MATLAB
MATLAB

| [[INLINE_IMAGE|https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/e/e1/MATLAB_R2013a_Win8_screenshot.png/320px-MATLAB_R2013a_Win8_screenshot.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/e/e1/MATLAB_R2013a_Win8_screenshot.png 1.5x|MATLAB R2013a Win8 screenshot.png|h181|w320]] MATLAB R2013a running on Windows 8 | |
| Developer(s) | MathWorks |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1984; 34 years ago(1984) |
| Stable release | R2018b / September 12, 2018; 2 months ago(2018-09-12) |
| Preview release | None [±] |
| Written in | C, C++, Java |
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, and Linux[9] |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64 |
| Type | Numerical computing |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | mathworks.com |
MATLAB (matrix laboratory) is a multi-paradigm numerical computing environment and proprietary programming language developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages, including C, C++, C#, Java, Fortran and Python.
Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numerical computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine, allowing access to symbolic computing abilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and model-based design for dynamic and embedded systems.
As of 2018, MATLAB has more than 3 million users worldwide.
[7] MATLAB users come from various backgrounds of engineering, science, and economics.
| [[INLINE_IMAGE|https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/e/e1/MATLAB_R2013a_Win8_screenshot.png/320px-MATLAB_R2013a_Win8_screenshot.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/e/e1/MATLAB_R2013a_Win8_screenshot.png 1.5x|MATLAB R2013a Win8 screenshot.png|h181|w320]] MATLAB R2013a running on Windows 8 | |
| Developer(s) | MathWorks |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 1984; 34 years ago(1984) |
| Stable release | R2018b / September 12, 2018; 2 months ago(2018-09-12) |
| Preview release | None [±] |
| Written in | C, C++, Java |
| Operating system | Windows, macOS, and Linux[9] |
| Platform | IA-32, x86-64 |
| Type | Numerical computing |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | mathworks.com |
History
Cleve Moler, the chairman of the computer science department at the University of New Mexico, started developing MATLAB in the late 1970s. [33] He designed it to give his students access to LINPACK and EISPACK without them having to learn Fortran. It soon spread to other universities and found a strong audience within the applied mathematics community. Jack Little, an engineer, was exposed to it during a visit Moler made to Stanford University in 1983. Recognizing its commercial potential, he joined with Moler and Steve Bangert. They rewrote MATLAB in C and founded MathWorks in 1984 to continue its development. These rewritten libraries were known as JACKPAC. [59] In 2000, MATLAB was rewritten to use a newer set of libraries for matrix manipulation, LAPACK. [94]
MATLAB was first adopted by researchers and practitioners in control engineering, Little's specialty, but quickly spread to many other domains. It is now also used in education, in particular the teaching of linear algebra, numerical analysis, and is popular amongst scientists involved in image processing. [33]
Syntax
The MATLAB application is built around the MATLAB scripting language.
Common usage of the MATLAB application involves using the Command Window as an interactive mathematical shell or executing text files containing MATLAB code. [94]
Variables
Variables are defined using the assignment operator, = .
MATLAB is a weakly typed programming language because types are implicitly converted. [94] It is an inferred typed language because variables can be assigned without declaring their type, except if they are to be treated as symbolic objects, [94] and that their type can change. Values can come from constants, from computation involving values of other variables, or from the output of a function. For example:
Vectors and matrices
A simple array is defined using the colon syntax: initial : increment : terminator.
For instance:
defines a variable named array (or assigns a new value to an existing variable with the name array ) which is an array consisting of the values 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9.
That is, the array starts at 1 (the initial value), increments with each step from the previous value by 2 (the increment value), and stops once it reaches (or to avoid exceeding) 9 (the terminator value).
the increment value can actually be left out of this syntax (along with one of the colons), to use a default value of 1.
assigns to the variable named ari an array with the values 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, since the default value of 1 is used as the incrementer.
Indexing is one-based, [94] which is the usual convention for matrices in mathematics, although not for some programming languages such as C, C++, and Java.
