Mongolian People's Army

Mongolian People's Army

| Mongolian People's Army | |
|---|---|
| Монголын Ардын Арми | |
| Founded | March 1921 |
| Disbanded | February 1992 |
| Service branches | Mongolian People's Army Ground Forces Mongolian People's Air Force |
| Headquarters | Ulaanbaatar |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 18 |
| Conscription | Yes |
| Reaching military age annually | 200,000 (1988) |
| Reserve personnel | 15,000 |
| Industry | |
| Foreign suppliers | |
| Related articles | |
| Ranks | Military ranks of the Mongolian People's Republic |
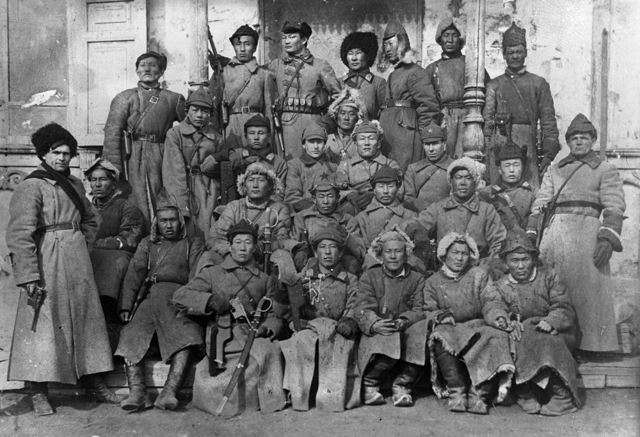

Mongolian People's Army soldiers and Soviet commanders in 1920s, the uniform was the same as that of Red Army
The Mongolian People's Army (Mongolian: Монголын Ардын Арми or Монгол Ардын Хувьсгалт Цэрэг) or Mongolian People's Revolutionary Army was an institution of the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party constituting as the armed forces of the Mongolian People's Republic.
It was established on 18 March 1921 as a secondary army under Soviet Red Army command during the 1920s and during World War II. In 1992, the army's structure changed and then reorganized and renamed as the General Purpose Force.
| Mongolian People's Army | |
|---|---|
| Монголын Ардын Арми | |
| Founded | March 1921 |
| Disbanded | February 1992 |
| Service branches | Mongolian People's Army Ground Forces Mongolian People's Air Force |
| Headquarters | Ulaanbaatar |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 18 |
| Conscription | Yes |
| Reaching military age annually | 200,000 (1988) |
| Reserve personnel | 15,000 |
| Industry | |
| Foreign suppliers | |
| Related articles | |
| Ranks | Military ranks of the Mongolian People's Republic |
Creation of the army
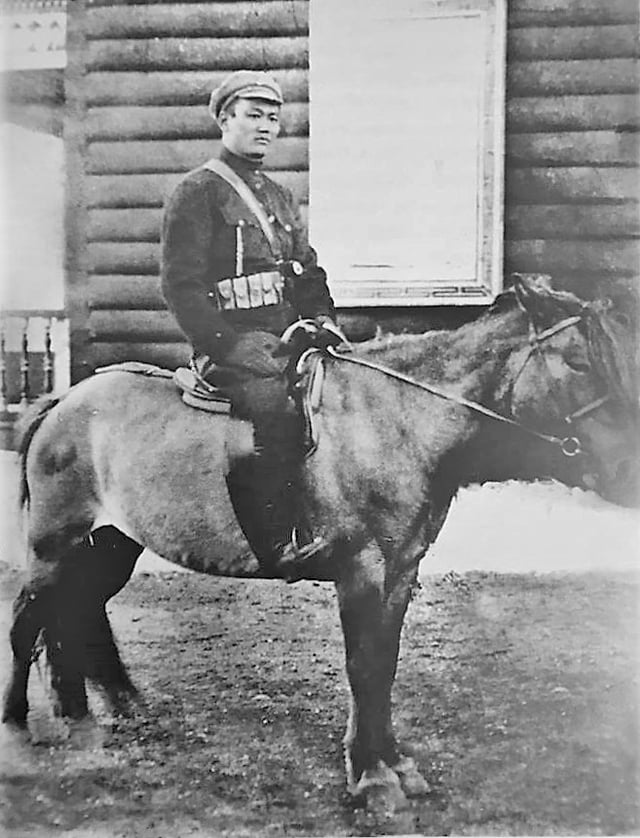

Sükhbaatar is one of the founders of People's Army
One of the first actions of the new Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party authorities was the creation of a native communist army in 1920 under the leadership of adept cavalry commander Damdin Sükhbaatar in order to fight against Russian troops from the White movement and Chinese forces. The MPRP was aided by the Russian SFSR Red Army, which helped to secure the Mongolian People's Republic and remained in its territory until at least 1925.
