Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport

Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport

Madrid-Barajas | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | ENAIRE | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | Aena | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Madrid, Spain | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | District of Barajas, Madrid | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 610 m / 2,000 ft | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 40°28′20″N 003°33′39″W [68] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | aena.es [69] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2018) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport (Spanish: Aeropuerto Adolfo Suárez Madrid-Barajas [aeɾoˈpweɾto aˈðolfo ˈswaɾeð maˈðɾið βaˈɾaxas]) (IATA: MAD, ICAO: LEMD),[5] commonly known as Madrid–Barajas Airport, is the main international airport serving Madrid in Spain. At 3,050 ha (7,500 acres) in area, it is the second largest airport in Europe by physical size behind Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport.[6][7] In 2018, 57.9 million passengers used Madrid–Barajas, making it the country's largest and busiest airport and Europe's sixth busiest.
The airport opened in 1928, and has grown to be one of the most important aviation centres of Europe. Located within the city limits of Madrid, it is just 9 km (6 mi) from the city's financial district and 13 km (8 mi) northeast of the Puerta del Sol or Plaza Mayor de Madrid, Madrid's historic centre. The airport name derives from the adjacent district of Barajas, which has its own metro station on the same rail line serving the airport. Barajas serves as the gateway to the Iberian peninsula from the rest of Europe and the world, and is a particularly key link between Europe and Latin America. The airport is the primary hub and maintenance base for Iberia and Air Europa. Consequently, Iberia is responsible for more than 40% of Barajas' traffic. The airport has five passenger terminals named T1, T2, T3, T4 and T4S.
Madrid-Barajas | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | ENAIRE | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | Aena | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Madrid, Spain | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | District of Barajas, Madrid | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 610 m / 2,000 ft | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 40°28′20″N 003°33′39″W [68] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | aena.es [69] | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2018) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
History
Early years
The airport was constructed in 1927, opening to national and international air traffic on 22 April 1931, although regular commercial operations began two years later. A small terminal was constructed with a capacity for 30,000 passengers a year, in addition to several hangars and the building of the Avión Club. The first regular flight was established by Lineas Aéreas Postales Españolas (LAPE) with its route to Barcelona. In the 1930s, flights started to serve some European and African destinations, the first international flights from the airport.
Originally, the flight field was a large circle bordered in white with the name of Madrid in its interior, unpaved, consisting of land covered with natural grass. It was not until the 1940s that the flight field was paved and new runways were designed. The first runway which started operation in 1944 was 1,400 metres long and 45 metres wide.[8] By the end of the decade the airport had three runways, none of which exist today. In the late 1940s, scheduled flights to Latin America and the Philippines started.
In the 1950s, the airport supported over half a million passengers, increasing to five runways and scheduled flights to New York City began. The National Terminal, currently T2, began construction in 1954 and opened later that year. In the Plan of Airports of 1957, Barajas Airport is classified as a first-class international airport. By the 1970s, large jets were landing at Barajas, and the growth of traffic mainly as a result of tourism exceeded forecasts. At the beginning of the decade, the airport reached the 1.2 million passengers, double that envisaged in the Plan of Airports of 1957.
In the 1970s, with the boom in tourism and the arrival of the Boeing 747, the airport reached 4 million passengers and began the construction of the international terminal (current T1). In 1974, Iberia, L.A.E. introduced the shuttle service between Madrid and Barcelona, a service with multiple daily frequencies and available without prior reservation.
The 1982 FIFA World Cup brought significant expansion and modernisation of the airport's two existing terminals.[8]
In the 1990s, the airport expanded further. In 1994, the first cargo terminal was constructed and the control tower was renovated. In 1997, it opened the North Dock, which is used as an exclusive terminal for Iberia's Schengen flights. In 1998, it inaugurated a new control tower, 71 m tall and then in 1999 the new South Dock opened, which implies an expansion of the international terminal. During this time, the distribution of the terminals changed: The south dock and most of the International Terminal were now called T1, the rest of the International Terminal and Domestic Terminal were now called T2 and the north dock was called T3.
In November 1998, the new runway 18R-36L started operations (replacing the previous 18–36), 4,400 m long, one of the largest in Europe under expansion plans called Major Barajas. In 2000, it began the construction of new terminals T4 and its satellite, T4S, designed by architects Antonio Lamela, Richard Rogers and Luis Vidal. Two parallel runways to the existing ones were also built.
