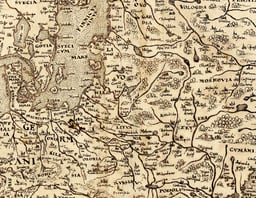
Livonia
Livonia
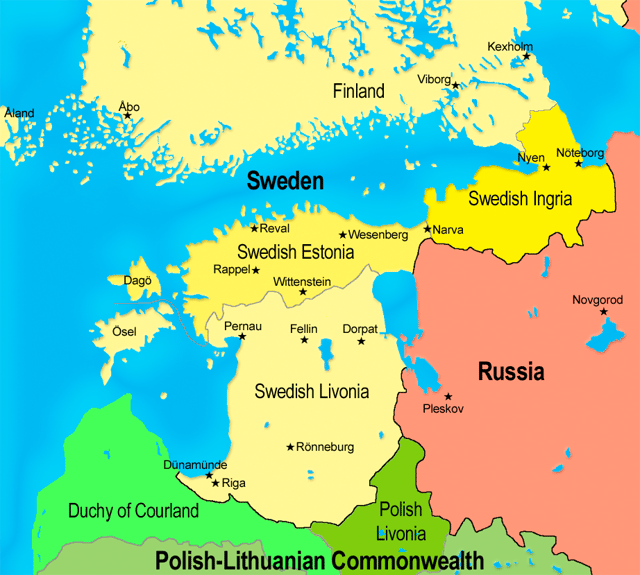
Swedish Livonia and Swedish Estonia in the 17th century
Livonia (Livonian: Līvõmō, Estonian: Liivimaa, German and Scandinavian languages: Livland, Latvian and Lithuanian: Livonija, Polish: Inflanty, archaic English Livland,[1] Liwlandia; Russian: Лифляндия, romanized: Liflyandiya) is a historical region on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the Livonians, who lived on the shores of present-day Latvia.
By the end of the 13th century the name was extended to most of present-day Estonia and Latvia that had been conquered during the Livonian Crusade (1193–1290) by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword. Medieval Livonia, or Terra Mariana, reached its greatest extent after Saint George's Night Uprising that in 1346 forced Denmark to sell the Duchy of Estonia (northern Estonia conquered by Denmark in the 13th century) to the State of the Teutonic Order. Livonia, as understood after the retreat of Denmark in 1346, bordered on the Gulf of Finland in the north, Lake Peipus and Russia to the east, and Lithuania to the south.
As a consequence of the Livonian War in the 16th century, the territory of Livonia was reduced to the southern half of Estonia and the northern half of Latvia.
The indigenous inhabitants of Livonia were various Finnic tribes in the north and Baltic tribes in the south. The descendants of the crusaders formed the nucleus of the new ruling class of Livonia after the Livonian Crusade, and eventually became known as Baltic Germans.
History
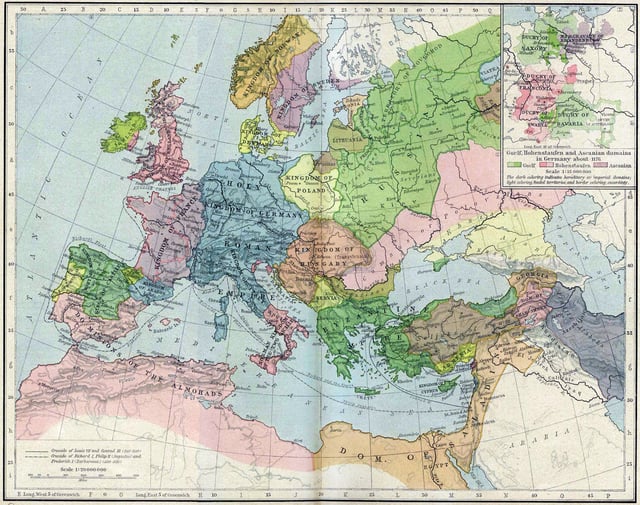
Livonia in Europe, 1190 AD
Beginning in the 12th century, Livonia was an area of economic and political expansion by Danes and Germans, particularly by the Hanseatic League and the Cistercian Order. Around 1160, Hanseatic traders from Lübeck established a trading post on the site of the future city of Riga, which Albrecht von Buxthoeven founded in 1201.[1] He ordered the construction of a cathedral and became the first Prince-Bishop of Livonia.