Matrices can be defined by separating the elements of a row with blank space or comma and using a semicolon to terminate each row.
The list of elements should be surrounded by square brackets: [].
Parentheses: () are used to access elements and subarrays (they are also used to denote a function argument list).
Sets of indices can be specified by expressions such as "2:4", which evaluates to [2, 3, 4].
For example, a submatrix taken from rows 2 through 4 and columns 3 through 4 can be written as:
A square identity matrix of size n can be generated using the function eye, and matrices of any size with zeros or ones can be generated with the functions zeros and ones, respectively.
Transposing a vector or a matrix is done either by the function transpose or by adding prime after a dot to the matrix. Without the dot MATLAB will perform conjugate transpose.
Most MATLAB functions can accept matrices and will apply themselves to each element.
For example, mod(2*J,n) will multiply every element in "J" by 2, and then reduce each element modulo "n".
MATLAB does include standard "for" and "while" loops, but (as in other similar applications such as R), using the vectorized notation often produces code that is faster to execute. This code, excerpted from the function magic.m, creates a magic square M for odd values of n (MATLAB function meshgrid is used here to generate square matrices I and J containing 1:n).
Structures
MATLAB has structure data types.
[94] Since all variables in MATLAB are arrays, a more adequate name is "structure array", where each element of the array has the same field names.
In addition, MATLAB supports dynamic field names [94] (field look-ups by name, field manipulations, etc.). Unfortunately, MATLAB JIT does not support MATLAB structures, therefore just a simple bundling of various variables into a structure will come at a cost.
Functions
When creating a MATLAB function, the name of the file should match the name of the first function in the file.
Valid function names begin with an alphabetic character, and can contain letters, numbers, or underscores.
Functions are often case sensitive.
Function handles
Classes and object-oriented programming
MATLAB supports object-oriented programming including classes, inheritance, virtual dispatch, packages, pass-by-value semantics, and pass-by-reference semantics. [9] However, the syntax and calling conventions are significantly different from other languages. MATLAB has value classes and reference classes, depending on whether the class has handle as a super-class (for reference classes) or not (for value classes). [9]
Method call behavior is different between value and reference classes.
For example, a call to a method
can alter any member of object only if object is an instance of a reference class.
An example of a simple class is provided below.
When put into a file named hello.m
, this can be executed with the following commands:
Graphics and graphical user interface programming
MATLAB supports developing applications with graphical user interface (GUI) features. MATLAB includes GUIDE [9] (GUI development environment) for graphically designing GUIs. [9] It also has tightly integrated graph-plotting features. For example, the function plot can be used to produce a graph from two vectors x and y. The code:
produces the following figure of the sine function :
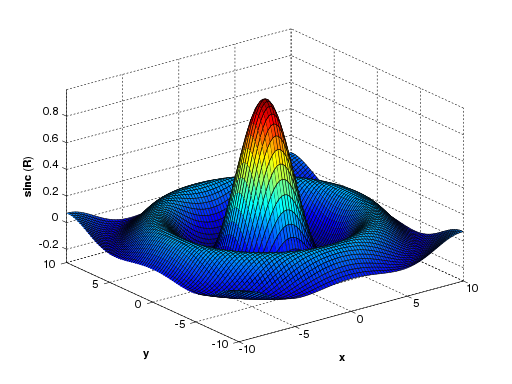
A MATLAB program can produce three-dimensional graphics using the functions surf, plot3 or mesh.
[X,Y]=meshgrid( | [X,Y]=meshgrid( | |
| This code produces a **wireframe ** 3D plot of the two-dimensional unnormalized sinc function : | This code produces a surface 3D plot of the two-dimensional unnormalized sinc function : | |
 |  |
In MATLAB, graphical user interfaces can be programmed with the GUI design environment (GUIDE) tool.