Development since the 2000s
The new terminals and runways were completed in 2004, but administrative delays and equipment, as well as the controversy over the redeployment of terminals, delayed service until 5 February 2006.
Terminal 4, designed by Antonio Lamela, Richard Rogers and Luis Vidal, (winning team of the 2006 Stirling Prize) and TPS Engineers, (winning team of the 2006 IStructE Award for Commercial Structures)[9] was built by Ferrovial[10] and inaugurated on 5 February 2006. Terminal 4 is one of the world's largest airport terminals in terms of area, with 760,000 square meters (8,180,572 square feet) in separate landside and airside structures. It consists of a main building, T4 (470,000 m²) and a satellite building, T4S (290,000 m²), which are approximately 2.5 km apart. The new Terminal 4 is designed to give passengers a stress-free start to their journey. This is managed through careful use of illumination, with glass panes instead of walls and numerous skylights which allow natural light into the structure. With this new addition, Barajas is designed to handle 70 million passengers annually.
During the construction of Terminal 4, two more runways (15L/33R and 18L/36R) were constructed to aid in the flow of air traffic arriving and departing from Barajas. These runways were officially inaugurated on 5 February 2006 (together with the terminals), but had already been used on several occasions beforehand to test flight and air traffic manoeuvres. Thus, Barajas came to have four runways: two on a north–south axis and parallel to each other (separated by 1.8 km) and two on a northwest–southeast axis (and separated by 2.5 km). This allowed simultaneous takeoffs and landings into the airport, allowing 120 operations an hour (one takeoff or landing every 30 seconds).
Terminals 1, 2 and 3 are adjacent terminals that are home to SkyTeam and Star Alliance airlines. Terminal 4 is home to Iberia, its franchise Air Nostrum and all Oneworld partner airlines. Gate numbers are continuous in terminals 1, 2 and 3 (A1 to E89), but are separately numbered in terminal 4 (H, J, K and M, R, S, U in satellite building).
The Madrid–Barcelona air shuttle service, known as the "Puente Aéreo" (in Spanish), literally called "Air Bridge", is the busiest route between two European airports[11] with 55 daily flights in 2012.[12] The schedule has been reduced since the February 2008 opening of the Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line which covers the distance in 2 1⁄2 hours.
In 2007, the airport processed more than 52 million passengers. Barajas was voted "Best Airport" in the 2008 Condé Nast Traveller Reader Awards.[13]
In December 2010, the Spanish government announced plans to tender Madrid–Barajas airport to companies in the private sector for a period of up to 40 years.[14]
On 27 January 2012, Spanair suspended all flights affecting Madrid–Barajas as well as other domestic and international connections.[15] On 20 September 2012, both runways 15/33 were renamed as 14R/32L (the longest) and 14L/32R (the shortest).
On 1 August 2015, the first scheduled Airbus A380 flight landed in Madrid-Barajas in a daily service to Dubai by Emirates.