Livonian Brothers of the Sword 1204–1237
Bishop Albert of Riga (Albert of Buxhoeveden) founded the military order of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword (Latin: Fratres militiæ Christi Livoniae, German: Schwertbrüderorden) in 1202; Pope Innocent III sanctioned the establishment in 1204. The membership of the order comprised German "warrior monks". Alternative names of the order include the Christ Knights, Sword Brethren, and The Militia of Christ of Livonia. Following their defeat by Lithuania in the Battle of Saule in 1236, the surviving Brothers merged into the Teutonic Order as an autonomous branch and became known as the Livonian Order.
Albert, bishop of Riga (or Prince-Bishop of Livonia), founded the Brotherhood to aid the Bishopric of Riga in the conversion of the pagan Curonians, Livonians, Semigallians, and Latgalians living on the shores of the Gulf of Riga. From its foundation, the undisciplined Order tended to ignore its supposed vassalage to the bishops. In 1218, Albert asked King Valdemar II of Denmark for assistance, but Valdemar instead arranged a deal with the Brotherhood and conquered the north of Estonia for Denmark. The Brotherhood had its headquarters at Fellin (Viljandi) in present-day Estonia, where the walls of the Master's castle still stand. Other strongholds included Wenden (Cēsis), Segewold (Sigulda) and Ascheraden (Aizkraukle). The commanders of Fellin, Goldingen (Kuldīga), Marienburg (Alūksne), Reval (Tallinn), and the bailiff of Weißenstein (Paide) belonged to the five-member entourage of the Order's Master.
Pope Gregory IX asked the Brothers to defend Finland from the Novgorodian attacks in his letter of November 24, 1232;[2] however, no known information regarding the knights' possible activities in Finland has survived.
(Sweden eventually took over Finland after the Second Swedish Crusade in 1249.) In the Battle of Saule in 1236 the Lithuanians and Semigallians decimated the Order. This disaster led the surviving Brothers to become incorporated into the Order of Teutonic Knights in the following year, and from that point on they became known as the Livonian Order. They continued, however, to function in all respects (rule, clothing and policy) as an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order, headed by their own Master (himself de jure subject to the Teutonic Order's Grand Master).
Livonian Crusade 1206–1227
The Chronicle of Henry of Livonia from the 1220s gives a firsthand account of the Christianization of Livonia, granted as a fief by the Hohenstaufen Holy Roman Emperor, de facto but not known as the King of Germany, Philip of Swabia, to Bishop Albert of Buxthoeven, nephew of the Hartwig II, Archbishop of Bremen, who sailed with a convoy of ships filled with armed crusaders to carve out a Catholic territory in the east during the Livonian Crusade.
Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights 1237-1561
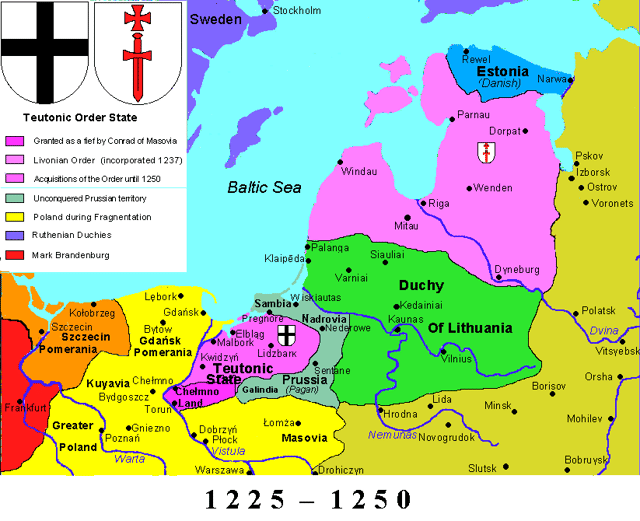
Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights.
