Northern red-bellied cooter
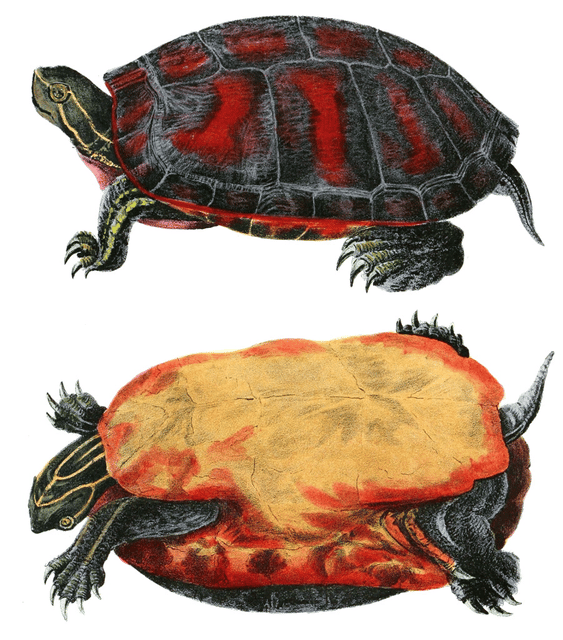
Northern red-bellied cooter

| Northern red-bellied cooter | |
|---|---|
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Family: | Emydidae |
| Genus: | Pseudemys |
| Species: | P. rubriventris |
| Binomial name | |
| Pseudemys rubriventris (LeConte, 1830)[2] | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
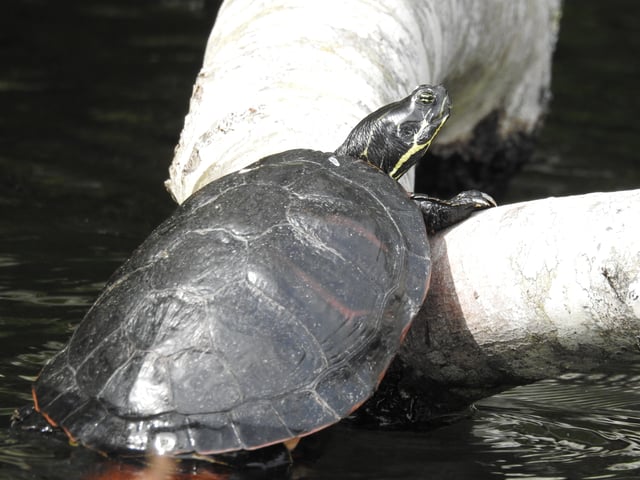

A northern red-bellied cooter in Long Pond in Plymouth, Massachusetts in July 2016.
A fairly large river turtle, it averages about 29 to 30 cm (11 to 12 in) in length and weighs on average around 3 kg (6.6 lb), although large females can measure up to 40 cm (16 in) in length.[4] It is endemic to the United States. The current range of the red-bellied turtle includes a population in Massachusetts which was previously considered a distinct subspecies (Pseudemys rubriventris bangsi) as well as the coastal areas of New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia and North Carolina.
The red-bellied turtle has appeared on Pennsylvania Fish Commission lists of endangered amphibians and reptiles since 1978 (McCoy 1985). By 1985 the red-bellied turtle was known to exist in Pennsylvania only in isolated colonies in a few counties (McCoy 1985). Small (less than thirty individuals) colonies were known in Manor and Silver lakes in Bucks county, the Tinicum wetlands in Philadelphia and Delaware counties, the West Branch of Conococheague Creek in Franklin County and possibly Springton Reservoir in Delaware county (McCoy 1985). The red-bellied turtle is a threatened[5] species within Pennsylvania. However, it is listed as "Endangered" by the US Fish and Wildlife Service as well as the Massachusetts Division of Fisheries and Wildlife.[6]
The potential threats to red-bellied turtle populations are numerous. For example: wetland loss, habitat fragmentation, pollution, collecting of turtles for pets, food or other trophies, competition with the invasive red-eared slider turtle for food, habitat, basking sites or nesting sites, and the potential for hybridization with red-eared slider turtles.
The Massachusetts wildlife preserve foundation has started to repopulate the turtles by placing them in many south-eastern Massachusetts ponds. One example is at Long and Little Long Pond in Plymouth, Massachusetts, where the population is starting to regrow.
| Northern red-bellied cooter | |
|---|---|
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Family: | Emydidae |
| Genus: | Pseudemys |
| Species: | P. rubriventris |
| Binomial name | |
| Pseudemys rubriventris (LeConte, 1830)[2] | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