Following the death of former Spanish Prime Minister, Adolfo Suárez, in 2014, the Spanish Ministry of Public Works and Transport announced[16] that the airport would be renamed Aeropuerto Adolfo Suárez, Madrid–Barajas. This renaming seeks recognition for Suárez's role as the first Prime Minister of Spain after the restoration of democracy and his key participation in the transition to democracy after the dictatorship of Francisco Franco.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
As of June 2019, the following airlines serve 193 regular scheduled and charter routes to and from Madrid:[17]
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aegean Airlines | Athens |
| Aer Lingus | Dublin |
| Aeroflot | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Aerolíneas Argentinas | Buenos Aires–Ezeiza |
| Aeroméxico | Mexico City |
| airBaltic | Riga |
| Air Algérie | Algiers |
| Air Arabia Maroc | Tangier |
| Air Canada | Toronto–Pearson |
| Air China | Beijing–Capital, São Paulo–Guarulhos |
| Air Europa | A Coruña, Alicante, Amsterdam, Asturias, Asunción, Barcelona, Bilbao, Bogotá, Brussels, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Cancún, Caracas, Casablanca, Cordoba (AR), Düsseldorf, Fortaleza (begins 1 December 2019),[18] Frankfurt, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Guayaquil, Havana, Ibiza, Lanzarote, Lima, Lisbon, London–Gatwick, Málaga, Marrakesh, Medellín–JMC, Miami, Milan–Malpensa, Montevideo, Munich, New York–JFK, Palma de Mallorca, Panama City–Tocumen, Paris–Orly, Porto, Puerto Iguazú, Punta Cana, Quito, Recife, Rome–Fiumicino, Salvador, San Pedro Sula, Santa Cruz de la Sierra–Viru Viru, Santo Domingo–Las Americas, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Seville, Tel Aviv, Tenerife–North, Tunis, Valencia, Venice, Vigo, Zürich Seasonal: Alghero,[19] Athens, Copenhagen, Stockholm–Arlanda |
| Air France | Paris–Charles de Gaulle[20] |
| Air India | Delhi |
| Air Moldova | Chișinău |
| Air Serbia | Belgrade |
| Air Transat | Montréal–Trudeau[21] |
| Alitalia | Milan–Linate, Rome–Fiumicino |
| American Airlines | Dallas/Fort Worth, Miami, New York–JFK, Philadelphia Seasonal: Charlotte |
| Avianca | Bogotá, Cali, Medellín–JMC |
| Beijing Capital Airlines | Chengdu, Hangzhou |
| Blue Air | Bacău, Bucharest |
| Boliviana de Aviación | Cochabamba, Santa Cruz de la Sierra–Viru Viru |
| British Airways | London–Heathrow |
| Brussels Airlines | Brussels |
| Bulgaria Air | Sofia |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| Ceiba Intercontinental Airlines | Malabo |
| China Eastern Airlines | Beijing–Capital, Shanghai–Pudong, Xi'an |
| Cubana de Aviación | Havana, Santiago de Cuba |
| Czech Airlines | Prague |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta, New York–JFK |
| easyJet | Berlin–Tegel, Bristol, Edinburgh, Lisbon, Liverpool, London–Gatwick, London–Luton, Lyon, Milan–Malpensa, Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| easyJet Switzerland | Basel/Mulhouse, Geneva |
| EgyptAir | Cairo |
| El Al | Tel Aviv |
| Emirates | Dubai–International |
| Estelar Latinoamerica | Caracas[22] |
| Ethiopian Airlines | Addis Ababa, Dublin (ends 27 October 2019)[23] |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi |
| Evelop Airlines | Cancún, Havana, Punta Cana Seasonal: Mauritius |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Hainan Airlines | Shenzhen |