Livonia consisted of the following subdivisions:
a state ruled by the Livonian Order founded by Albert in 1202, which was assimilated into the Teutonic Knights in 1237;
the Bishopric of Riga (an archbishopric since 1255);
the Bishoprics of Courland, Ösel-Wiek, and Dorpat, where Albert's brother Hermann established himself as the prince-bishop (Terra Mariana). The conquest of Livonia by the Germans is described in the Livonian Rhymed Chronicle.
Livonian Order 1237–1561

Medieval Livonia ca. 1260.
The Livonian Order was a largely autonomous branch of the Teutonic Knights (or Teutonic Order) and a member of the Livonian Confederation from 1418–1561. After being defeated by Lithuania in the 1236 Battle of Saule, the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword were incorporated into the Teutonic Knights as the Livonian Order in 1237. Between 1237 and 1290, the Livonian Order conquered all of Courland, Livonia, and Semigallia, but their attack on northern Russia was repelled in the Battle of Rakvere (1268). In 1346, after St. George's Night Uprising the Order bought the rest of Estonia from King Valdemar IV of Denmark. Life within the Order's territory is described in the Chronicle of Henry of Livonia and the Livonian Rhymed Chronicle. The Teutonic Order fell into decline following its defeat in the Battle of Grunwald in 1410 and the secularization of its Prussian territories by Albert of Brandenburg in 1525, but the Livonian Order managed to maintain an independent existence. During many years of Livonian War (1558–1582), however, they suffered a decisive defeat by troops of Muscovite Russia in the Battle of Ergeme in 1560 and continued living under great threat. Letters to the Emperor arrived from many European countries, warning, that Moscow has its eyes on much more than only a few harbors or the province of Liefland... the East Sea (Ostsee-Baltic Sea and the West Sea (Atlantic) are equally in danger. Duke Barnim the Elder, 50 years duke of Pomerania, warned, that never before did he experience the fear than now, where even in his land, where people send by Moscow are everywhere. At stake was the Narva-Trade-Route and practically all trade in the North, and with that all of Europe. Due to religious upheavals of the Reformation the empire could not send troops, which it could not afford and which were too far away anyway. Prussia was not able to help for much of the same reason, and Duke Albrecht was under continuous ban by the emperor. The Hanseatic League was greatly weakened by this and the city state of Luebeck fought its last great war. The emperor Maximilian II diffused the greatest threat by remaining on friendly terms with the czar, but not sending him troops as requested, in his struggles with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Czar Ivan of Moscow installed Duke Magnus as King of Livonia.
This was opposed by the other forces.
The Livonian Order saw no other way than to seek protection from Sigismund II Augustus, the King of Poland and the Grand Duke of Lithuania, who had intervened in a war between Bishop William of Riga and the Brothers in 1557. After coming to an agreement with Sigismund II Augustus and his representatives (especially Mikołaj "the Black" Radziwiłł), the last Livonian Master, Gotthard Kettler, secularized the Order and converted to Lutheranism. In the southern part of the Brothers' lands he created the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia for his family. Most of the remaining lands were seized by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The north of Estonia was taken back by Denmark and Sweden.
From the 14th to the 16th centuries, Middle Low German as spoken in the towns of the Hanseatic League was the established language, but was subsequently succeeded by High German as official language in the course of the 16th and 17th centuries.[3]
Livonian Confederation 1418–1561
The five Ecclesiastical states of the Holy Roman Empire in Medieval Livonia were organized into the Livonian Confederation in 1418.[4] A diet or Landtag was formed in 1419. The city of Walk was chosen as the site of the diet.
Livonian War 1558–1583
Europe, 1550.