1930s conflicts
Initially during the native revolts of the early 1930s and the Japanese border probes beginning in the mid-1930s, Soviet Red Army troops in Mongolia amounted to little more than instructors for the native army and as guards for diplomatic and trading installations.
However, in the 1939 Battles of Khalkhin Gol (or Nomonhan) heavily armed Red Army forces under Georgy Zhukov assisted by Mongolian troops under Khorloogiin Choibalsan decisively defeated Imperial Japanese Army forces under Michitarō Komatsubara.
Cold war era
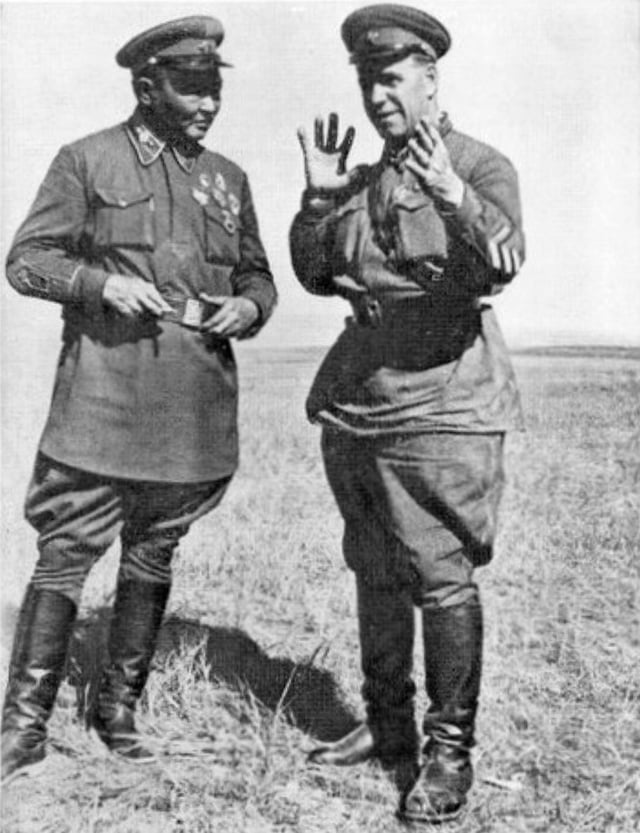

Georgy Zhukov and Khorloogiin Choibalsan (left) consult during the Battle of Khalkhin Gol
During the Pei-ta-shan Incident, elite Qinghai Chinese Muslim cavalry were sent by the Chinese Kuomintang to destroy the Mongols and the Russians positions in 1947.[1]
The military of Mongolia's purpose was national defense, protection of local communist establishments, and collaboration with Soviet forces in future military actions against exterior enemies, up until the 1990 Democratic Revolution in Mongolia.
Political indoctrination
The central Political Administration Unit was established in the army in 1921 to supervise the work of political commissars (Politruk) and party cells in all army units and to provide a political link with the Central Committee of the MPRP in the army. The unit served to raise morale and to prevent enemy political propaganda. Up to one third of army units were members of the party and others were in the Mongolian Revolutionary Youth League.
The Red Mongol Army received sixty percent of the government budget in early years and it to expanded from 2,560 men in 1923 to 4,000 in 1924 and to 7,000 in 1927. The native armed forces stayed linked to Soviet Red Army intelligence groups and NKVD, Mongolian secret police, and Buryat Mongol Comintern agents acted as administrators and represented the real power in the country albeit under direct Soviet guidance.
Training

By 1926 the government planned to train 10,000 conscripts annually and to increase the training period to six months. Chinese intelligence reports in 1927 indicated that between 40,000 and 50,000 reservists could be mustered at short notice. In 1929 a general mobilization was called to test the training and reserve system. The expected turnout was to have been 30,000 troops but only 2,000 men presented. This failure initiated serious reforms in recruiting and training systems.
Strength
In 1921–1927, the land forces, almost exclusively horsemen, numbered about 17,000 mounted troops and boasted more than 200 heavy machine guns, 50 mountain howitzers, 30 field guns, seven armored cars, and a maximum of up to 20 light tanks.
