Socialist International; in 2006, Papandreou succeeded him as President of the Socialist International.
High Commissioner for Refugees
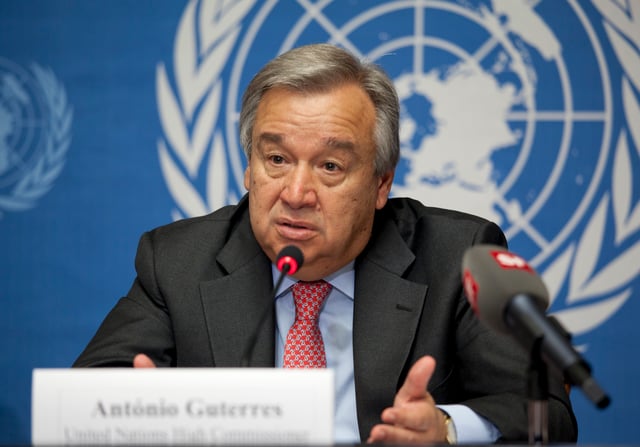

António Guterres, 2012
As High Commissioner, Guterres headed one of the world's largest humanitarian organizations, one which at the end of his term had more than 10,000 staff working in 126 countries providing protection and assistance to over 60 million refugees, returnees, internally displaced people and stateless persons. His time in office was marked by a fundamental organizational reform, cutting staff and administrative costs in the UNHCR's Geneva head office and expanding UNHCR's emergency response capacity during the worst displacement crisis since the Second World War.[24][25]
On March 19–23, 2006, Guterres visited Beijing, China, and expressed his objection to repatriation of North Korean refugees by the Chinese government.[26][27]
In a February 2007 NPR interview devoted mainly to the plight of Iraqi refugees, Guterres said that this was one of the greatest refugee crises in the Middle East since 1948. Among poorly publicized refugee crises, he cited those in the Central African Republic and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.[28] During his final years as High Commissioner, he worked chiefly to secure international aid for the refugees of the Syrian civil war, calling the refugee crisis an "existential" one for host countries (such as Lebanon and Jordan), and describing additional aid as a "matter of survival" for the refugees.[29] He was an outspoken advocate for a more coordinated and humane approach by European countries to the Mediterranean refugee crisis.[30] In June 2013, he launched a US$5 billion aid effort, its biggest ever, to help up to 10.25 million Syrians that year.[31]
In what was widely considered a very effective PR move, Guterres appointed American actress Angelina Jolie as his Special Envoy to represent UNHCR and himself at the diplomatic level in 2012.[32] Together they visited the Kilis Oncupinar Accommodation Facility in Turkey (2012);[33] the Zaatari refugee camp in Jordan (2013);[34] and the Maritime Squadron of the Armed Forces of Malta (2015). They also appeared jointly before the United Nations Security Council (2015).[35]
In early 2015, the General Assembly voted to extend Guterres' mandate by 61⁄2 months to 31 December, on recommendation of United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon. In light of the European migrant crisis, the UNHCR's 98-member executive committee (EXCOM) later requested that Ban recommend extending Guterres' term by a further year. However, Ban disregarded the request.[36] Guterres left office on 31 December 2015, having served the second-longest term as High Commissioner in the organization's history, after Prince Sadruddin Aga Khan.[37]
United Nations Secretary-General
Candidacy
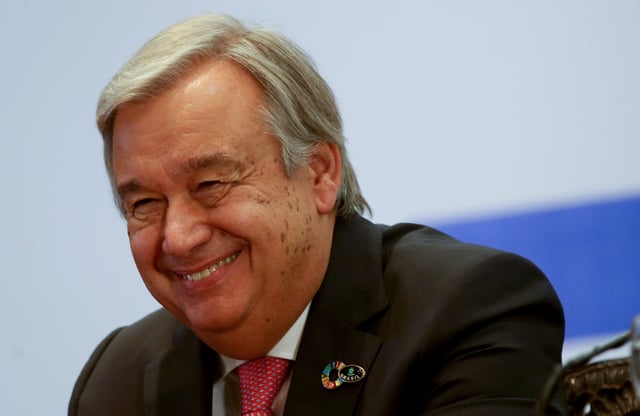

António Guterres, 2016

Guterres with Brazilian President Michel Temer in Brasilia, Brazil, 31 October 2016

Guterres and U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry shake hands, 4 November 2016

Guterres with Russian President Vladimir Putin and Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov, 24 November 2016
Guterres became United Nations Secretary-General on 1 January 2017, following his formal election by the UN General Assembly on 13 October 2016.[40]
On 29 February 2016, Guterres submitted his nomination as Portugal's candidate for the 2016 UN Secretary-General selection.[41] This was the first time candidates for Secretary-General had to present their platform in public hearings in the UN General Assembly, a process during which Guterres emerged as a much stronger candidate than had been initially expected, given that he fit the bill on neither the gender nor the geographic scores.[42]
