Manatee County Sheriff's Office

Manatee County Sheriff's Office

Manatee County | |
|---|---|
County | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Florida | |
 Florida's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | January 9, 1855 |
| Named for | Florida manatee |
| Seat | Bradenton |
| Largest city | Bradenton |
| Area | |
| • Total | 893 sq mi (2,310 km2) |
| • Land | 743 sq mi (1,920 km2) |
| • Water | 150 sq mi (400 km2) 16.8% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2017) | 385,571[4] |
| • Density | 519/sq mi (200/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Area code | 941 |
| Congressional district | 16th |
| Website | www.mymanatee.org [63] |
| Country | USA |
| Type | Public |
| Established | 1964 |
| Location | 1301 Barcarrota Blvd West Bradenton, Florida 14203 |
| Coordinates | 27°29′55.2″N 82°34′29″W [64] |
| Branches | 6 |
| Collection | |
| Items collected | Books, Movies, Newspapers |
| Size | 30,000 |
| Access and use | |
| Population served | 322,000 |
| Members | 20,000 |
| Other information | |
| Budget | $25,000 |
| Staff | 120 |
| Website | www.mymanatee.org/library [65] |
Manatee County is a county in the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2010 US Census, the population was 322,833.[5] Manatee County is part of the North Port-Sarasota-Bradenton Metropolitan Statistical Area. Its county seat and largest city is Bradenton.[6] The county was created in 1855 and named for the Florida manatee[7], Florida's official marine mammal.
Manatee County | |
|---|---|
County | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Florida | |
 Florida's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | January 9, 1855 |
| Named for | Florida manatee |
| Seat | Bradenton |
| Largest city | Bradenton |
| Area | |
| • Total | 893 sq mi (2,310 km2) |
| • Land | 743 sq mi (1,920 km2) |
| • Water | 150 sq mi (400 km2) 16.8% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2017) | 385,571[4] |
| • Density | 519/sq mi (200/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Area code | 941 |
| Congressional district | 16th |
| Website | www.mymanatee.org [63] |
| Country | USA |
| Type | Public |
| Established | 1964 |
| Location | 1301 Barcarrota Blvd West Bradenton, Florida 14203 |
| Coordinates | 27°29′55.2″N 82°34′29″W [64] |
| Branches | 6 |
| Collection | |
| Items collected | Books, Movies, Newspapers |
| Size | 30,000 |
| Access and use | |
| Population served | 322,000 |
| Members | 20,000 |
| Other information | |
| Budget | $25,000 |
| Staff | 120 |
| Website | www.mymanatee.org/library [65] |
History
Prehistoric History
The area now known as Manatee County had been inhabited by Native Americans for thousands of years.
De Soto Expedition
The southern mouth of the Manatee River was likely the landing site of the De Soto Expedition and is the location of the U.S. National Park Service's De Soto National Memorial.
Settlement
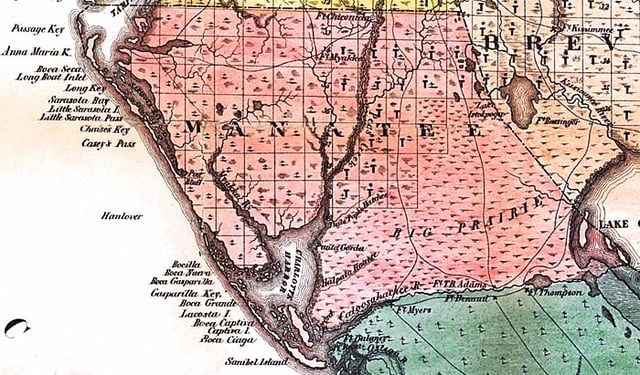
Map of Manatee County as it existed in 1856, one year after it was created.
The area was opened to settlement in 1842. The first two settlers were Joseph Braden and Hector Braden who moved into an area near the Manatee River, The two had lost their land for their plantations in Northern Florida during the Panic of 1837. They were said to have heard about that there was abundant land in the area. The brothers moved into a log cabin 5 miles north of the mouth of the Manatee River. Four years later Hector had drowned while trying to cross the Manatee River on his horse during a hurricane. Despite this tragic event, Joseph decided that he would still build his sugar plantation, the Braden sugar mill at the mouth of the Manatee River and the Braden River. He later built a dock where Main Street was at and fortified the area near his house building a stockade. A few years later in 1851, he would build the Braden Castle, which was made out of tabby and served as his residence. It would later become a popular tourist attraction in the early 1900s with Tin Can Tourists. He would only stay there for the next six years before moving to Tallahassee.[9]
Manatee County had the Gamble Plantation, a sugar plantation that was one of the South's finest.