Basic units and motorization

Mongolian People's Army renactors in 2006.
The basic unit was the 2,000-man cavalry regiment consisting of three squadrons. Each 600-plus-man squadron was divided into five companies, a machine gun company, and an engineer unit. Cavalry regiments were organized into larger units--brigades or divisions—which included artillery and service support units. The chief advantage of this force was mobility over the great distances in Mongolia: small units were able to cover more than 160 km in 24 hours.
List of Mongolian Army divisions and other units
1st Cavalry Division
2nd Cavalry Division
3rd Cavalry Division
4th Cavalry Division
5th Cavalry Division
6th Cavalry Division
7th Cavalry Division
8th Cavalry Division
9th Cavalry Division
10th Cavalry Division
7th Motorized Armored Brigade
3rd Separate Tank Regiment
3rd Artillery Regiment
Aviation Mixed Division
Chemical defence-engineering regiment
Army ranks and insignia
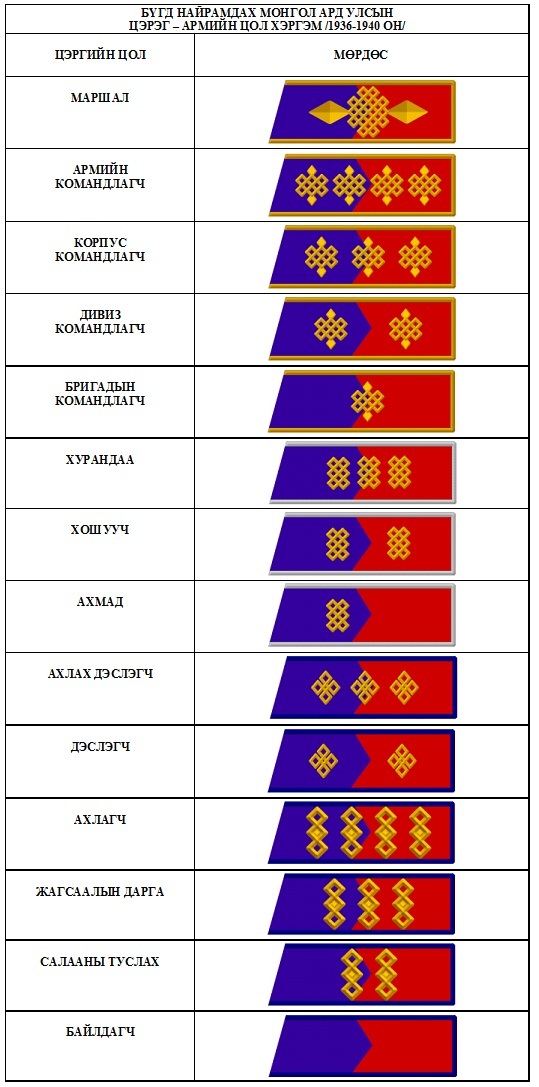
Rank Insignia of the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Army until 1944
Conscript soldiers
- Private (PVT)Lance Corporal (LCPL)Corporal (CPL)Senior Corporal (SCPL)
NCO's
- Junior Sergeant (JSGT)Sergeant (SGT)Senior Sergeant (SSG)Training Sergeany (TSGT) = (SM)Sergeant MajorLead Sergeant (LSGT) or Command Sergeant Major (CSM)
Officers
- 2nd Lieutenant (2LT)1st Lieutenant (1LT)Captain (CPT)Major (MAJ)Lieutenant Colonel (LTC)Colonel (COL)Brigadier General (Br Gen)Major General (MAJ GEN)Lieutenant General (LT GEN)General (GEN)
Uniform

A Soviet-Russian and Mongolian tiled mural at the World War II Zaisan Memorial, Ulan-Bator, from the People's Republic of Mongolia era.