| Iberia | A Coruña, Asturias, Athens, Barcelona, Basel/Mulhouse, Bilbao, Bogotá, Boston,[24] Brussels, Budapest, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Cairo (resumes 2 March 2020),[25] Caracas, Chicago–O'Hare, Córdoba, Dakar–Diass, Düsseldorf, Florence, Frankfurt, Geneva, Gran Canaria, Granada, Guatemala City, Guayaquil (resumes 13 December 2019),[26] Hamburg, Havana, Jerez de la Frontera, Lima, Lisbon, London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Marrakesh, Medellín–JMC, Menorca, Mexico City, Miami, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Montevideo, Munich, New York–JFK, Oran, Oslo–Gardermoen, Panama City, Paris–Orly, Porto, Prague, Quito, Rio de Janeiro–Galeão, Rome–Fiumicino, San José, San Juan, San Salvador, Santander, Santiago, Santiago de Compostela, Santo Domingo–Las Americas, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Shanghai–Pudong, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Tel Aviv, Tokyo–Narita, Venice, Vienna, Vigo, Zagreb, Zürich Seasonal: Bastia,[27] Bergen, Corfu,[27] Dubrovnik,[28] Genoa, Moscow–Domodedovo, Olbia, Saint Petersburg, San Francisco, Split |
| Iberia Express | Amsterdam, Berlin–Tegel, Birmingham, Copenhagen, Dublin, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Ibiza, La Palma, Lanzarote, London–Gatwick, Lyon, Málaga, Manchester, Nantes, Naples, Nice, Palma de Mallorca, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Rennes, Santiago de Compostela, Seville, Tenerife–North, Tenerife–South Seasonal: Bari, Bucharest, Cagliari, Cork, Edinburgh, Heraklion, Kraków, Malta, Menorca, Mykonos, Palermo,[29] Reykjavik–Keflavik, Santorini, Toulouse, Zadar[30][31] |
| Iberia Regional | A Coruña (resumes 28 October 2019),[32] Alicante, Algiers, Almería, Asturias, Badajoz, Bologna, Bordeaux, Casablanca, Châlons-Vatry,[33] Frankfurt, Granada, Ibiza, Jerez de la Frontera, Lisbon, Logroño (ends 26 October 2019),[34][35] Lyon, Málaga, Marrakesh, Marseille, Melilla, Menorca, Nantes, Nice, Palma de Mallorca, Pamplona, San Sebastián, Santander, Seville, Strasbourg, Tangier, Toulouse, Turin, Valencia, Vigo, Zürich Seasonal: Biarritz, Faro, Funchal, Malta, Split, Verona |
| Icelandair | Seasonal: Reykjavík–Keflavík |
| KLM | Amsterdam |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| LATAM Brasil | São Paulo–Guarulhos |
| LATAM Chile | Frankfurt, Santiago de Chile, São Paulo–Guarulhos |
| LATAM Ecuador | Guayaquil (ends 13 December 2019)[36] |
| LATAM Perú | Lima |
| Lauda | Vienna |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Luxair | Luxembourg |
| Middle East Airlines | Beirut |
| Norwegian Air Shuttle | Copenhagen, Gran Canaria, London–Gatwick, Los Angeles, New York–JFK, Oslo–Gardermoen, Palma de Mallorca, Reykjavik–Keflavik, Stockholm–Arlanda, Tenerife–North Seasonal: Boston, Catania, Dubrovnik, Marrakech |
| Pegasus Airlines | Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen |
| Plus Ultra Líneas Aéreas | Caracas, Guayaquil, Lima, Quito |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca |
| Royal Jordanian | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Ryanair | Athens (begins 28 October 2019),[37] Bari, Beauvais, Bergamo, Berlin–Schönefeld, Birmingham, Bologna, Bratislava (ends 25 October 2019), Brussels, Bucharest, Budapest, Cagliari, Catania, Charleroi, Cologne/Bonn, Copenhagen, Dublin, Eindhoven, Fes, Frankfurt (ends 25 October 2019), Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Hamburg (ends 5 November 2019), Ibiza, Kiev–Boryspil (begins 27 October 2019),[37] Kraków, Lanzarote, London–Stansted, Luxembourg, Malta, Manchester, Marrakech, Marseille, Milan–Malpensa, Naples, Nuremberg (ends 5 November 2019), Ouarzazate (ends 5 November 2019), Palermo, Palma de Mallorca, Pisa, Porto, Prague, Rabat, Rome–Ciampino, Santiago de Compostela, Sofia, Tangier, Tenerife–North, Tenerife–South, Vilnius (ends 25 October 2019), Warsaw–Modlin, Wroclaw (ends 26 October 2019) Seasonal: Menorca |
