River Spey

River Spey

| River Spey | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | Scotland |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| ⁃ location | Loch Spey (grid referenceNN419937 [11]) |
| ⁃ coordinates | 57°00′26″N 4°36′18″W [12] |
| Mouth | |
⁃ location | Moray Firth at Spey Bay |
| Length | 107 mi (172 km) |
| Basin size | 3,008 km2(1,161 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| ⁃ average | 64 m3/s (2,300 cu ft/s)[1] |
Ramsar Wetland | |
| Official name | River Spey - Insh Marshes |
| Designated | 2 February 1997 |
| Reference no. | 889[2] |
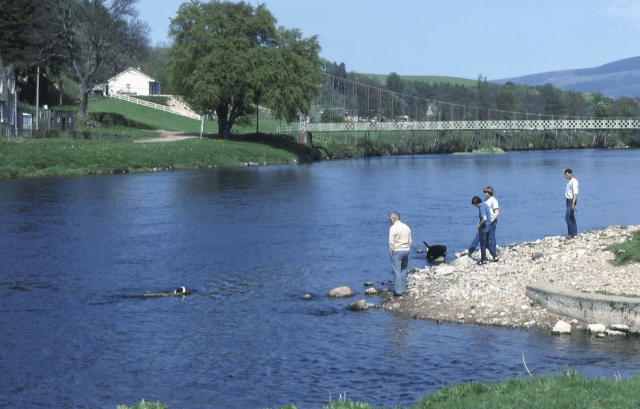
The River Spey (Scottish Gaelic: Uisge Spè) is a river in the northeast of Scotland. It is the ninth longest river in the United Kingdom, as well as the third longest and fastest-flowing river in Scotland. It is important for salmon fishing and whisky production.
| River Spey | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | Scotland |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| ⁃ location | Loch Spey (grid referenceNN419937 [11]) |
| ⁃ coordinates | 57°00′26″N 4°36′18″W [12] |
| Mouth | |
⁃ location | Moray Firth at Spey Bay |
| Length | 107 mi (172 km) |
| Basin size | 3,008 km2(1,161 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| ⁃ average | 64 m3/s (2,300 cu ft/s)[1] |
Ramsar Wetland | |
| Official name | River Spey - Insh Marshes |
| Designated | 2 February 1997 |
| Reference no. | 889[2] |
Etymology
Course
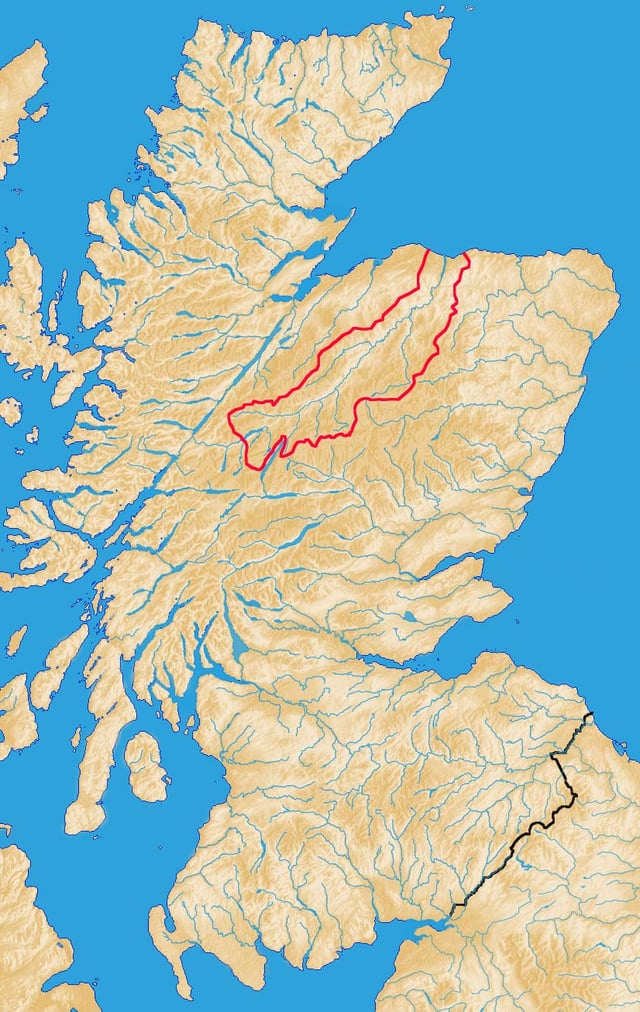
Catchment of the River Spey within Scotland.
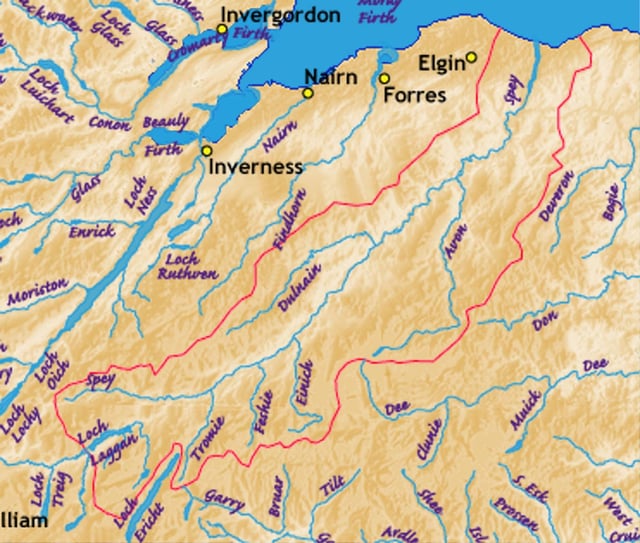
Tributaries of the River Spey.
The Spey is 107 miles (172 km) long. It rises at over 1,000 feet (300 m) at Loch Spey in Corrieyairack Forest in the Scottish Highlands, 10 miles (16 km) south of Fort Augustus. The river descends through Newtonmore and Kingussie, crossing Loch Insh before reaching Aviemore, giving its name to Strathspey. From there it flows the remaining 60 miles (97 km) north-east to the Moray Firth, reaching the sea 5 miles (8 km) west of Buckie.[4]
On some sections of its course, the Spey changes course frequently, either gradually as a result of deposition and erosion from normal flow, or in a matter of hours as a result of spate. The Spey spates quickly due to its wide mountainous catchment area as a result of rainfall or snow-melt.
Insh Marshes, areas of roughly two miles (3 km) on either side of the Spey in the lower reaches are designated by Scottish Natural Heritage as a Site of Special Scientific Interest, as are the extensive shingle systems at Spey Bay.
Tributaries
After leaving Loch Spey the river gathers numerous burns in the Corrieyarack, Sherramore and Glenshirra Forests. The first sizeable tributary is the Markie Burn which drops out of Glen Markie to the north to enter the waters of Spey impounded behind the Spey Dam. A further mile downstream the River Mashie enters from Strath Mashie to the south.
The River Truim enters on the right bank a couple of miles above Newtonmore and the Highland Calder enters from Glen Banchor on the left bank at Spey Bridge at Newtonmore. At Kingussie the Spey is joined on its left bank by the River Gynack which runs through the town and 1 1⁄2 miles (2.4 km) downstream it is joined by the River Tromie which enters on the right bank.
The sizeable River Feshie joins on the right bank at Kincraig and the River Druie does likewise at Aviemore.
Several miles downstream the River Nethy joins from the east near Nethy Bridge and the River Dulnain originating in the Monadhliath contributes a considerable flow from the west near Dulnain Bridge.
Between Grantown-on-Spey and Craigellachie, the Burn of Tulchan and Allt a Gheallaidh join from the west whilst the Spey's most important tributary, the River Avon joins from the east. The Allt Arder and Knockando Burn also join from the west near Knockando.
The River Fiddich enters from the right at Craigellachie and the Burn of Rothes enters from the left at Rothes. Downstream more burns enter the Spey, the most important of which are the Burn of Mulben, Red Burn and Burn of Fochabers.
Industry
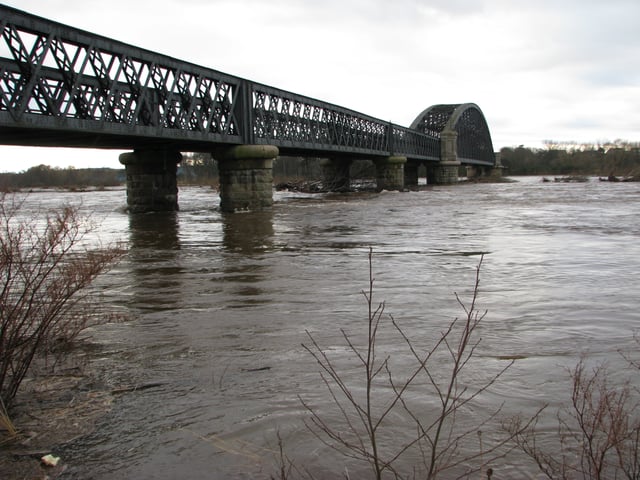