When Manatee County was created in 1855, it included all of what are now Charlotte County, DeSoto County, Glades County, Hardee County, Highlands County, Sarasota County and part of Lee County[10]
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 893 square miles (2,310 km2), of which 743 square miles (1,920 km2) is land and 150 square miles (390 km2) (%) is water.[11]
Adjacent counties
Hillsborough County – north
Polk County – northeast
Hardee County – east
DeSoto County – southeast
Sarasota County – south
State & Nationally protected areas

A great egret in Myakka River State Park
De Soto National Memorial
Passage Key National Wildlife Refuge
Lake Manatee State Park
Terra Ceia Preserve State Park
Myakka River State Park
Madira Bickel Mound State Archaeological Site
Rivers
Manatee River Wares Creek Braden River Gamble Creek
Lakes
Ward Lake
Lake Parrish
Lake Manatee
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 854 | — | |
| 1870 | 1,931 | 126.1% | |
| 1880 | 3,544 | 83.5% | |
| 1890 | 2,895 | −18.3% | |
| 1900 | 4,663 | 61.1% | |
| 1910 | 9,550 | 104.8% | |
| 1920 | 18,712 | 95.9% | |
| 1930 | 22,502 | 20.3% | |
| 1940 | 26,098 | 16.0% | |
| 1950 | 34,704 | 33.0% | |
| 1960 | 69,168 | 99.3% | |
| 1970 | 97,115 | 40.4% | |
| 1980 | 148,442 | 52.9% | |
| 1990 | 211,707 | 42.6% | |
| 2000 | 264,002 | 24.7% | |
| 2010 | 322,833 | 22.3% | |
| Est. 2017 | 385,571 | [12] | 19.4% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[13] 1790-1960[14] 1900-1990[15] 1990-2000[16] 2010-2015[5] | |||
In 2017, the U.S. Census Bureau estimated that the county's population was 385,571. The racial makeup of the county was 86.2% White, 9.2% Black or African American, 0.5% Native American, 1.8% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, and 1.8% from two or more races. 16.1% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.[17]
As of the census[18] of 2000, there were 264,002 people, 112,460 households, and 73,773 families residing in the county. The population density was 356/sq mi (138/km2). There were 138,128 housing units at an average density of 186/sq mi (72/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 86.36% White, 8.19% Black or African American, 0.28% Native American, 0.90% Asian, 0.05% Pacific Islander, 2.84% from other races, and 1.39% from two or more races. 9.30% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
In 2000 there were 112,460 households out of which 23.00% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.70% were married couples living together, 9.40% had a female householder with no husband present, and 34.40% were non-families. 28.40% of all households were made up of individuals and 15.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.29 and the average family size was 2.78.
In the county, the population was spread out with 20.70% under the age of 18, 6.50% from 18 to 24, 24.60% from 25 to 44, 23.30% from 45 to 64, and 24.90% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 44 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.50 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.50 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $38,673, and the median income for a family was $46,576. Males had a median income of $31,607 versus $25,007 for females. The per capita income for the county was $22,388. About 7.10% of families and 10.10% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.30% of those under age 18 and 6.20% of those age 65 or over.
Economy
Bealls of Florida has its headquarters and was founded 1915 in unincorporated Manatee County.[19][20]
Tropicana was founded here in the 1950s. They were later bought by PepsiCo but continue to produce products there today.
Libraries
The Manatee County Public Library System offers a collection of adult, young adult, and children's materials, as well as a genealogy section and the Eaton Florida History Reading Room. Public computers for all to use are available at all library locations. The library's online resources include licensing to OverDrive, Inc., Hoopla (digital media service), and Freegal Music. The library also hosts an online digital collection featuring historic images and documents from Manatee County during the late nineteenth century to early 1980's.[1] [66] Additionally, Ask a Librarian, the on-line Florida librarian reference service is available through the Manatee County Public Library System.[21] The library system also offers E-Books, E-Audio, music, and movies through five databases located on their website .
The libraries also offer extensive programming that includes author luncheons, children's story-times, summer reading programs, job fairs, and book discussion groups. Special events held annually include Mana-con, a comic book convention, and the Teen Recycled Fashion Show.