| Saudia | Jeddah, Riyadh |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Geneva, Zürich |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon |
| TAP Express | Lisbon, Porto |
| TAROM | Bucharest |
| Transavia France | Paris–Orly |
| TUI fly Belgium | Casablanca |
| Tunisair | Tunis |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul[38] |
| Ukraine International Airlines | Kiev–Boryspil, Lviv |
| United Airlines | Newark Seasonal: Washington–Dulles |
| Volotea | Bordeaux, Genoa, Nantes Seasonal: Alghero,[39] Bastia |
| Vueling | Barcelona, Florence, Ibiza, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Rome–Fiumicino Seasonal: Menorca |
| Wamos Air | Cancún, Punta Cana |
| Wizz Air | Bucharest, Budapest, Cluj-Napoca, Craiova, Sibiu, Sofia, Timișoara, Vienna,[40] Warsaw–Chopin (resumes 1 June 2020)[41] |
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| ASL Airlines Belgium | Brussels, Liège |
| Atlantic Airlines | Liège |
| Cygnus Air | Frankfurt, Gran Canaria, Tenerife–North |
| DHL Aviation | Beijing–Capital, Casablanca, Copenhagen, East Midlands, Frankfurt, Leipzig/Halle, London–Heathrow, Miami, Milan–Malpensa, Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Emirates Sky Cargo | Dubai–Al Maktoum |
| FedEx Feeder | Dublin, Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Kalitta Air | Miami |
| MASkargo | Frankfurt, Kuala Lumpur–International |
| Qatar Airways Cargo | Doha |
| Swiftair | Algiers, Athens, Barcelona, Bilbao, Casablanca, Gran Canaria, Larnaca, Lisbon, Milan–Malpensa, Palma de Mallorca, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Stockholm–Arlanda, Tenerife–North[42] |
| Turkish Airlines Cargo | Algiers, Belgrade, Casablanca, Houston-Intercontinental, Istanbul–Atatürk. Miami[43] |
| UPS Airlines | Casablanca, Chicago–O'Hare, Cologne/Bonn, London–Stansted |
Traffic and statistics
Passenger numbers
| Passengers | Aircraft Movements | Cargo (tonnes) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 34,050,215 | 375,558 | 295,944 |
| 2002 | 33,915,302 | 368,029 | 295,711 |
| 2003 | 35,855,861 | 383,804 | 307,026 |
| 2004 | 38,718,614 | 401,503 | 341,177 |
| 2005 | 42,146,784 | 415,704 | 333,138 |
| 2006 | 45,799,983 | 434,959 | 325,702 |
| 2007 | 52,110,787 | 483,292 | 325,201 |
| 2008 | 50,846,494 | 469,746 | 329,187 |
| 2009 | 48,437,147 | 435,187 | 302,863 |
| 2010 | 49,863,504 | 433,683 | 373,380 |
| 2011 | 49,671,270 | 429,390 | 394,154 |
| 2012 | 45,195,014 | 373,185 | 359,362 |
| 2013 | 39,735,618 | 333,056 | 346,602 |
| 2014 | 41,833,374 | 342,601 | 366,645 |
| 2015 | 46,828,279 | 366,605 | 381,069 |
| 2016 | 50,420,583 | 378,150 | 415,774 |
| 2017 | 53,402,506 | 387,566 | 470,795 |
| 2018 | 57,891,340 | 409,832 | 518,858 |
| 2019 (AGO YTD) | 41,018,730 | 283,504 | 353,043 |
| Source: Aena Statistics[3] | |||
Route statistics
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Barcelona | 2,341,062 | Air Europa, Iberia, Vueling |
| 2 | Palma de Mallorca | 1,816,204 | Air Europa, Air Nostrum, Iberia Express, Norwegian Air International, Ryanair |
| 3 | Gran Canaria | 1,511,303 | Air Europa, Iberia Express, Norwegian Air International, Ryanair |
| 4 | Tenerife (North) | 1,382,264 | Air Europa, Iberia Express, Norwegian Air International, Ryanair |
| 5 | Bilbao | 743,844 | Air Europa, Iberia, Swiftair |
| 6 | Ibiza | 730,162 | Air Europa, Air Nostrum, Iberia Express, Ryanair, Vueling |
| 7 | A Coruña | 621,971 | Air Europa, Iberia |
| 8 | Santiago de Compostela | 608,003 | Iberia, Iberia Express, Ryanair |
| 9 | Vigo | 594,044 | Air Europa, Air Nostrum, Iberia Express, Swiftair |