On 5 October, the 15-member United Nations Security Council announced that they had agreed to nominate Guterres, after an informal secret ballot in which he gained 13 "encourage" votes and two "no opinion" votes.[43][44] The Security Council officially nominated Guterres by adopting a formal resolution on 6 October. A week later, he was formally elected by the United Nations General Assembly in its seventy-first session. Guterres took office on 1 January 2017.[45]
The UN's role in the Haiti cholera outbreak has been widely discussed and criticized[46] after the Ban Ki-moon administration denied the issue for several months. According to the Boston-based Institute for Justice & Democracy in Haiti as well as numerous conclusive scientific studies, the UN is the proximate cause for bringing cholera to Haiti. Peacekeepers sent to Haiti from Nepal in 2010 were carrying asymptomatic cholera and failed to treat their waste properly before dumping it into one of Haiti's main water streams.[47] During his UNSG informal dialogue, Jamaica, on behalf of the Caribbean Community, asked if the UN should assume liability for any deaths within local populations that result from the introduction of infectious disease by its peacekeepers. Jamaica also asked if Guterres believes compensation should be provided.[48] Guterres responded by calling the situation a "particularly complex question". He says that it is difficult to preserve diplomatic immunity while also ensuring there is no impunity, but that he would "pay a lot of attention in trying to find the right equilibrium between these two aspects that are absolutely crucial".[48] In a UN General Assembly meeting in late October 2016, the representative from Haiti called the UN's current and future response to the cholera epidemic "a litmus test of the system's commitment to the promotion of human rights".[49] Though many had hoped Guterres' term would mark a break with the inaction that characterized Ban Ki-moon's response to the epidemic, Guterres has done little to signal a commitment to cholera victims in Haiti. As of April 2017, five months into Guterres' term as Secretary-General, only $10 million had been contributed to the $400 million fund to fight cholera and provide material assistance to victims the UN announced in 2016.[50]
In 2016, Anders Kompass exposed the sexual assault of children by peacekeepers in the Central African Republic and, as a consequence, was dismissed by Ban Ki-moon's administration before being rehabilitated in court.[51] During the United Nations Secretary-General Candidate informal dialogues, Guterres indicated it was completely unacceptable that there be UN forces committing human rights violations such as rape and sexual violence. "All of us together—states and UN—must do our utmost to ensure that any kind of action of this type is severely punished," remarked Guterres.[48] The United States raised the question of international tribunals to try peacekeepers for their crimes. Guterres responded by saying an independent jurisdiction would be excellent but that "the only way to get there is through a new compact with all key parties—true contributors, financial contributors—and to make sure that there is an adjustment in the relation between countries, the UN, and the support those that are contributing with troops receive, in order to be able to do it much better."[48] He also indicated that there is a gap between theoretical zero tolerance and the ineffective zero tolerance that actually exists on the ground and needs to be overcome.