Interfacing with other languages
MATLAB can call functions and subroutines written in the programming languages C or Fortran. [9] A wrapper function is created allowing MATLAB data types to be passed and returned. MEX files (MATLAB executables) are the dynamically loadable object files created by compiling such functions. [9] [9] Since 2014 increasing two-way interfacing with Python was being added. [9] [25]
Libraries written in Perl, Java, ActiveX or .NET can be directly called from MATLAB, [25] [25] and many MATLAB libraries (for example XML or SQL support) are implemented as wrappers around Java or ActiveX libraries. Calling MATLAB from Java is more complicated, but can be done with a MATLAB toolbox [25] which is sold separately by MathWorks, or using an undocumented mechanism called JMI (Java-to-MATLAB Interface), [25] [25] (which should not be confused with the unrelated Java Metadata Interface that is also called JMI). Official MATLAB API for Java was added in 2016. [43]
Libraries also exist to import and export MathML. [25]
License
MATLAB is a proprietary product of MathWorks, so users are subject to vendor lock-in. [4] [24] Although MATLAB Builder products can deploy MATLAB functions as library files which can be used with .NET [42] or Java [98] application building environment, future development will still be tied to the MATLAB language.
Each toolbox is purchased separately.
If an evaluation license is requested, the MathWorks sales department requires detailed information about the project for which MATLAB is to be evaluated.
If granted (which it often is), the evaluation license is valid for two to four weeks.
A student version of MATLAB is available as is a home-use license for MATLAB, Simulink, and a subset of Mathwork's Toolboxes at substantially reduced prices.
Alternatives
MATLAB has a number of competitors.
[1] Commercial competitors include Mathematica, TK Solver, Maple, and IDL. There are also free open source alternatives to MATLAB, in particular GNU Octave, Scilab, FreeMat, and SageMath, which are intended to be mostly compatible with the MATLAB language; the Julia programming language also initially used MATLAB-like syntax. Among other languages that treat arrays as basic entities (array programming languages) are APL, Fortran 90 and higher, S-Lang, as well as the statistical languages R and S. There are also libraries to add similar functionality to existing languages, such as IT++ for C++, Perl Data Language for Perl, ILNumerics for .NET, NumPy / SciPy / matplotlib for Python, SciLua/ Torch for Lua, SciRuby for Ruby, and Numeric.js for JavaScript.
GNU Octave is unique from other alternatives because it treats incompatibility with MATLAB as a bug (see MATLAB Compatibility of GNU Octave), therefore, making GNU Octave a superset of the MATLAB language.
Release history
| Version[21] | Release name | Number | Bundled JVM | Year | Release date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MATLAB 1.0 | 1984 | |||||
| MATLAB 2 | 1986 | |||||
| MATLAB 3 | 1987 | |||||
| MATLAB 3.5 | 1990 | Ran on DOS but needed at least a 386 processor; version 3.5m needed math coprocessor | ||||
| MATLAB 4 | 1992 | Ran on Windows 3.1x and Macintosh | ||||
| MATLAB 4.2c | 1994 | Ran on Windows 3.1x, needed a math coprocessor | ||||
| MATLAB 5.0 | Volume 8 | 1996 | December 1996 | Unified releases across all platforms | ||
| MATLAB 5.1 | Volume 9 | 1997 | May 1997 | |||
| MATLAB 5.1.1 | R9.1 | |||||
| MATLAB 5.2 | R10 | 1998 | March 1998 | Last version working on classic Macs | ||
| MATLAB 5.2.1 | R10.1 | |||||
| MATLAB 5.3 | R11 | 1999 | January 1999 | |||
| MATLAB 5.3.1 | R11.1 | November 1999 | ||||