| 10 | Oviedo | 479,819 | Iberia |
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
| 1 | 1,518,927 | Air Europa, easyJet, Iberia, TAP Express, TAP Portugal | |
| 2 | 1,416,801 | British Airways, Iberia | |
| 3 | 1,331,515 | Air Europa, Iberia, Transavia France | |
| 4 | 1,219,320 | Air Europa, Alitalia, Iberia, Vueling | |
| 5 | 1,140,881 | Air France, easyJet, Iberia Express, Vueling | |
| 6 | 1,084,662 | Air Europa, Air Nostrum, Iberia, LATAM Chile, Lufthansa, Ryanair | |
| 7 | 1,040,832 | Air Europa, Iberia Express, KLM | |
| 8 | 1,029,019 | Air Europa, easyJet, Iberia Express, Norwegian Air International | |
| 9 | 1,010,197 | Air Europa, Brussels Airlines, Iberia, Ryanair | |
| 10 | 860,506 | Air Europa, Iberia, Lufthansa | |
| 11 | 758,112 | Air Europa, Iberia, Ryanair, TAP Express, TAP Air Portugal | |
| 12 | 643,336 | Air Europa, Iberia, Swiss International Air Lines | |
| 13 | 575,329 | easyJet Switzerland, Iberia, Swiss International Air Lines | |
| 14 | 544,202 | Air Europa, easyJet, Iberia | |
| 15 | 535,487 | Aer Lingus, Iberia Express, Ryanair | |
| 16 | 472,339 | Air Europa, Iberia | |
| 17 | 471,436 | Ryanair | |
| 18 | 457,564 | Alitalia, Iberia | |
| 19 | 444,589 | Blue Air, Iberia Express, Ryanair, TAROM, Wizz Air | |
| 20 | 427,951 | Air Europa, Iberia | |
| 21 | 392,004 | Air Nostrum, Iberia Express, Ryanair | |
| 22 | 381,112 | Ryanair | |
| 23 | 359,128 | Eurowings, Iberia, Laudamotion | |
| 24 | 354,787 | easyJet, Iberia Express | |
| 25 | 339,420 | Iberia Express, Norwegian Air International, Ryanair | |
| 26 | 331,040 | Turkish Airlines | |
| 27 | 321,265 | Aegean Airlines, Iberia | |
| 28 | 314,757 | Czech Airlines, Iberia, Ryanair | |
| 29 | 306,054 | Ryanair | |
| 30 | 286,816 | Air Nostrum, Ryanair | |
| 31 | 282,094 | Iberia, Ryanair, Wizz Air | |
| 32 | 255,373 | Aeroflot | |
| 33 | 237,412 | Air Nostrum, easyJet, Iberia Express | |
| 34 | 217,273 | Iberia Express, Ryanair | |
| 35 | 208,235 | Air Nostrum, Ryanair | |
| 36 | 207,568 | Iberia, Norwegian Air International | |
| 37 | 202,765 | Ryanair | |
| 38 | 201,828 | Bulgaria Air, Ryanair, Wizz Air | |
| 39 | 196,713 | Finnair, Norwegian Air International | |
| 40 | 194,725 | Iberia, Ryanair |
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 883,716 | Air Europa, Avianca, Iberia | |
| 2 | 866,449 | Aerolíneas Argentinas, Air Europa, Iberia | |
| 3 | 849,947 | Air Europa, American Airlines, Delta Air Lines, Iberia, Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 4 | 782,073 | Aeroméxico, Iberia | |
| 5 | 708,340 | Air Europa, American Airlines, Iberia | |
| 6 | 663,374 | Air Europa, Iberia, LATAM, Plus Ultra Líneas Aéreas | |
| 7 | 644,113 | Air China, Air Europa, Iberia, LATAM | |
| 8 | 521,449 | Emirates | |
| 9 | 517,857 | Air Europa, El Al, Iberia, Smartwings | |
| 10 | 514,532 | Air Europa, Cubana de Aviación, Evelop Airlines, Iberia | |
| 11 | 477,868 | Iberia, LATAM | |
| 12 | 393,140 | Air Europa, Iberia | |
| 13 | 341,907 | Air Europa, Iberia, Norwegian Air International, Ryanair | |
| 14 | 339,131 | Qatar Airways | |
| 15 | 310,982 | Air Europa, Evelop Airlines, Wamos Air | |
| 16 | 238,613 | Air Europa, Iberia | |
| 17 | 226,612 | Air Europa, Evelop Airlines, Wamos Air | |
| 18 | 221,509 | Air Europa, Iberia | |
| 19 | 215,481 | Air Europa, Estelar Latinoamerica, Iberia, Plus Ultra Líneas Aéreas | |
| 20 | 202,764 | Iberia, Royal Air Maroc | |
| 21 | 201,123 | Iberia | |
| 22 | 193,955 | Air Arabia Maroc, Air Nostrum, Royal Air Maroc Express, Ryanair | |
| 23 | 187,712 | Air Europa, Boliviana de Aviación | |
| 24 | 179,628 | Etihad Airways | |
| 25 | 176,991 | Iberia | |