Manatee County participates in the Little Free Library program. The Palmetto Branch will place their Little Free Library in 2015, and then all six Manatee County Libraries will have them. Several Manatee County Parks have Little Free Libraries including Emerson Point Preserve, Robinson Preserve, Greenbrook Park, Bennett Park, Jigg's Landing and Conservatory Park.[22][23]
The library system serves the residents of Manatee County with six locations:
Central - Bradenton
Palmetto - Palmetto
Braden River - Bradenton
Island - Holmes Beach
South Manatee - Bradenton
Rocky Bluff - Ellenton
Talking Book Library is administered through the Bureau of Braille and Talking Books Library, Daytona [2] [67]
History of libraries
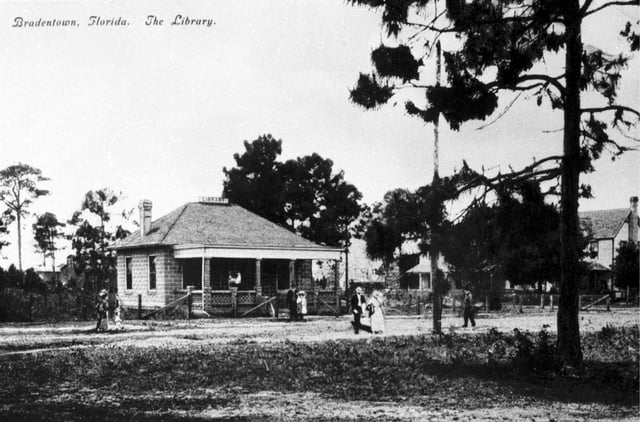

Original Bradentown Library

Palmetto's Carnegie Library, built in 1914.

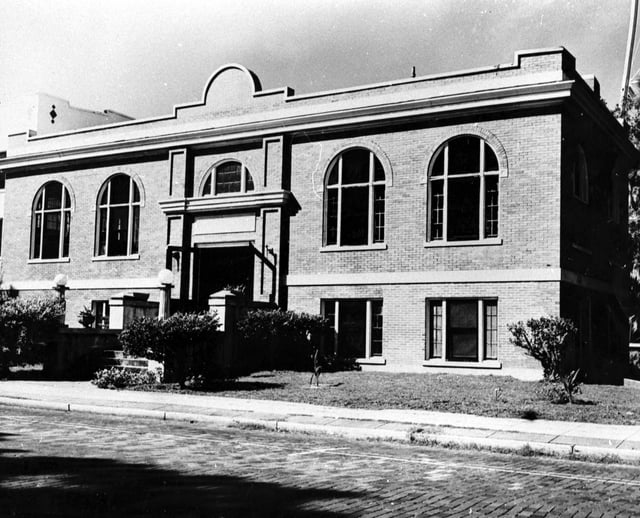
Bradenton's Carnegie Library, built in 1918.
Public libraries in Manatee County began in the year 1898 with a privately owned rental library created by Mrs. Julia Fuller in the Mrs. Bass Dry Goods store. The first independent library building in the county was opened in Bradenton in 1907, followed by Palmetto building a Carnegie Library in 1914 and Bradenton doing the same in 1918. For much of the 20th century, libraries in both cities were free to city residents while county residents had to pay a non-resident fee. In 1964, the city library associations in Bradenton and Palmetto merged with the Manatee County government to create what is now known as the Manatee County Public Library System. This was followed by the establishment of a bookmobile for rural areas in late 1964 and a Talking Books program for the blind in 1966.
As demands on the bookmobile grew and the library collection outstripped the existing buildings in Bradenton and Palmetto, the first branch of the Manatee County Public Library system was built in Bayshore in 1967, followed by a new branch on East Ninth Street in 1969 and an Island branch in 1971, the last of which later moved into a new building in 1983. A new building for the Palmetto Library was built in 1969, eventually followed by the modern Central Public Library in downtown Bradenton in 1978.
The 1990s saw a period of rapid growth for Manatee County, and the library system grew to accommodate, with the Braden River, Rocky Bluff, and South Manatee branches opening in 1991, 1994, and 1998, respectively, and the Braden River branch subsequently moved to a new building in 1997, bringing the Manatee County Library System to its modern state.