Tenure as Secretary-General

Guterres with U.S. President Donald Trump, 2 October 2017

Guterres, Qatar's Emir Tamim bin Hamad and NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg, 2018
On 1 January 2017, on his first day at the helm of the United Nations as Secretary-General, António Guterres pledged to make 2017 a year for peace. "Let us resolve to put peace first," said Guterres, in an appeal for peace.[52]
On April 12, 2017, Guterres appointed an 8-member Independent Panel[53] to assess, enhance effectiveness of UN-Habitat after Adoption of New Urban Agenda [102] . The recommendation [103] of the panel to establish an independent coordinating mechanism, ‘UN-Urban’[54] however was received with criticism from urban experts and the African Urban Institute [104] .[55]
On 20 June 2017, however, "Secretary-General Antonio Guterres warned the Trump administration ... that if the United States disengages from many issues confronting the international community it will be replaced..."[56]
After the violence during the Catalan independence referendum of 1 October 2017, Guterres trusted the Spanish institutions to look for a solution to the crisis.[58] The same message he gave when Catalonia declared the independence on 27 October 2017 but the solution should be made under the constitutional framework.[59]
Guterres criticized the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen and the naval, land and air blockade of Yemen. The blockade has further aggravated the severe humanitarian crisis in the country.[60] Guterres said that the intervention in Yemen "is a stupid war. I think this war is against the interests of Saudi Arabia and the Emirates... (and) of the people of Yemen."[61]
Guterres opposed President Donald Trump's decision to recognize Jerusalem as Israel's capital.[62]
In March 2018, Guterres said the population of Syria's Eastern Ghouta was living in "hell on earth". In one district, 93% of buildings had been damaged or destroyed by December, according to UN satellite imagery analysis. A recent wave of bombings has caused further destruction.[63]
Guterres called the 2018 North Korea–United States summit a "crucial milestone" for nuclear disarmament. Guterres urged both sides to "seize this momentous opportunity" and offered UN assistance to achieve the goal of dismantling North Korea's nuclear weapons program.[64]
In August 2018, Guterres called for an independent investigation into a Saudi Arabian-led coalition air strike in Yemen that killed 51 civilians including 40 children.[65]
In September 2018, during his address to the 73rd United Nations General Assembly, Guterres became the first Secretary to recognize that advancing technology will disrupt labor markets like never before and we should begin to consider stronger safety nets like Universal Basic Income.[67][68][69]
In 2019, human rights groups criticized Guterres for being "silent" as China sends ethnic Uyghurs and other predominantly Muslim ethnic minorities in China's north-western province of Xinjiang to the massive re-education camps. Human Rights Watch chief Kenneth Roth said that Guterres "has been notably silent on one of the most important, .. the most brazen human rights abuses, .. because he is worried about upsetting the Chinese."[70]
In September 2019, Guterres condemned Israeli PM's plans to annex the eastern portion of the occupied West Bank known as the Jordan Valley.[71]
Other activities
Dag Hammarskjöld Fund for Journalists, Chairman of the Honorary Advisory Council[72]
Caixa Geral de Depósitos, Advisor to the Board (2003–2005)
Champalimaud Foundation, Member of the Vision Award Jury[73]
Clean Cooking Alliance, Member of the Leadership Council[74]
Club of Madrid, Member (since 2002)[75]
European Council on Foreign Relations (ECFR), Member
International Gender Champions (IGC), Member[76]
European Regional Innovation Awards, Chairman of the Jury (2004)
Friends of Europe, Member of the Board of Trustees
Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation, Non-Executive Member of the Board of Trustees (2013–2018)[77]
World Economic Forum (WEF), Member of the Global Agenda Council on Humanitarian Assistance (2008-2009)[78]
Personal life
In 1972, Guterres married child psychiatrist[15] Luísa Amélia Guimarães e Melo, with whom he had two children, Pedro Guimarães e Melo Guterres (b. 1977) and Mariana Guimarães e Melo de Oliveira Guterres (b. 1985). His wife died of cancer at the Royal Free Hospital in London in 1998 at the age of 51.[79][10][80]
In addition to his native Portuguese, Guterres speaks English, French, and Spanish.[84]
Recognition
Honours
Portuguese