| MATLAB 6.0 | R12 | 12 | 1.1.8 | 2000 | November 2000 | First release with bundled Java virtual machine (JVM) |
| MATLAB 6.1 | R12.1 | 1.3.0 | 2001 | June 2001 | ||
| MATLAB 6.5 | R13 | 13 | 1.3.1 | 2002 | July 2002 | |
| MATLAB 6.5.1 | R13SP1 | 2003 | ||||
| MATLAB 6.5.2 | R13SP2 | Last release for IBM/AIX, Alpha/TRU64, and SGI/IRIX[41] | ||||
| MATLAB 7 | R14 | 14 | 1.4.2 | 2004 | June 2004 | Introduced anonymous and nested functions[60] Re-introduced for Mac (under Mac OS X) |
| MATLAB 7.0.1 | R14SP1 | October 2004 | ||||
| MATLAB 7.0.4 | R14SP2 | 1.5.0 | 2005 | March 7, 2005 | Support for memory-mapped files[76] | |
| MATLAB 7.1 | R14SP3 | 1.5.0 | September 1, 2005 | |||
| MATLAB 7.2 | R2006a | 15 | 1.5.0 | 2006 | March 1, 2006 | |
| MATLAB 7.3 | R2006b | 16 | 1.5.0 | September 1, 2006 | HDF5-based MAT-file support | |
| MATLAB 7.4 | R2007a | 17 | 1.5.0_07 | 2007 | March 1, 2007 | Newbsxfunfunction to apply element-by-element binary operation with singleton expansion enabled[92] |
| MATLAB 7.5 | R2007b | 18 | 1.6.0 | September 1, 2007 | Last release for Windows 2000 and PowerPC Mac; License Server support for Windows Vista;[6]new internal format for P-code | |
| MATLAB 7.6 | R2008a | 19 | 1.6.0 | 2008 | March 1, 2008 | Major enhancements to object-oriented programming abilities with a new class definition syntax,[31]and ability to manage namespaces with packages[50] |
| MATLAB 7.7 | R2008b | 20 | 1.6.0_04 | October 9, 2008 | New Map data structure:[66]upgrades to random number generators[87] | |
| MATLAB 7.8 | R2009a | 21 | 1.6.0_04 | 2009 | March 6, 2009 | First release for Microsoft 32-bit & 64-bit Windows 7, new external interface to.NET Framework[104] |
| MATLAB 7.9 | R2009b | 22 | 1.6.0_12 | September 4, 2009 | First release for Intel 64-bit Mac, and last for Solaris SPARC; new use for the tilde operator (~) to ignore arguments in function calls[12][27] | |
| MATLAB 7.9.1 | R2009bSP1 | 1.6.0_12 | 2010 | April 1, 2010 | bug fixes. | |
| MATLAB 7.10 | R2010a | 23 | 1.6.0_12 | March 5, 2010 | Last release for Intel 32-bit Mac | |
| MATLAB 7.11 | R2010b | 24 | 1.6.0_17 | September 3, 2010 | Add support for enumerations[46] | |
| MATLAB 7.11.1 | R2010bSP1 | 1.6.0_17 | 2011 | March 17, 2011 | bug fixes and updates | |
| MATLAB 7.11.2 | R2010bSP2 | 1.6.0_17 | April 5, 2012[63] | bug fixes | ||
| MATLAB 7.12 | R2011a | 25 | 1.6.0_17 | April 8, 2011 | Newrngfunction to control random number generation[85][101][11] | |
| MATLAB 7.13 | R2011b | 26 | 1.6.0_17 | September 1, 2011 | Access-change parts of variables directly in MAT-files, without loading into memory;[39]increased maximum local workers with Parallel Computing Toolbox from 8 to 12[61] | |
| MATLAB 7.14 | R2012a | 27 | 1.6.0_17 | 2012 | March 1, 2012 | Last version with 32-bit Linux support.[82] |
| MATLAB 8 | R2012b | 28 | 1.6.0_17 | September 11, 2012 | First release with Toolstrip interface;[100]MATLAB Apps.[13]redesigned documentation system | |
| MATLAB 8.1 | R2013a | 29 | 1.6.0_17 | 2013 | March 7, 2013 | New unit testing framework[28] |
| MATLAB 8.2 | R2013b | 30 | 1.7.0_11 | September 6, 2013[44] | Built in Java Runtime Environment (JRE) updated to version 7;[62]New table data type[79] | |
| MATLAB 8.3 | R2014a | 31 | 1.7.0_11 | 2014 | March 7, 2014[91] | Simplified compiler setup for building MEX-files; USB Webcams support in core MATLAB; number of local workers no longer limited to 12 with Parallel Computing Toolbox |
| MATLAB 8.4 | R2014b | 32 | 1.7.0_11 | October 3, 2014 | New class-based graphics engine (a.k.a. HG2);[106]tabbing function in GUI;[18]improved user toolbox packaging and help files;[32]new objects for time-date manipulations;[49]Git-Subversion integration in IDE;[65]big data abilities with MapReduce (scalable to Hadoop);[81]newpypackage for using Python from inside MATLAB,[38]new engine interface to call MATLAB from Python;[17]several new and improved functions:webread(RESTful web services with JSON/XML support),tcpclient(socket-based connections),histcounts,histogram,animatedline, and others | |