Awards and Recognition
2016 Library of the Year- Florida Library Association in recognition of the Manatee County Public Library System for the outstanding service it provides to the community[26]
2016 Betty Davis Miller Youth Services Award- Florida Library Association in recognition of Teen Recycled Fashion Show[27]
2016 Lifetime Achievement Award- Florida Library Association in recognition of Kevin Beach, for a long-standing, distinguished record of professional achievements and accomplishments.[28]
2016 Outstanding Friends Member- Florida Library Association in recognition of the outstanding service of Doris Pope, president of the Friends of the Rocky Bluff Library[29]
2015 Keep Manatee Beautiful Recycling Award- Government Category in recognition of the Recycled Dreams Teen Fashion Show of Recycled Materials[30]
2014 Libraries Change People's Lives Award- Florida Library Association in recognition of expanded Hispanic Services [31]
2013 Library Innovation Award- Florida Library Association in recognition of expanded services, programs, and activities focusing on community needs[32]
2013 Betty Davis Miller Youth Services Award- Florida Library Association in recognition of Mana-Con Comics Convention[33]
Education
Primary and secondary education
Manatee County School District – Public K-12 School district serving all of Manatee County
Higher education
Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine (LECOM) Bradenton – Private, non-profit graduate school of medicine, dentistry, and pharmacy
State College of Florida, Manatee–Sarasota (SCF) – Public, four-year state college, branch campus of State College of Florida
Communities
Cities
Anna Maria
Bradenton
Bradenton Beach
Holmes Beach
Palmetto
Town
Longboat Key
Census-designated places
Bayshore Gardens
Cortez
Ellenton
Memphis
Samoset
South Bradenton
West Bradenton
West Samoset
Whitfield
Unincorporated places
Duette
Village of the Arts
Myakka City
Oneco
Parrish
Terra Ceia
Rubonia
Gillette
Palm View
Memphis Heights
Palma Sola
Manavista
Fort Hamer
Manhattan
Oak Knoll
Waterbury
Verna
Marsh Island
Snead Island
Rattlesnake Key
Rye
Elwood Park
Ward Lake
Cedar Hammock
Willow
Foxleigh
Lake Manatee
Tara
Lakewood Ranch
Transportation
Manatee County has a county transportation service, MCAT. It serves this county, Pinellas County, and Sarasota County.[34]
Airports
Sarasota–Bradenton International Airport
Major Roads
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/93/I-75.svg/25px-I-75.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/93/I-75.svg/38px-I-75.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/93/I-75.svg/50px-I-75.svg.png 2x|I-75.svg|h25|w25]] I-75
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/54/I-275.svg/30px-I-275.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/54/I-275.svg/45px-I-275.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/54/I-275.svg/60px-I-275.svg.png 2x|I-275.svg|h24|w30]] I-275
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9a/US_19.svg/25px-US_19.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9a/US_19.svg/38px-US_19.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9a/US_19.svg/50px-US_19.svg.png 2x|US 19.svg|h25|w25]] U.S. Route 19
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/US_41.svg/25px-US_41.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/US_41.svg/38px-US_41.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/US_41.svg/50px-US_41.svg.png 2x|US 41.svg|h25|w25]] U.S. Route 41
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/US_301.svg/30px-US_301.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/US_301.svg/45px-US_301.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/US_301.svg/60px-US_301.svg.png 2x|US 301.svg|h24|w30]] U.S. Route 301
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5f/Florida_64.svg/25px-Florida_64.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5f/Florida_64.svg/38px-Florida_64.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5f/Florida_64.svg/50px-Florida_64.svg.png 2x|Florida 64.svg|h25|w25]] State Road 64
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ab/Florida_70.svg/25px-Florida_70.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ab/Florida_70.svg/38px-Florida_70.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/ab/Florida_70.svg/50px-Florida_70.svg.png 2x|Florida 70.svg|h25|w25]] State Road 70
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/08/Florida_684.svg/30px-Florida_684.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/08/Florida_684.svg/45px-Florida_684.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/08/Florida_684.svg/60px-Florida_684.svg.png 2x|Florida 684.svg|h24|w30]] State Road 684 (Cortez Road)
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bd/CR_610_jct.svg/25px-CR_610_jct.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bd/CR_610_jct.svg/38px-CR_610_jct.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bd/CR_610_jct.svg/50px-CR_610_jct.svg.png 2x|CR 610 jct.svg|h25|w25]] University Parkway
Waterways
Intracoastal Waterway
Manatee River
Ports
Port Manatee
Government
Political history
Manatee County is part of the strongly Republican Sun Belt. The area became a Republican stronghold following World War II and has remained so since: the last Democrat to win Manatee County was Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1944.[35]
Law enforcement and justice
Sheriff's Office
Unincorporated Manatee County is served by the Manatee County Sheriff's Office.[36]
Justice
Circuit Court
Manatee County is a part of the Twelfth Circuit Court of Florida.