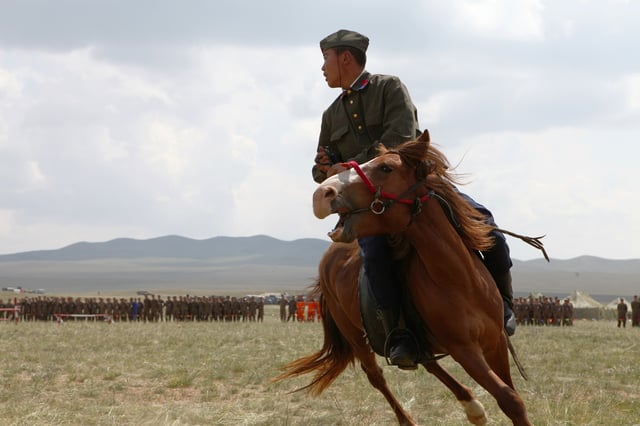

A horseman with Soviet-style uniform performs during the opening ceremony for exercise Khaan Quest 2013 at the Five Hills Training Area in Mongolia Aug. 3, 2013
Because establishment of the Armed Forces was based on a Soviet military system in 1920s, the Mongolian People's Army used similar uniforms with the Red Army, only with Mongolian distinctions. Until 1924, People's Army personnel wore traditional deel, which had their respective shoulder insignias. In the mid-1930s, the army adopted Soviet Gymnasterka and developed its true rank and distinction system. All personnel were distinct by their sleeve and collar insignias from the general population when the gymnastyorka was rather popular. After the Battle of Khalkhin Gol, slight modifications were made. In 1944 all uniforms and insignia were significantly changed to include shoulder insignia and camouflage cloaks, similar to Soviet uniform modifications but on olive green.
From the 1960s, the equipment and uniforms of the Mongolian People's Army were included a program to modernize the military. As before, the Mongolian People's Army (a Warsaw pact ally) was similar to the Soviet Red Army in appearance and structure.
Military actions
Units of Mongolian People's Army were supported and allied with the Soviet Red Army in the Battle of Khalkhin Gol in 1939 and on the western flank of the Soviet invasion of Manchuria in 1945. Domestically, it took part in the suppression of the 1932 armed uprising. It also involved in many border conflicts against Manchukuo and the Kwantung Army (one of the largest parts of the Imperial Japanese Army) and the Chinese National Revolutionary Army. The Imperial Japanese Army recorded 152 minor incidents on the border of Manchuria between 1932 and 1934. The number of incidents increased to over 150 per year in 1935 and 1936, and the scale of incidents became larger.
In January 1935, the first armed battle, Halhamiao incident (哈爾哈廟事件, Haruhabyō jiken) occurred on the border between Mongolia and Manchukuo.[2] Scores of Mongolian cavalry units engaged with a Manchukuo army patrol unit near the Buddhist temple of Halhamiao. The Manchukuo Army incurred slight casualties, including a Japanese military advisor.
Between December 1935 and March 1936, the Orahodoga incident (オラホドガ事件, Orahodoga jiken)(ja) and the Tauran incident (タウラン事件, Tauran jiken) (ja) occurred. In these battles, both the Japanese and Mongolian Armies use a small number of armoured fighting vehicles and military aircraft.
Stalinist repressions against Mongolian People's Army
Light equipment
Soviet Union PPSh-41
Soviet Union PPSh-43
Russia and Soviet Union Russian M1910 Maxim
Soviet Union SG-43 Goryunov
Soviet Union DShK
Soviet Union Degtyaryov machine gun
Artillery and mortars
Soviet Union 76 mm regimental gun M1927
Soviet Union 37 mm anti-tank gun M1930 (1-K)
Soviet Union 45 mm anti-tank gun M1937 (53-K)
Soviet Union 76 mm regimental gun M1943
Multiple Rocket Launchers
Soviet Union Katyusha - 150
Anti-aircraft Weapon
Although little attention was paid to anti-aircraft weaponry in the Mongolian People's Army, a few dozen units of Soviet origin were known to be distributed to light armored outfits.
Vehicles
Soviet Union GAZ-61
Soviet Union GAZ-64
Soviet Union GAZ-67
Soviet Union ZIS-5
Soviet Union GAZ–MM
Soviet Union ZiS-42
United States Studebaker US6
United States Dodge WC-51
Armoured corps
Under Soviet support campaign for mechanization, the army formed its first mechanized unit in 1922. Also it was by structure in the ground force half-mechanization cavalry in the other units distributed to light armored vehicles until 1943. It began to process to motorised since 1943. This is a list of Mongolian People's Army tanks and armour during the 1922s-World War II period.
Armoured cars
Russia Austin Putilov- 2/3
Soviet Union FAI- 15
Soviet Union BA-6
Soviet Union BA-10
Soviet Union BA-64
Light Tanks
Soviet Union T-27- 10
Soviet Union BT-5 - ? (Unknown number)
Soviet Union BT-7 - 27
Medium Tanks

A World War II memorial in Ulaanbaatar, featuring a T-34-85 tank.