| MATLAB 8.5 | R2015a | 33 | 1.7.0_60 | 2015 | March 5, 2015 | Last release supporting Windows XP and Windows Vista |
| MATLAB 8.5 | R2015aSP1 | 1.7.0_60 | October 14, 2015 | |||
| MATLAB 8.6 | R2015b | 34 | 1.7.0_60 | September 3, 2015 | New MATLAB execution engine (a.k.a. LXE);[2]graphanddigraphclasses to work with graphs and networks;[22]MinGW-w64 as supported compiler on Windows;[34]Last version with 32-bit support | |
| MATLAB 9.0 | R2016a | 35 | 1.7.0_60 | 2016 | March 3, 2016 | Live Scripts: interactive documents that combine text, code, and output (in the style of Literate programming);[51]App Designer: a new development environment for building apps (with new kind of UI figures, axes, and components);[64]pause execution of running programs using a Pause Button |
| MATLAB 9.1 | R2016b | 36 | 1.7.0_60 | September 15, 2016 | define local functions in scripts;[80]automatic expansion of dimensions (previously provided via explicit call tobsxfun);tallarrays for Big data;[93]newstringtype;[59]new functions to encode/decode JSON;[59]official MATLAB Engine API for Java[43] | |
| MATLAB 9.2 | R2017a | 37 | 1.7.0_60 | 2017 | March 9, 2017 | MATLAB Online: cloud-based MATLAB desktop accessed in a web browser;[59]double-quoted strings; newmemoizefunction for Memoization; expanded object properties validation;[59]mocking framework for unit testing;[59]MEX targets 64-bit by default; newheatmapfunction for creating heatmap charts[59] |
| MATLAB 9.3 | R2017b | 38 | 1.8.0_121 | September 21, 2017 | ||
| MATLAB 9.4 | R2018a | 39 | 1.8.0_144 | 2018 | March 15, 2018[59] | |
| MATLAB 9.5 | R2018b | 40 | 1.8.0_152 | September 12, 2018 |
The number (or release number) is the version reported by Concurrent License Manager program FLEXlm.
For a complete list of changes of both MATLAB and official toolboxes, consult the MATLAB release notes.
File extensions
MATLAB
- .mMATLAB code (function, script, or class).matMATLAB data (binary file for storing variables).mex* (.mexw32,.mexw64,.mexglx,.mexa64,.mexmaci64,...)MATLAB executable MEX-files[59](platform specific, e.g. ".mexmac" for the Mac, ".mexglx" for Linux, etc.[59]).pMATLAB content-obscured.m file (P-code[94]).mlxMATLAB live script[94][94].figMATLAB figures (created with GUIDE).mlappMATLAB apps (created with App Designer[94]).mlappinstallMATLAB packaged App Installer[94].mlpkginstallsupport package installer (add-on for third-party hardware)[94].mltx,.mltbxpackaged custom toolbox[94][94][94].prjproject file used by various solutions (packaged app/toolbox projects, MATLAB Compiler/Coder projects, Simulink projects).rptreport setup file created by MATLAB Report Generator[94]
Simulink
- .mdlSimulink Model.mdlpSimulink Protected Model.slxSimulink Model (SLX format).slxpSimulink Protected Model (SLX format)
Simscape
- .sscSimscape[94]Model
MuPAD
- .mnMuPAD Notebook.muMuPAD Code.xvc,.xvzMuPAD Graphics
Third-party
- .jktGPU Cache file generated by Jacket for MATLAB (AccelerEyes).mumMATLAB CAPE-OPEN Unit Operation Model File (AmsterCHEM)
Easter eggs
Several easter eggs exist in MATLAB. [94] These include hidden pictures, [94] and jokes. For example, typing in "spy" used to generate a picture of the spies from Spy vs Spy, but now displays an image of a dog. Typing in "why" randomly outputs a philosophical answer. Other commands include "penny", "toilet", "image", and "life". Not every Easter egg appears in every version of MATLAB.