Portugal: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/41/PRT_Order_of_Christ_-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/80px-PRT_Order_of_Christ-Grand_Cross_BAR.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/41/PRT_Order_of_Christ-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/120px-PRT_Order_of_Christ-Grand_Cross_BAR.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/41/PRT_Order_of_Christ-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/160px-PRT_Order_of_Christ-_Grand_Cross_BAR.png 2x|PRT Order of Christ - Grand Cross BAR.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Christ (9 June 2002)[85]
Portugal: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/PRT_Order_of_Liberty_-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/80px-PRT_Order_of_Liberty-Grand_Cross_BAR.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/PRT_Order_of_Liberty-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/120px-PRT_Order_of_Liberty-Grand_Cross_BAR.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ad/PRT_Order_of_Liberty-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/160px-PRT_Order_of_Liberty-_Grand_Cross_BAR.png 2x|PRT Order of Liberty - Grand Cross BAR.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Liberty (2 February 2016)[85]
Foreign
Belgium: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/22/Grand_Crest_Ordre_de_Leopold.png/80px-Grand_Crest_Ordre_de_Leopold.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/22/Grand_Crest_Ordre_de_Leopold.png/120px-Grand_Crest_Ordre_de_Leopold.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/22/Grand_Crest_Ordre_de_Leopold.png/160px-Grand_Crest_Ordre_de_Leopold.png 2x|Grand Crest Ordre de Leopold.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cordon of the Order of Leopold (9 October 2000)[86]
Brazil: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b2/BRA_Order_of_the_Southern_Cross_-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/80px-BRA_Order_of_the_Southern_Cross-Grand_Cross_BAR.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b2/BRA_Order_of_the_Southern_Cross-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/120px-BRA_Order_of_the_Southern_Cross-Grand_Cross_BAR.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b2/BRA_Order_of_the_Southern_Cross-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/160px-BRA_Order_of_the_Southern_Cross-_Grand_Cross_BAR.png 2x|BRA Order of the Southern Cross - Grand Cross BAR.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of the Southern Cross (23 July 1996)[86]
Chile: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/CHL_Order_of_Merit_of_Chile_-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/80px-CHL_Order_of_Merit_of_Chile-Grand_Cross_BAR.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/CHL_Order_of_Merit_of_Chile-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/120px-CHL_Order_of_Merit_of_Chile-Grand_Cross_BAR.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/CHL_Order_of_Merit_of_Chile-Grand_Cross_BAR.png/160px-CHL_Order_of_Merit_of_Chile-_Grand_Cross_BAR.png 2x|CHL Order of Merit of Chile - Grand Cross BAR.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Merit (30 September 2001)[86]
Cape Verde: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0f/Am%C3%ADlcar_Cabral_Order_-1st_Class%28Cabo_Verde%29.png/80px-Am%C3%ADlcar_Cabral_Order_-1st_Class%28Cabo_Verde%29.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0f/Am%C3%ADlcar_Cabral_Order_-1st_Class%28Cabo_Verde%29.png/120px-Am%C3%ADlcar_Cabral_Order_-1st_Class%28Cabo_Verde%29.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0f/Am%C3%ADlcar_Cabral_Order_-1st_Class%28Cabo_Verde%29.png/160px-Am%C3%ADlcar_Cabral_Order_-1st_Class%28Cabo_Verde%29.png 2x|Amílcar Cabral Order - 1st Class (Cabo Verde).png|h22|w80]] First Degree of the Order of Amílcar Cabral (27 April 2001)[86]
France: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/82/Ordre_national_du_Merite_GC_ribbon.svg/80px-Ordre_national_du_Merite_GC_ribbon.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/82/Ordre_national_du_Merite_GC_ribbon.svg/120px-Ordre_national_du_Merite_GC_ribbon.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/82/Ordre_national_du_Merite_GC_ribbon.svg/160px-Ordre_national_du_Merite_GC_ribbon.svg.png 2x|Ordre national du Merite GC ribbon.svg|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit (4 February 2002)[86]
Greece: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1a/GRE_Order_of_Honour_Grand_Cross_BAR.png/80px-GRE_Order_of_Honour_Grand_Cross_BAR.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1a/GRE_Order_of_Honour_Grand_Cross_BAR.png/120px-GRE_Order_of_Honour_Grand_Cross_BAR.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1a/GRE_Order_of_Honour_Grand_Cross_BAR.png/160px-GRE_Order_of_Honour_Grand_Cross_BAR.png 2x|GRE Order of Honour Grand Cross BAR.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Honour (17 March 2000)[86]
