Green Bay, Wisconsin
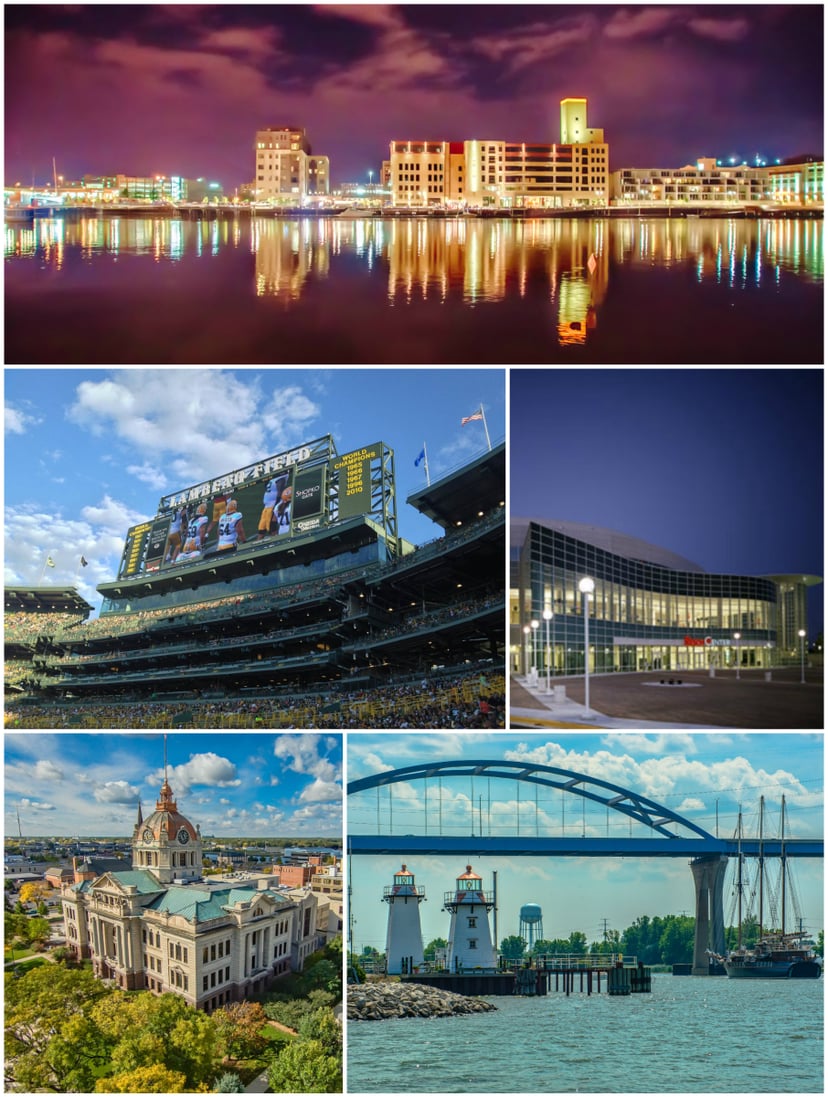

Green Bay, Wisconsin

Green Bay, Wisconsin | |
|---|---|
City | |
| Nicknames: "Titletown", "Bayland", "Bay City", "Packerland", and "Packer City" | |
 Location of Green Bay in Brown County, Wisconsin. | |
| Coordinates:44°30′48″N 88°0′57″W [81][2] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Wisconsin |
| County | Brown |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Eric Genrich |
| • Common Council[3] | Members
|
| Area | |
| • City | 55.76 sq mi (144.42 km2) |
| • Land | 45.48 sq mi (117.79 km2) |
| • Water | 10.28 sq mi (26.64 km2) |
| Elevation | 581 ft (177 m) |
| Population | |
| • City | 104,057 |
| • Estimate (2018)[6] | 104,879 |
| • Rank | US: 272nd |
| • Density | 2,311.41/sq mi (892.43/km2) |
| • Urban | 206,520 (US: 176th) |
| • Metro | 320,050 (US: 157th) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 54301-08, 54311, 54313, 54324, 54344 |
| Area code | 920 |
| FIPS code | 55-31000[7] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1565801[8] |
| Website | greenbaywi.gov [82] |
Green Bay is a city in and the county seat of Brown County in the U.S. state of Wisconsin,[9] at the head of Green Bay, a sub-basin of Lake Michigan, at the mouth of the Fox River. It is 581 feet (177 m) above sea level and 112 miles (180 km) north of Milwaukee. The population was 104,057 at the 2010 census.[7] Green Bay is the third-largest city in the state of Wisconsin, after Milwaukee and Madison, and the third-largest city on Lake Michigan's west shore, after Chicago and Milwaukee. Green Bay is home to the National Football League's Green Bay Packers.