Soviet Union T-34/76- 40
Soviet Union T-34/85- 33
Sps Tank destroyers
Soviet Union SU-100
Mongolian People's Army Air Force in 1925–1945
The Mongolian People's Army Aviation drastically improved with Soviet training and vastly ameliorated within a time span of several years. In May 1925, a Junkers F.13 entered service as the first aircraft in Mongolian civil and military-related aviation. In March 1931, the Soviet Union donated three Polikarpov R-1s to the Mongolian People's Army, with Mongolia further purchasing three R-1s.[3] In 1932, an uprising broke out against Collectivization, which saw both Soviet and Mongolian-operated R-1s taking part in actions against the rebellion. The aircraft carried out reconnaissance, leaflet dropping, and bombing missions[4] Chinese intelligence reports that in 1945 the Mongolian People's Air Force had been with a three-fighter and three-bomber aviation-regiment, and one flight training school and greater air squadrons. It was reported that headquartered in the Mukden Manchukuo spy-section in October 1944 air force whole units had been 180 aircraft and 1231 airmen. The Mongolian People's Army Aviation demonstrated its full potential during the Battle of Khalkhin Gol, which was its largest engagement. Apart from intercepting intruding aircraft, People's Aviation was used heavily to repress domestic rebel movements.
The Mongolian People's Air Force has operated a variety of aircraft types.
Trainer
Soviet Union Po-1
Soviet Union Po-2
Soviet Union Yakovlev UT-2
Soviet Union Yak-11
Bomber and ground-attack aircraft
Soviet Union Polikarpov R-1-Unknown number
Soviet Union Polikarpov R-5-40
Soviet Union Ilyushin Il-2-70
Fighter aircraft
Soviet Union Lavochkin La-5- 12
Soviet Union Polikarpov I-15- 50
Soviet Union Polikarpov I-15bis- Unknown number
Soviet Union Polikarpov I-16- 1
Soviet Union Yak-7- Unknown number
Soviet Union Yak-9- 34
Transport aircraft
Soviet Union Lisunov Li-2
Soviet Union Putilov Stal-3
Soviet Union Kalinin K-5
Soviet Union Yakovlev Yak-6
Soviet Union Yakovlev AIR-6
Germany Junkers F-13
Germany Junkers W 33- 1
Japan Nakajima Ki-34-12
Mongolian People's Army capability (1950-1990)
| Equipment | Origin | Versions | Number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Battle Tank/Medium Tank | ||||
| SU-100 | Self-propelled gun | 10[5] | ||
| T-34/85 | Medium Tank | 40[5] | ||
| T-54 | 250[5] | |||
| T-55 | 250[5] | |||
| T-62 | Main Battle Tank | 100[5] | ||
| Infantry Fighting Vehicle/Armored Personnel Carrier | ||||
| BMP-1 | Infantry Fighting Vehicle | 400[5] | ||
| BTR-40 | Wheeled armoured personnel carrier | 200[5] | ||
| BTR-60 | 50[5] | |||
| BTR-152 | ||||
| BRDM-1 | Armored Personnel Carrier | 150[5] | ||
| BRDM-2 | Armored Personnel Carrier | 120[5] | ||
| Multiple rocket launcher | ||||
| BM-21 Grad | 122 mm Multiple rocket launcher | 130[5] | ||
| Towed artillery | ||||
| 85 mm divisional gun D-44 | 85 mm divisional gun | unknown number | ||
| 122 mm gun M1931/37 (A-19) | 122 mm towed gun | 20[5] | ||
| 152 mm howitzer M1943 (D-1) | 152 mm field gun | unknown number | ||
| 122 mm howitzer 2A18 (D-30) | 122 mm howitzer | 50[5] | ||
| 122 mm howitzer M1938 (M-30) | 100[5] | |||
| 130 mm towed field gun M1954 (M-46) | 130 mm towed field gun | unknown number | ||
| 152 mm howitzer-gun M1937 (ML-20) | 152 mm howitzer gun | |||
| Mortar | ||||