Italy: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/ITA_OMRI_2001_GC_BAR.svg/80px-ITA_OMRI_2001_GC_BAR.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/ITA_OMRI_2001_GC_BAR.svg/120px-ITA_OMRI_2001_GC_BAR.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8d/ITA_OMRI_2001_GC_BAR.svg/160px-ITA_OMRI_2001_GC_BAR.svg.png 2x|ITA OMRI 2001 GC BAR.svg|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic (3 December 2001)[86][87]
Japan: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c4/JPN_Kyokujitsu-sho_1Class_BAR.svg/80px-JPN_Kyokujitsu-sho_1Class_BAR.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c4/JPN_Kyokujitsu-sho_1Class_BAR.svg/120px-JPN_Kyokujitsu-sho_1Class_BAR.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c4/JPN_Kyokujitsu-sho_1Class_BAR.svg/160px-JPN_Kyokujitsu-sho_1Class_BAR.svg.png 2x|JPN Kyokujitsu-sho 1Class BAR.svg|h22|w80]] Grand Cordon of the Order of the Rising Sun (4 April 2002)[86]
Mexico: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fe/GC_Aguila_Azteca_Categoria_Especial_MEX.png/80px-GC_Aguila_Azteca_Categoria_Especial_MEX.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fe/GC_Aguila_Azteca_Categoria_Especial_MEX.png/120px-GC_Aguila_Azteca_Categoria_Especial_MEX.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fe/GC_Aguila_Azteca_Categoria_Especial_MEX.png/160px-GC_Aguila_Azteca_Categoria_Especial_MEX.png 2x|GC Aguila Azteca Categoria Especial MEX.png|h22|w80]] Sash of Special Category of the Order of the Aztec Eagle (2 July 1999)[86]
Poland: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3f/POL_Order_Zaslugi_RP_kl1_BAR.png/80px-POL_Order_Zaslugi_RP_kl1_BAR.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3f/POL_Order_Zaslugi_RP_kl1_BAR.png/120px-POL_Order_Zaslugi_RP_kl1_BAR.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3f/POL_Order_Zaslugi_RP_kl1_BAR.png/160px-POL_Order_Zaslugi_RP_kl1_BAR.png 2x|POL Order Zaslugi RP kl1 BAR.png|h22|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Republic of Poland (22 September 1997)[86]
Spain: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/89/ESP_Charles_III_Order_GC.svg/80px-ESP_Charles_III_Order_GC.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/89/ESP_Charles_III_Order_GC.svg/120px-ESP_Charles_III_Order_GC.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/89/ESP_Charles_III_Order_GC.svg/160px-ESP_Charles_III_Order_GC.svg.png 2x|ESP Charles III Order GC.svg|h23|w80]] Grand Cross of the Order of Charles III (8 September 2000)[88]
Spain: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fe/Order_of_Isabella_the_Catholic_-Sash_of_Collar.svg/80px-Order_of_Isabella_the_Catholic-Sash_of_Collar.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fe/Order_of_Isabella_the_Catholic-Sash_of_Collar.svg/120px-Order_of_Isabella_the_Catholic-Sash_of_Collar.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fe/Order_of_Isabella_the_Catholic-Sash_of_Collar.svg/160px-Order_of_Isabella_the_Catholic-_Sash_of_Collar.svg.png 2x|Order of Isabella the Catholic - Sash of Collar.svg|h22|w80]] Collar of the Order of Isabella the Catholic (14 June 2002)[89]
Tunisia: Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic (4 April 2002)[86]
Uruguay: [[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3b/Order_of_the_Oriental_Republic_of_Uruguay_%281992%29_-ribbon_bar.png/80px-Order_of_the_Oriental_Republic_of_Uruguay%281992%29_-ribbon_bar.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3b/Order_of_the_Oriental_Republic_of_Uruguay%281992%29_-ribbon_bar.png/120px-Order_of_the_Oriental_Republic_of_Uruguay%281992%29_-ribbon_bar.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3b/Order_of_the_Oriental_Republic_of_Uruguay%281992%29_-ribbon_bar.png/160px-Order_of_the_Oriental_Republic_of_Uruguay%281992%29_-_ribbon_bar.png 2x|Order of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (1992) - ribbon bar.png|h22|w80]] Grand Officer of the Order of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay (10 December 1998)[86]
Honorary degrees
2010 – Honorary Doctorate, University of Beira Interior[90]
2014 – Honorary Doctorate, Meiji University[91]
2016 – Honorary Doctorate of Laws, Carleton University[92]
2016 – Honorary Doctorate, University of Coimbra[93]
2016 – Honorary Doctorate, European University of Madrid[94]
2017 – Honorary Doctorate, University of South Carolina[95]
Other awards
2005 – Personality of the Year by the Associação de Imprensa Estrangeira em Portugal (AIEP)
2007 – Freedom Award
2009 – Calouste Gulbenkian International Prize (shared with the Peace Research Institute in the Middle East)
2009 – Forbes List of The World's Most Powerful People in 2009[96]
2015 – W. Averell Harriman Democracy Award
2015 – The National German Sustainability Award [105]
2019 – Charlemagne Prize
See also
Climate change mitigation