| 26 | 173,371 | Avianca | |
| 27 | 169,848 | United Airlines | |
| 28 | 167,906 | Iberia | |
| 29 | 156,161 | American Airlines | |
| 30 | 153,778 | Iberia, Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 31 | 152,493 | Cathay Pacific | |
| 32 | 150,496 | China Eastern Airlines, Iberia | |
| 33 | 145,072 | Avianca, Iberia | |
| 34 | 138,947 | Air Europa, LATAM Ecuador | |
| 35 | 135,586 | Delta Air Lines | |
| 36 | 127,709 | American Airlines | |
| 37 | 123,570 | Iberia | |
| 38 | 120,075 | Iberia | |
| 39 | 116,632 | Iberia | |
| 40 | 113,149 | Air Canada |
Airline market share
| Rank | Airline | Passengers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Iberia | 14,055,597 |
| 2 | Air Europa | 7,783,953 |
| 3 | Ryanair | 6,697,100 |
| 4 | Iberia Express | 4,987,319 |
| 5 | Air Nostrum (Iberia Regional) | 2,920,535 |
| 6 | easyJet | 1,495,941 |
| 7 | Norwegian Air International | 1,327,493 |
| 8 | Vueling | 1,223,888 |
| 9 | Lufthansa | 821,380 |
| 10 | Air France | 685,821 |
| 11 | American Airlines | 652,298 |
| 12 | TAP Portugal | 645,461 |
| 13 | Avianca | 586,573 |
| 14 | KLM | 558,590 |
| 15 | British Airways | 540,788 |
Medical care
Ground transport
Rail
The Madrid Metro Line connects the airport with city centre station Nuevos Ministerios in Madrid's financial district. The Barajas Line 8 provides a fast route from the underground stations at Terminal 2 (access to T1 and T3) and Terminal 4 into central Madrid. The metro also provides links to stations on the Spanish railway network.
In October 2006, a bid was launched for the construction of a Cercanías link between Chamartín Station and Terminal 4. Now finished, this single Cercanías Line (C-1) links Madrid Barajas Terminal 4, with Chamartín Station and Atocha AVE high-speed train stations.[47] In June 2011 a decision was made to equip this link with dual gauge which will allow AVE high-speed trains to reach the airport station.[48]
Metropolitan Bus
EMT (Madrid Municipal Transport Company) runs regular public bus services between the airport and Madrid (Avenida de América station): bus 200 runs as a complete line – dropping passengers at departures of terminals 1, 2 and 4 before collecting passengers in the reverse order at arrivals. The EMT public night bus service N4 (nicknamed "Buho", Owl) also services from Madrid downtown (Plaza Cibeles) to Barajas (Plaza de los Hermanos Falcó y Alvarez de Toledo, 400m from the airport through a passageway above the highway). EMT also have an express bus linking Barajas airport to Renfe's Atocha Station, the main rail station in Madrid, during day and Plaza Cibeles during night. Unlike the two services mentioned above, this line runs 24 hours of the day during all the days of the year.[51]
CRTM (Consorcio Regional de Transportes de Madrid) runs four bus services between the airport and nearby cities in the metropolitan area:
822: T1 - Coslada - San Fernando de Henares
824: T2 - Torrejón de Ardoz - Alcalá de Henares
827: Canillejas - T4 - Alcobendas - Universidad Autónoma de Madrid - Tres Cantos
828: Canillejas - T4 - Alcobendas - Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
Long distance coaches
From terminals T1 and T4 the bus company Avanzabus operates routes to Ávila, Castellón, Salamanca, Valencia y Zamora. From terminal T4 the Alsa bus company runs services to the cities of Zaragoza, Barcelona, Valladolid, León, Murcia, Alicante, Gijón, Oviedo, Lugo, Coruña, Santiago de Compostela, Burgos, Vitoria, San Sebastián, Santander, Bilbao, Logroño and Pamplona. From terminal T1 the Socibus company runs services to the major cities in Andalusia: Huelva, Córdoba, Cadiz, Jerez and Seville.