The River Spey in spate at the Garmouth old rail bridge
The river traditionally supported many local industries, from the salmon fishing industry to shipbuilding. At one stage, Garmouth functioned as the shipbuilding capital of Britain, with timber from the forests around Aviemore and Aberlour being rafted down to create wooden-hulled ships.
The river is known by anglers for the quality of its salmon and trout fishing, including a particular form of fly fishing where the angler uses a double-handed fly rod to throw a 'Spey cast' whereby the fly and the line do not travel behind the fisher (thereby keeping these away from the bushes and trees lining the banks behind him or her). This type of cast was developed on the Spey.
Speyside distilleries produce more whisky than any other region.
The Speyside Way, a long-distance footpath, follows the river through the County of Moray.
The River Spey is unusual in that its speed increases as it flows closer to the sea, due to a broadly convex long-profile. The mean flow is around 16 metres per second (36 mph) making it the fastest flowing river in Scotland, and possibly the UK (depending on what constitutes a river). The Spey does not meander, although it rapidly moves its banks. South of Fochabers a high earth barrier reinforces the banks, but the river has broken through on several occasions, removing a large portion of Garmouth Golf Course, sections of wall surrounding Gordon Castle, parts of the Speyside Way and some of the B9104 road.
The Spey railway bridge (pedestrianised as of 2010) Spey Bay to Garmouth was originally designed with its main span over the main flow of the river, however before construction was completed the river had changed its course and was running at one end of the bridge.
Settlements
Starting from the source
Laggan
Newtonmore
Inverdruie
Aviemore
Boat of Garten
Grantown on Spey
Cromdale
Mains of Dalvey
Advie
Ballindalloch
Pitchroy
Blacksboat
Marypark
Knockando
Carron
Speyview
Aberlour
Craigellachie
Dandalieth
Rothes
Crofts
Newlands of Dundurcas
Garbity
Ordiequish
Fochabers
Upper Dallachy
Stynie
Garmouth
Kingston on Spey
Spey Bay