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor once again asked for help of Gustav I of Sweden, and The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569) also began direct negotiations with Gustav, but nothing resulted because on September 29, 1560, Gustav I Vasa died. The chances for success of Magnus and his supporters looked particularly good in 1560 (and 1570). In the former case, he had been recognised as their sovereign by The Bishopric of Ösel-Wiek and The Bishopric of Courland, and as their prospective ruler by the authorities of The Bishopric of Dorpat; The Bishopric of Reval with the Harrien-Wierland gentry were on his side; Livonian Order conditionally recognised his right of ownership of Estonia (Principality of Estonia). Then along with Archbishop Wilhelm von Brandenburg of The Archbishopric of Riga and his Coadjutor Christoph von Mecklenburg, Kettler gave to Magnus the portions of The Kingdom of Livonia, which he had taken possession of, but they refused to give him any more land.
Once Eric XIV of Sweden became king he took quick actions to get involved in the war. He negotiated a continued peace with Muscovy and spoke to the burghers of Reval city. He offered them goods to submit to him as well as threatening them. By June 6, 1561 they submitted to him contrary to the persuasions of Kettler to the burghers. The King's brother Johan married the Polish princess Catherine Jagiellon. Wanting to obtain his own land in Livonia, he loaned Poland money and then claimed the castles they had pawned as his own instead of using them to pressure Poland. After Johan returned to Finland, Erik XIV forbade him to deal with any foreign countries without his consent.
Shortly after that Erik XIV started acting quickly lost any allies he was about to obtain, either from Magnus or the Archbishop of Riga. Magnus was upset he had been tricked out of his inheritance of Holstein. After Sweden occupied Reval, Frederick II of Denmark made a treaty with Erik XIV of Sweden in August 1561. The brothers were in great disagreement and Frederick II negotiated a treaty with Ivan IV on August 7, 1562 in order to help his brother obtain more land and stall further Swedish advance. Erik XIV did not like this and The Northern Seven Years' War between The Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II and Magnus were not faring well. But in 1568 Erik XIV became insane and his brother Johan III took his place.
Johan III ascended to the throne of Sweden and due to his friendship with Poland he began a policy against Muscovy. He would try to obtain more land in Livonia and exercise strength over Denmark. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Sigismund II Augustus of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, know that he was ready for peace. On December 15, 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded.
It is, however, more difficult to estimate the scope and magnitude of the support Magnus received in Livonian cities.
Compared to the Harrien-Wierland gentry, the Reval city council, and hence probably the majority of citizens, demonstrated a much more reserved attitude towards Denmark and King Magnus of Livonia.
Nevertheless, there is no reason to speak about any strong pro-Swedish sentiments among the residents of Reval.
The citizens who had fled to The Bishopric of Dorpat or had been deported to Muscovy hailed Magnus as their saviour until 1571.
The analysis indicates that during the Livonian War a pro-independence wing emerged among the Livonian gentry and townspeople, forming the so-called "Peace Party". Dismissing hostilities, these forces perceived an agreement with Muscovy as a chance to escape the atrocities of war and avoid the division of Livonia. That is why Magnus, who represented Denmark and later struck a deal with Ivan the Terrible, proved a suitable figurehead for this faction.