See also
Comparison of numerical analysis software
List of numerical analysis software
Notes
. MathWorks. 2003 . Retrieved February 7, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
(PDF) . Computer History Museum . Retrieved December 6, 2016 . So APL, Speakeasy, LINPACK, EISPACK, and PL0 were the predecessors to MATLAB.
Bezanson, Jeff; Karpinski, Stefan; Shah, Viral; Edelman, Alan (February 14, 2012).. Julia Language . Retrieved December 1, 2016 .
Eaton, John W. (May 21, 2001). (PDF) . Texas-Wisconsin Modeling and Control Consortium . Retrieved December 1, 2016 .
. Scilab . Retrieved December 1, 2016 .
The MathWorks (April 2018). (PDF) .
Cleve Moler (December 2004). . Retrieved April 15, 2007 .
. Altius Directory . Retrieved December 17, 2010 .
Moler, Cleve (January 2000).. Cleve's Corner. MathWorks . Retrieved December 20, 2008 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MATLAB. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. Symbolic Math Toolbox. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
, Loren Shure, MATLAB Central, March 26, 2012: "function calls on structs, cells, and function handles will not benefit from JIT optimization of the function call and can be many times slower than function calls on purely numeric arguments"
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks.
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks.
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2014 .
. MathWorks. April 30, 2011 . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
Smith, S. T. (2006). MATLAB: Advanced GUI Development. Dog Ear Publishing. ISBN 978-1-59858-181-2.
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
Spielman, Dan (February 10, 2004).. Yale University, Computer Science Department . Retrieved May 20, 2008 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved June 13, 2015 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved June 13, 2015 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved November 7, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved June 7, 2010 .
Altman, Yair (April 14, 2010).. Undocumented Matlab . Retrieved June 7, 2010 .
Kaplan, Joshua. "matlabcontrol JMI".
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
Germundsson, Roger (September 30, 1998).. *Wolfram Research *. Wolfram Library Archive.
rsmenon; szhorvat (2013). . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
Weitzel, Michael (September 1, 2006).. MathWorks - File Exchange . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
Goering, Richard (October 4, 2004).. EE Times.
Stafford, Jan (May 21, 2003).. SearchOpenSource.com . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. Bloomberg news. March 1, 2012.
. Reuters. September 2, 2014.
Steinhaus, Stefan (February 24, 2008)..
Moler, Cleve (January 2006).. News & Notes Newsletter. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 6, 2015 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks. September 3, 2010 . Retrieved February 8, 2011 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved March 11, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
. Retrieved January 22, 2014 .
MathWorks Support Team (June 4, 2015).. Versions of MATLAB prior to R2012a are fully supported on 32-bit Linux. After R2012a, MATLAB is no longer supported on 32-bit Linux.
Shure, Loren (September 2012)..
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks. September 2013.
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 17, 2018 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved March 11, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved September 15, 2016 .
. mathworks.com . Retrieved August 20, 2017 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved April 10, 2017 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved April 10, 2017 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved April 10, 2017 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved April 10, 2017 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved April 5, 2018 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved January 25, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 21, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 21, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 21, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 6, 2016 .
. Lynda.com . Retrieved August 6, 2016 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved October 3, 2014 .
. MathWorks . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
. MathWorks - MATLAB Answers. February 25, 2011 . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .
Eddins, Steve (October 17, 2006). . Retrieved August 14, 2013 .