Meñli I Giray

Meñli I Giray

| Meñli I | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khan of Crimea | |||||
| Reign | 1468 – 1475 1478 – 1515 | ||||
| Predecessor | Nur Devlet | ||||
| Successor | Mehmed I | ||||
| Born | 1445 | ||||
| Died | 17 April 1515 | ||||
| Burial | Bakhchisaray | ||||
| Spouse | Nur Sultan Khatun Zayan Sultan Khatun Makhdum Sultan Khatun | ||||
| Issue |
| ||||
| |||||
| House | Giray | ||||
| Father | Hacı I Giray | ||||
| Full name | |||||
| Meñli Giray | |||||
Meñli I Giray (Crimean Tatar: I Meñli Geray, ۱منكلى كراى) (1445–1515), also spelled as Mengli I Giray, was a khan of the Crimean Khanate (1466, 1469–1475, 1478–1515) and the sixth son of Hacı I Giray.[1]
| Meñli I | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khan of Crimea | |||||
| Reign | 1468 – 1475 1478 – 1515 | ||||
| Predecessor | Nur Devlet | ||||
| Successor | Mehmed I | ||||
| Born | 1445 | ||||
| Died | 17 April 1515 | ||||
| Burial | Bakhchisaray | ||||
| Spouse | Nur Sultan Khatun Zayan Sultan Khatun Makhdum Sultan Khatun | ||||
| Issue |
| ||||
| |||||
| House | Giray | ||||
| Father | Hacı I Giray | ||||
| Full name | |||||
| Meñli Giray | |||||
Biography
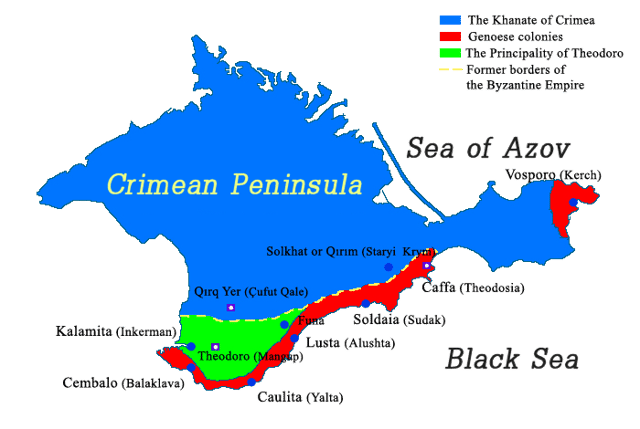
Crimea at the time of Mengli Girai
Struggle for power (1466-78): [2] It took Mengli twelve years to establish himself as khan. When Haji Girai died power went to his eldest son Nur Devlet. Mengli revolted. He was supported by the Crimean nobility while Nur Devlet was supported by the Great Horde. In 1467 Mengli occupied the capital of Kyrk-Er (Chufut-Kale) but was soon driven out by Nur Devlet and fled to the Genoese at Kaffa. In June 1468 a delegation of nobles elected him khan at Kaffa. He, the nobles and a Genoese detachment marched on the capital. After six months Nur Devlet was expelled and fled to the North Caucasus, but was captured and imprisoned in the Genoese fortress at Sudak.
During his second reign (1469-75) he made an anti-Turkish alliance with Principality of Theodoro. In the summer of 1469 a Turkish fleet burned some villages near Kaffa. From late 1473 Eminek made himself head of the Shirin clan which held the eastern peninsula of Crimea. He became the second most powerful man in the country and was often hostile to Mengli.
In March 1475 the nobles replaced Mengli with his elder brother Hayder of Crimea. Mengli fled to Kaffa. In May 1475 a large Turkish fleet arrived at Kaffa seeking to subordinate the Genoese. They took Kaffa and other Genoese forts and the Principality of Theodoro. Mengli, who had supported the Genoese, was captured and taken to Istanbul. Nur Devlet was released from prison and restored as a Turkish vassal. Nur Devlet’s third reign (1475-78) was unsuccessful. In the winter of 1477/78 Crimea was briefly conquered by Janibeg, a nephew of Akhmed Khan of the Great Horde. Eminek wrote to the sultan asking that Mengli be restored. In the spring of 1478 Mengli was released and arrived at Crimea with a Turkish fleet and Turkish soldiers. He was joined by Eminek’s troops, Nur Devlet was driven out and Mengli became khan as a Turkish vassal.
Third reign (1478-1515): He made a great contribution to the development of Crimean Tatar statehood. He founded the fortress of Özü.[3]
In 1480, Meñli entered into a treaty of alliance with Ivan III, Grand Duke of Muscovy. The alliance was directed against Poland-Lithuania, the Great Horde and the Khanate of Astrakhan. This was an important factor in the Great stand on the Ugra river which led to Russian independence from the Great Horde.
In 1502, Meñli defeated the last khan of the Golden Horde and took control over its capital, Saray. He proclaimed himself Khagan (Emperor), claiming legitimacy as the successor of the Golden Horde's authority over the Tatar khaganates in the Caspian-Volga region.
Meñli was buried in the Dürbe (or türbe) of Salaçıq in Bakhchysarai. In that city, he commissioned Zıncırlı Medrese (medrese with chains) in Salaçıq (1500), Dürbe in Salaçıq (1501), and "Demir Qapı" (Iron Gate) portal in the Bakhchisaray Palace (by Aloisio the New) (1503).
Meñli often depended on troops from the Crimea's numerous Italian trading cities, and Genoese mercenaries formed a significant part of his army.
For his raids on Lithuania see Crimean-Nogai Raids for years 1480-1511.
Family
Meñli was a father of Mehmed I Giray and Sahib I Giray.[4]
Meñli's wives were:
Zayan (Shayan) Sultan Khatun, daughter of Prince Yadigar, bey of the Sedjeuts;
Makhdum Sultan Khatun, daughter of King Inarmaz Mirza, King of Circassia;
Nur Sultan Khatun, daughter of Prince Timur ibn Mansur, bey of the Manghits.