The Peace Party, however, had its own armed forces – scattered bands of household troops (Hofleute) under diverse command, which only united in action in 1565 (Battle of Pärnu, 1565 and Siege of Reval, 1565), in 1570–1571 (Siege of Reval, 1570-1571; 30 weeks), and in 1574–1576 (first on Sweden's side, then came the sale of Ösel–Wiek to the Danish Crown, and the loss of the territory to Tsardom of Russia). In 1575 after Muscovy attacked Danish claims in Livonia, Frederick II dropped out of the competition as well as the Holy Roman Emperor. After this Johan III held off on his pursuit for more land due to Muscovy obtaining lands that Sweden controlled. He used the next two years of truce to get in a better position. In 1578, he resumed the fight for not only Livonia, but also everywhere due to an understanding he made with Rzeczpospolita. In 1578 Magnus retired to Rzeczpospolita and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
Duchy of Livonia 1561–1621
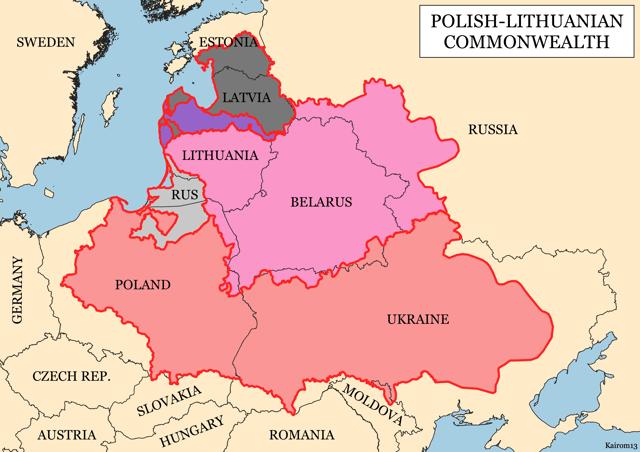
Outline of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth with its major subdivisions after the 1618 Truce of Deulino, superimposed on present-day national borders. Crown of the Kingdom of Poland Grand Duchy of Lithuania Duchy of Livonia Duchy of Prussia, Polish fief Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, Commonwealth fief
In 1561, during the Livonian War, Livonia fell to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania[5][6][7] with vassal dependency from Lithuania.[7] Eight years later, in 1569, when the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Kingdom of Poland formed Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Livonia became a joint domain administered directly by the king and grand duke.[5][7][8][9][10][11] Having rejected peace proposals from its enemies, Ivan the Terrible found himself in a difficult position by 1579, when Crimean Khanate devastated Muscovian territories and burnt down Moscow (see Russo-Crimean Wars), the drought and epidemics have fatally affected the economy, Oprichnina had thoroughly disrupted the government, while The Grand Principality of Lithuania had united with The Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569) and acquired an energetic leader, Stefan Batory, supported by Ottoman Empire (1576). Stefan Batory replied with a series of three offensives against Muscovy, trying to cut The Kingdom of Livonia from Muscovian territories. During his first offensive in 1579, with 22,000 men, he retook Polotsk; during the second, in 1580, with 29,000-strong army, he took Velikie Luki, and in 1581 with a 100,000-strong army he started the Siege of Pskov. Frederick II of Denmark and Norway had trouble continuing the fight against Muscovy unlike Sweden and Poland. He came to an agreement with John III in 1580 giving him the titles in Livonia. That war would last from 1577 to 1582. Muscovy recognized Polish–Lithuanian control of Ducatus Ultradunensis only in 1582. After Magnus von Lyffland died in 1583, Poland invaded his territories in The Duchy of Courland and Frederick II decided to sell his rights of inheritance. Except for the island of Œsel, Denmark was out of the Baltic by 1585. As of 1598 Inflanty Voivodeship was divided onto:
Wenden Voivodeship (województwo wendeńskie, Kieś)
Dorpat Voivodeship (województwo dorpackie, Dorpat)
Parnawa Voivodeship (województwo parnawskie, Parnawa)
Based on a guarantee by Sigismund II Augustus from the 1560s, the German language retained its official status.[3]
Kingdom of Livonia 1570–1578
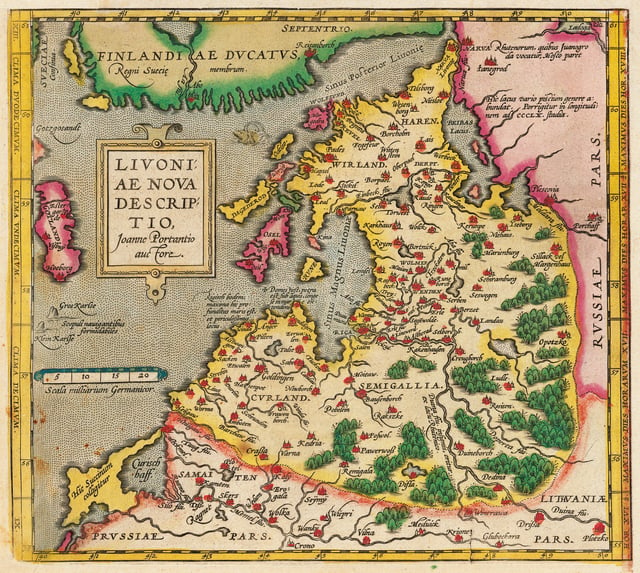
Livonia, as shown in the map of 1573 of Theatrum orbis terrarum.