Airport People Mover
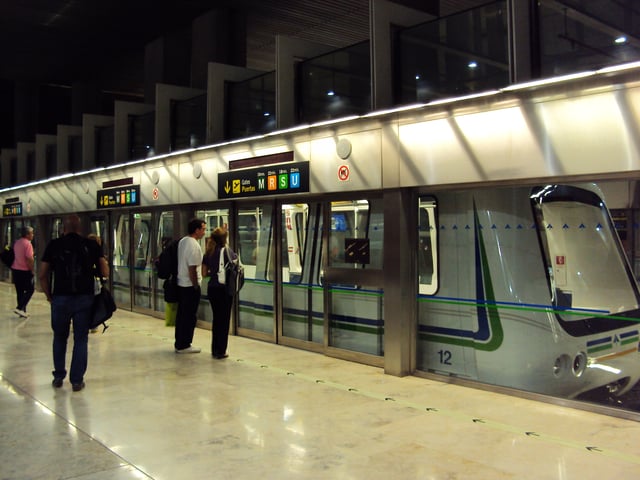

Automated People Mover that links Terminal 4 and the Terminal 4 Satellite
In early 2006, the first driverless transit system in Spain and the longest airport people mover system in Europe began transporting passengers between the new terminal (T4) and a new satellite terminal (T4S). Deploying the CITYFLO 550 automatic train control technology, the system is the only mode of transportation for passengers between the two terminals, which are spaced more than two kilometres apart.[52] Bombardier became the only contractor for the completely underground shuttle system, including the construction of the civil works, operation and maintenance of the system.
Airport parking
Long- and short-term car parking is provided at the airport with seven public parking areas. P1 is an outdoor car park located in front of the terminal building; P2 is an indoor car park with direct access to terminals T2 and T3. A Parking 'Express' facility, available for short periods only, is located at Terminal 2 and dedicated long-term parking is also available with 1,655 spaces; a free shuttle operates between the long-stay car park and all terminals. There are also VIP car parks.
Incidents and accidents
On 30 September 1972, Douglas C-47B EC-AQE of Spantax crashed on take-off. The aircraft was being used for training duties and the student pilot over-rotated and stalled. One of the six people on board was killed.[53]
On 29 July 1979, as part of a triple attack, a bomb placed by ETA political-military killed three people.[54]
On 27 November 1983, Avianca Flight 011 crashed while attempting to land. Flight 011 struck a series of hills, causing the plane's right wing to break off. The 747 then cartwheeled, shattering into five pieces before coming to rest upside-down. Only 11 of the 169 passengers survived – there were no survivors among the 23 crew.[55]
On 7 December 1983, an Iberia 727 operating as Iberia Flight 350[56] collided during takeoff with Aviaco Flight 134, a DC-9[57] The Aviaco DC-9 had accidentally entered the runway as the Iberia flight was taking off.[58] Ninety-three people were killed, including 51 from the Iberia 727 and 42 from the Aviaco DC-9.
On 15 July 2006, the winglet of a Thai Airways International Boeing 747-400 HS-TGY operating flight TG943 from Madrid Barajas Airport in Spain to Rome Leonardo da Vinci-Fiumicino Airport cut off the tail of an Air France ERJ-145 while taxiing to the runway for take-off. No injuries were reported.[59]
On the morning of 30 December 2006, an explosion took place in the carpark building module D attached to Terminal 4. Authorities received a bomb threat at approximately 8:15 local time (7:15 GMT), with the caller stating that a car bomb carried with 800 kg of explosive would explode at 9:00 local time (8:00 GMT).[60] After receiving the warning, police were able to evacuate part of the airport.[61] Later, an anonymous caller stated that ETA claims responsibility for the bombing.[62] As a result of the explosion, two Ecuadorians who were sleeping in their cars died. The whole module D of the car park was levelled creating around 40,000 tonnes of debris. It took workers six days to recover the body of the second victim from the rubble.
On 20 August 2008, Spanair Flight 5022 which was travelling to Gran Canaria, veered off to the right and into the ground while climbing immediately after lifting off from runway 36L at 14:45 local time. The McDonnell Douglas MD-82 with registration "EC-HFP", was carrying 172 people, including 162 passengers.[63] In the accident, 154 people were killed, two were seriously injured and 12 were slightly injured. Prime Minister Zapatero ordered three days of national mourning.[64]
On 3 December 2010, during the Spanish air traffic controllers strike, Madrid–Barajas Airport remained inoperative when all Spanish air traffic controllers walked out in a coordinated wildcat strike. Following the walkout, the Spanish Government authorized the Spanish military to assume operation of air traffic control.[65] On the morning of 4 December, the government declared a "State of Alert", ordering on the controllers back to work. Shortly after the measure was implemented, controllers started returning to work and the strike was called off.[66]