Green Bay is the principal city of the Green Bay Metropolitan Statistical Area, which covers Brown, Kewaunee, and Oconto counties;[10] the MSA had a combined population of 306,241 at the 2010 census.[7]
Green Bay is an industrial city with several meatpacking plants, paper mills, and a port on Green Bay, an arm of Lake Michigan known locally as "the Bay of Green Bay". Green Bay hosts the Neville Public Museum, with exhibitions of art, history, and science; the Children's Museum; and the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay.
Green Bay, Wisconsin | |
|---|---|
City | |
| Nicknames: "Titletown", "Bayland", "Bay City", "Packerland", and "Packer City" | |
 Location of Green Bay in Brown County, Wisconsin. | |
| Coordinates:44°30′48″N 88°0′57″W [81][2] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Wisconsin |
| County | Brown |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Eric Genrich |
| • Common Council[3] | Members
|
| Area | |
| • City | 55.76 sq mi (144.42 km2) |
| • Land | 45.48 sq mi (117.79 km2) |
| • Water | 10.28 sq mi (26.64 km2) |
| Elevation | 581 ft (177 m) |
| Population | |
| • City | 104,057 |
| • Estimate (2018)[6] | 104,879 |
| • Rank | US: 272nd |
| • Density | 2,311.41/sq mi (892.43/km2) |
| • Urban | 206,520 (US: 176th) |
| • Metro | 320,050 (US: 157th) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 54301-08, 54311, 54313, 54324, 54344 |
| Area code | 920 |
| FIPS code | 55-31000[7] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1565801[8] |
| Website | greenbaywi.gov [82] |
History
Samuel de Champlain, the founder of New France, commissioned Jean Nicolet to form a peaceful alliance with Native Americans in the western areas, whose unrest interfered with French fur trade, and to search for a shorter trade route to China through Canada. Nicolet and others had learned from other First Nations of the Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) people, who identified as "People of the Sea", and believed they must reside on or near the Pacific Ocean.[11] Champlain had also heard about natural resources in the area, including fertile soil, forests, and animals. Nicolet began his journey for this new land shortly before winter in 1634.[12] In what later became a French fur-trading route, he sailed up the Ottawa River, through Lake Nipissing and down the French River to Lake Huron, then through the straits of Michilimackinac into Lake Michigan. He is believed to have landed at Red Banks, near the site of the modern-day city of Green Bay, Wisconsin.[13]
From the trading post La Baie des Puants to the town La Baie verte
When Nicolet arrived in the Green Bay area, he encountered the Menominee, as this was their territory. He also met the Ho-Chunk, also known as the Winnebago, a people who spoke a Sioux language. The Winnebago hunted, fished, and cultivated corn, bean, squash, and tobacco. Wild rice, which they had incorporated as a dietary staple, grew in abundance along the riverbanks. They regularly harvested and cooked this, along with a wide variety of nuts, berries, and edible roots of the woods.[16] The tribe had clearly distinguished gender roles. The men typically hunted and fished for food, and the women processed game and other foods in cooking. They prepared and made clothing from the furs as well as using other parts of animals for tools, cord, etc. Women also had a role in the political process, as no action could be taken without agreement of half of the women. Nicolet stayed with this tribe for about a year, becoming an ally. He helped open up opportunities for trade and commerce with them before returning to Quebec.[16]
A few months after Nicolet returned to Quebec, Champlain died. His death halted other journeys to La Baie Verte (French for "The Green Bay"). Père Claude Allouez sent Nicolas Perrot to La Baie. After this, the French avoided the area for some decades, because of the intensity of First Nations and European conflicts in the east. In 1671, a Jesuit Mission was set up in the area. A fort was added in 1717 and gradually associated development took place. The town was incorporated in 1754. As Great Britain took control of French areas during the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War in some areas of North America, this town came under British control in 1761. The French ceded their North American lands East of the Mississippi River to the British following defeat in 1763.
The first permanent French settlers were Charles de Langlade and his family from Canada, who moved to Green Bay in 1765, becoming the first European-American settlers in today's Wisconsin. Langlade, called the "Founder and Father of Wisconsin", was an Ottawa war chief with a French father. He is credited with planning the ambush of British General Braddock and George Washington in the French and Indian War. The Grignons, Porliers and Lawes, who followed, brought Canadian-French culture with them. Colorful "jack-knife Judge" Reaume dispensed British justice in the territory.[16] These early French settlers set the tone for many who followed.