The armies of Ivan the Terrible were initially successful, taking Polotsk (1563) and Parnawa (1575) and overrunning much of Grand Duchy of Lithuania up to Vilnius. Eventually, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Kingdom of Poland formed the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1569 under the Union of Lublin. Eric XIV of Sweden did not like this and the Northern Seven Years' War between the Free City of Lübeck, Denmark, Poland, and Sweden broke out. While only losing land and trade, Frederick II of Denmark and Magnus von Lyffland of the Œsel-Wiek did not fare well. But in 1569, Erik XIV became insane and his brother John III of Sweden took his place. After all parties had been financially drained, Frederick II let his ally, King Zygmunt II August, know that he was ready for peace. On December 15, 1570, the Treaty of Stettin was concluded.
In the next phase of the conflict, in 1577 Ivan IV took advantage of the Commonwealth's internal strife (called the war against Gdańsk in Polish historiography), and during the reign of Stefan Batory in Poland, invaded Livonia, quickly taking almost the entire territory, with the exception of Riga and Reval. In 1578, Magnus of Livonia recognized the sovereignty of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (not ratified by the Sejm of Poland-Lithuania, or recognized by Denmark). The Kingdom of Livonia was beaten back by Muscovy on all fronts. In 1578, Magnus of Livonia retired to The Bishopric of Courland and his brother all but gave up the land in Livonia.
Swedish Livonia 1629–1721

The Baltics in the 17th century
Sweden was given roughly the same area as the former Duchy of Livonia after the 1626–1629 Polish–Swedish War. The area, usually known as Swedish Livonia, became a very important Swedish dominion, with Riga being the second largest Swedish city and Livonia paying for one third of the Swedish war costs. Sweden lost Swedish Livonia, Swedish Estonia and Ingria to the Russian Empire almost 100 years later, by the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710 and the Treaty of Nystad in 1721.
Livonian Voivodeship 1620s–1772
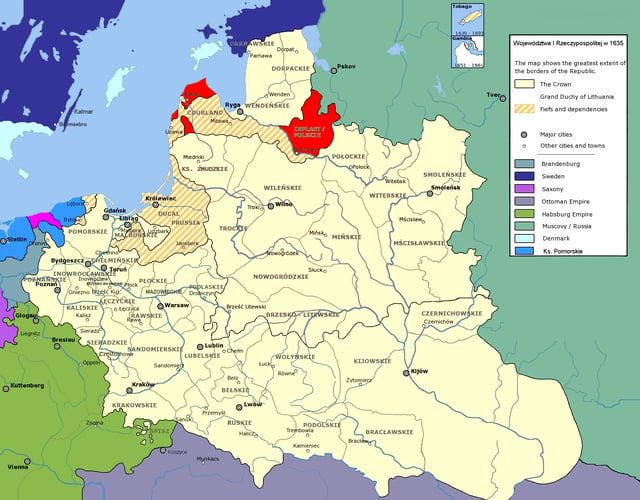
Inflanty Voivodeship, 1620s–1772.
The Livonian Voivodeship (Lithuanian: Livonijos vaivadija; Polish: Województwo inflanckie) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Duchy of Livonia, part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, since it was formed in the 1620s out of the Wenden Voivodeship till the First Partition of Poland in 1772.
Riga Governorate 1721–1796
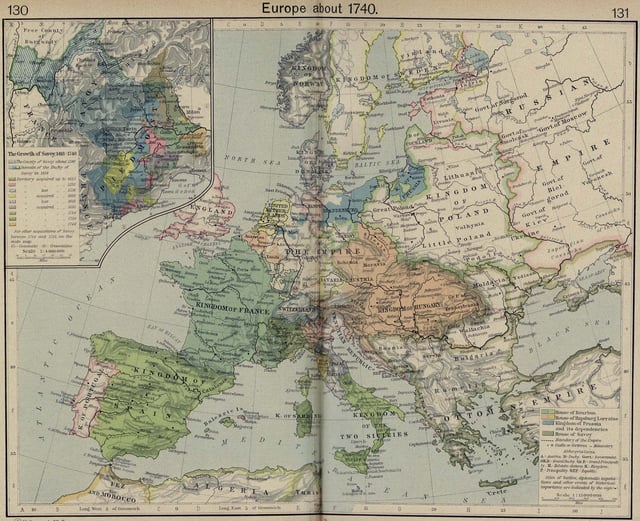
Europe, 1740.