| BM-37 | 82 mm calibre mortar | unknown number | ||
| PM-43 | 120 mm calibre smoothbore mortar | |||
| M-160 | 160 mm Divisional mortar | |||
| Anti-tank gun | ||||
| SPG-9 | 73 mm anti-tank gun | unknown number | ||
| 85 mm antitank gun D-48 | 85 mm anti-tank gun | |||
| 100 mm field gun M1944 (BS-3) | 100 mm field gun | 25[5] | ||
| T-12 antitank gun | 100 mm anti-tank gun | 25[5] | ||
Mongolian People's Army Air Force (1950-1990)
| Name | Origin | Type | Versions | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fighter aircraft | |||||
| Polikarpov I-15 | Fighter | I-15 | 1+[6] | ||
| Polikarpov I-16 | I-16 | 1+[6] | |||
| Polikarpov Po-2 Mule | U-2a | 20[6] | |||
| Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 Fagot | MiG-15bis | 48[6] | |||
| Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17 Fresco | MiG-17F | 36[6] | |||
| Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 Fishbed | MiG-21PFM/MF | 30+12[5][6] | |||
| Bomber | |||||
| Polikarpov R-Z | Light Bomber | R-Z | unknown number[6] | ||
| Transport aircraft | |||||
| Boeing 727 | Narrow-body jet airliner | Boeing 727-200 | unknown number[6] | ||
| Tupolev Tu-104 Camel | Transport aircraft | Tu-104 | 2[5] | ||
| Tupolev Tu-154 Careless | Tu-154B-2 | unknown number[6] | |||
| Ilyushin Il-2 Bark | Il-2 | Could be up to 72 | |||
| Ilyushin Il-12 Coach | Il-12 | ||||
| Ilyushin Il-14 Crate | Il-14 | 6[5] | |||
| Antonov An-2 Colt | An-2 | 30[6] | |||
| Antonov An-12 Cub | An-12 | 15[6] | |||
| Antonov An-14 Clod | An-14 | 2[6] | |||
| Antonov An-24 Coke | An-24 | 22[6] | |||
| Antonov An-26 Curl | An-26 | 4[6] | |||
| Antonov An-32 Cline | An-32 | 1[6] | |||
| Harbin Y-12 | utility aircraft | Y-12 | 5[6] | ||
| PZL-104 Wilga | Wilga-2 | 3[6] | |||
| Training aircraft | |||||
| Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 Fagot | Transport aircraft | MiG-15UTI | 1[5] | ||
| Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17 Fresco | MiG-17PF | 8[5] | |||
| Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 Fishbed | MiG-21US | unknown number[5] | |||
| Yakovlev UT-2 Mink | UT-2 | 1+[6] | |||
| Yakovlev Yak-6 Frank | Yak-6 | unknown number[6] | |||
| Yakovlev Yak-9 Frank | Yak-9U | ||||
| Yakovlev Yak-11 Moose | Yak-11 | 10[5] | |||
| Yakovlev Yak-12 Creek | Yak-12 | unknown number[6] | |||
| Yakovlev Yak-18 Max | Yak-18 | 10[5] | |||
| Attack Helicopter | |||||
| Mil Mi-24 Hind | Attack helicopter | Mi-24D/V | 10[5] | Ground support/Anti tank | |
| Transport Helicopter | |||||
| Mil Mi-1 Hare | Light helicopter | Mi-1 | 5[5] | Transport | |
| Mil Mi-2 Hoplite | Mi-2 | 1[5] | |||
| Mil Mi-4 Hound | Mi-4A | 5[5] | |||
| Mil Mi-8 Hip | Mi-8T/MT | 10[5] | |||
| Kamov Ka-26 Hoodlum | Light utility | Ka-26 | unknown number[5] | ||
| SAM | |||||
| S-75 Dvina | Strategic SAM system | S-75 Dvina | 1[5] | 24 missiles[5] | |
| S-200 Angara/Vega/Dubna | S-200 | unknown number[7] | |||
| 9K31 Strela-1 | Vehicle-mounted SAM system | 9K31 Strela-1 | |||
| Strela-2 | Man portable SAM launcher | Strela-2 | 1250[5] | ||
| Air Defence Artillery | |||||
| ZPU-4 | Anti-aircraft machine gun | ZPU-4 | unknown number | ||
| ZU-23-2 | Anti-Aircraft Twin Autocannon | ZU-23-2 | |||
| ZSU-23-4 "Shilka" | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | ZSU-23-4 | |||
| S-60 | Autocannon | 57 mm S-60 | |||
| 61-K | Air defense gun | 37 mm M1939 | |||