Court of Appeals
Manatee County is part of the Second District of Appeals.
Recent presidential election results
| Year | GOP | DEM | Others |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 56.40% 101,944 | 39.40% 71,224 | 4.20% 7,589 |
| 2012 | 55.65% 85,627 | 43.22% 66,503 | 1.13% 1,736 |
| 2008 | 52.94% 80,721 | 45.93% 70,034 | 1.12% 1,712 |
| 2004 | 56.62% 81,318 | 42.66% 61,262 | 0.72% 1,041 |
| 2000 | 52.58% 58,023 | 44.61% 49,226 | 2.80% 3,095 |
| 1996 | 45.56% 44,136 | 43.24% 41,891 | 11.20% 10,851 |
| 1992 | 42.63% 42,725 | 33.77% 33,841 | 23.60% 23,654 |
| 1988 | 65.53% 51,187 | 34.08% 26,624 | 0.39% 302 |
| 1984 | 72.75% 55,793 | 27.24% 20,889 | 0.01% 6 |
| 1980 | 61.81% 40,535 | 33.06% 21,679 | 5.13% 3,362 |
| 1976 | 53.90% 29,300 | 44.78% 24,342 | 1.32% 718 |
| 1972 | 79.79% 32,664 | 19.68% 8,058 | 0.53% 218 |
| 1968 | 52.51% 18,247 | 23.85% 8,286 | 23.64% 8,214 |
| 1964 | 56.74% 17,147 | 43.26% 13,074 | |
| 1960 | 65.13% 16,462 | 34.87% 8,814 | |
| 1956 | 68.82% 11,904 | 31.18% 5,394 | |
| 1952 | 66.40% 9,055 | 33.60% 4,583 | |
| 1948 | 44.30% 3,371 | 36.35% 2,766 | 19.35% 1,473 |
| 1944 | 32.80% 2,218 | 67.20% 4,544 | |
| 1940 | 27.87% 1,983 | 72.13% 5,131 | |
| 1936 | 29.44% 1,455 | 70.56% 3,487 | |
| 1932 | 30.67% 1,280 | 69.33% 2,894 | |
| 1928 | 63.87% 2,705 | 34.76% 1,472 | 1.37% 58 |
| 1924 | 32.54% 629 | 55.04% 1,064 | 12.41% 240 |
| 1920 | 30.83% 884 | 62.43% 1,790 | 6.73% 193 |
| 1916 | 18.67% 289 | 66.73% 1,033 | 14.60% 226 |
| 1912 | 5.31% 55 | 68.73% 712 | 25.96% 269 |
| 1908 | 10.23% 93 | 70.85% 644 | 18.92% 172 |
| 1904 | 10.64% 91 | 69.24% 592 | 20.12% 172 |
Government officials
United States Senate
| Office | Senator | Party |
|---|---|---|
| Class 3 Senator | Marco Rubio | Republican |
| Class 1 Senator | Rick Scott | Republican |
United States House of Representatives
| District | Representative | Party |
|---|---|---|
| Florida's 16th Congressional District | Vern Buchanan | Republican |
Florida State Senate
| District | Senator | Party |
|---|---|---|
| 21 | Bill Galvano | Republican |
Florida House of Representatives
| District | Representative | Party |
|---|---|---|
| 70 | Wengay Newton | Democratic |
| 71 | Will Robinson | Republican |
| 73 | Tommy Gregory | Republican |
Manatee County Board of County Commissioners
The Manatee County Board of Commissioners include the following:
Public education
Other offices
Voter registration
Information as of January 12, 2019.[44]
| Voter registration and party enrollment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Number of voters | Percentage | |||
| Republican | 106,721 | 43.24% | |||
| Democratic | 74,909 | 30.35% | |||
| Others | 65,162 | 26.4% | |||
| Total | 246,792 | 100% | |||
See also
National Register of Historic Places listings in Manatee County, Florida