The Russian Empire conquered Swedish Livonia during the course of the Great Northern War and acquired the province in the Capitulation of Estonia and Livonia in 1710, confirmed by the Treaty of Nystad in 1721. Peter the Great confirmed German as the exclusive official language.[3] Russia then added Polish Livonia in 1772 during the Partitions of Poland.
Governorate of Livonia 1796–1918
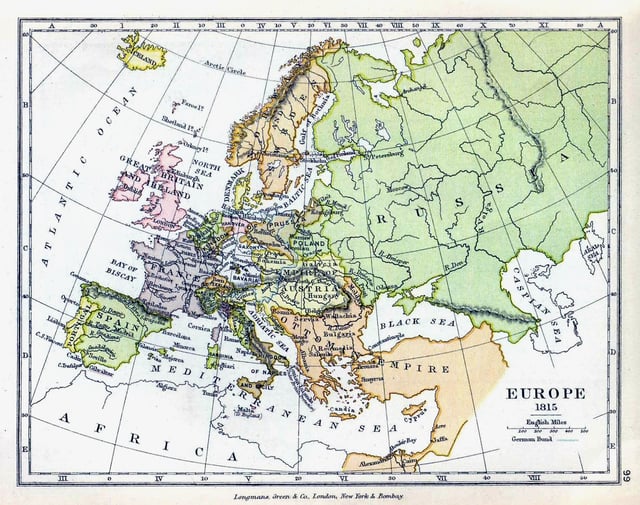
Europe, 1815.
In 1796 the Riga Governorate was renamed as the Governorate of Livonia (Russian: Лифляндская губе́рния / Liflyandskaya guberniya, Latvian: Vidzemes guberņa, Estonian: Liivimaa kubermang). Livonia remained within the Russian Empire until the end of World War I, when it was split between the newly independent states of Latvia and Estonia. In 1918–1920, both Soviet troops and German Freikorps fought against Latvian and Estonian troops for control over Livonia, but their attempts were defeated.
Governors-General of Estonia, Livonia, and Courland 1845–1876
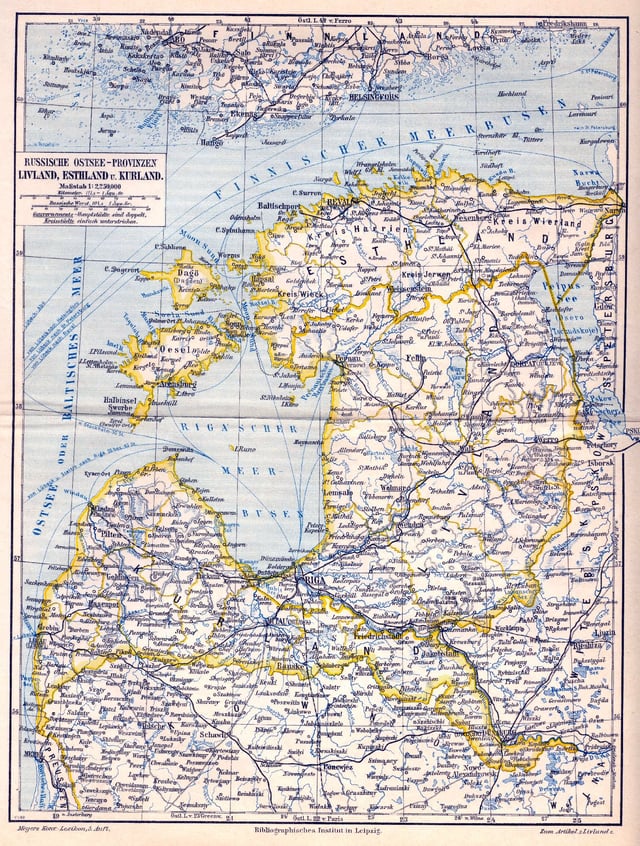
Livonia, 1898.
From 1845 to 1876, the Baltic governorates of Estonia, Livonia, and Courland—an area roughly corresponding to the historical medieval Livonia—were administratively subordinated to a common Governor-General. Amongst the holders of this post were Count Alexander Arkadyevich Suvorov[12] and Count Pyotr Andreyevich Shuvalov.
Vidzeme in Independent Latvia 1918–1940
Ostland 1941–1944
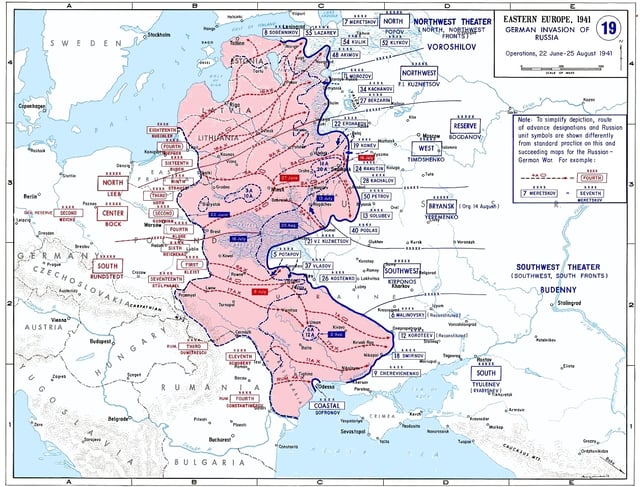
German advances from 22 June to 25 August 1941.
Ostland was one of the Reichskommissariats established, by a Decree of the Führer dated 17 July 1941, as administrative units of the "Großdeutsches Reich" (Greater Germany).
The structure of the Reichskommissariats was defined by the same decree.
Local administration in the Reichskommissariats was to be organized under a "National Director" (Reichskomissar) in Estonia, a "General Director" in Latvia and a "General Adviser" in Lithuania. The local administration of the Reichskommissariat Ostland was under Reichskomissar Hinrich Lohse. Below him there was an administrative hierarchy: a Generalkomissar led each Generalbezirke, Gebietskomissars and Hauptkommissars administered Kreigsbietes and Hauptgenbietes, respectively. Alfred Rosenberg's (Minister für die besetzten Ostgebiete (Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories) ministerial authority was, in practice, severely limited. The first reason was that many of the practicalities were commanded elsewhere: the Wehrmacht and the SS managed the military and security aspects, Fritz Saukel (Reich Director of Labour) had control over manpower and working areas, Hermann Göring and Albert Speer had total management of economic aspects in the territories and the Reich postal service administered the East territories' postal services. These German central government interventions in the affairs of Ostland, overriding the appropriate ministries was known as "Sonderverwaltungen" (special administration). Later, from September, the civil administration that had been decreed in the previous July was actually set up. Lohse and, for that matter, Koch would not bow to his authority seeking to administer their territories with the independence and authority of gauleiters. on 1 April 1942 an arbeitsbereich (lit. "working sphere", a name for the party cadre organisation outside the reich proper) was established in the civil administration part of the occupied Soviet territories, whereupon Koch and Lohse gradually ceased communication with him, preferring to deal directly with Hitler through Martin Bormann and the party chancellery. In the process they also displaced all other actors including notably the SS, except in central Belarus where HSSPF Erich von dem Bach-Zelewsky had a special command encompassing both military and civil administration territories and engaged in "anti-partisan" atrocities.
Baltic countries since 1990
The historical land of Livonia has been split between Latvia and Estonia ever since. The Livonian language is spoken by fewer than 100 individuals as a second language, and is understood to be fast approaching extinction. The last native Livonian speaker died in June 2013. The anthem (unofficial) of Livonians is Min izāmō, min sindimō sharing the melody of Finnish and Estonian anthems.
See also
|
|