The British take-over
Green Bay and Lake Winnebago on the 1835 Tourist's Pocket Map of Michigan among the "Mennomonie" villages of Wisconsin Territory
The British gradually took over Wisconsin during the French and Indian War, taking control of Green Bay in 1761 and gaining control of all of Wisconsin in 1763. Like the French, the British were interested in little but the fur trade. One notable event in the fur trading industry in Wisconsin occurred in 1791, when two free African Americans set up a fur trading post among the Menominee at present day Marinette. The first permanent settlers, mostly French Canadians, some Anglo-New Englanders and a few African American freedmen, arrived in Wisconsin while it was under British control. Charles Michel de Langlade is generally recognized as the first settler, establishing a trading post at Green Bay in 1745, and moving there permanently in 1764.[17] Settlement began at Prairie du Chien around 1781. The French residents at the trading post in what is now Green Bay, referred to the town as "La Bey", however British fur traders referred to it as "Green Bay", because the water and the shore assumed green tints in early spring. The old French title was gradually dropped, and the British name of "Green Bay" stuck. The region coming under British rule had virtually no adverse effect on the French residents as the British needed the cooperation of the French fur traders and the French fur traders needed the goodwill of the British. During the French occupation of the region licenses for fur trading had been issued scarcely and only to select groups of traders, whereas the British, in an effort to make as much money as possible from the region, issued licenses for fur trading freely, both to British and French residents. The fur trade in what is now Wisconsin reached its height under British rule, and the first self-sustaining farms in the state were established as well. From 1763 to 1780, Green Bay was a prosperous community which produced its own foodstuff, built graceful cottages and held dances and festivities.[18]
After Independence
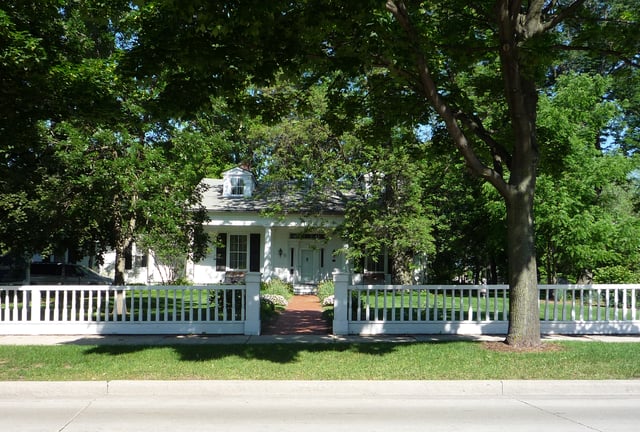

Built in 1837, the Hazelwood Historic House Museum is on the National Register of Historic Places and is now used as the Brown County Historical Society.[20]
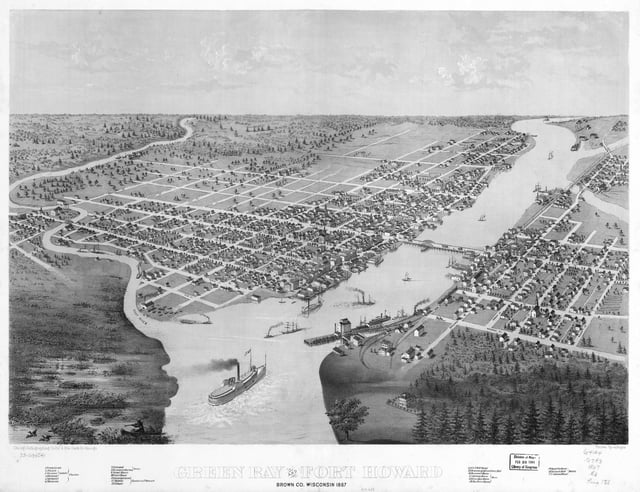
1867 bird's eye illustration of Green Bay
The Green Bay area was still under British control until the 1783 treaty formally ended the American Revolutionary War. Following the War of 1812, which in part was over disputes related to the border with Canada, the United States built Fort Howard on the Fox River in 1816 to protect its northern border.[16] Doty, Whitney, Arndt, Baird and Martin were among the many British-American settlers whose numbers pushed French culture into the background.[16] As British settlers in the area came to outnumber the French, they referred to the town as "Green Bay" (from the French: Baie Verte).
The Erie Canal was completed in 1825, linking New England with the Great Lakes. This led to the advance of Green Bay as a trading center. The end of the Black Hawk War in 1832 also gave impetus to settlement of the region. Most of the settlers were farmers from New England who began using the Erie Canal to pour into Wisconsin. As more and more New England settlers arrived, Green Bay developed into a trading center for this population.[19]
Wisconsin's first newspaper, The Green Bay Intelligencer, was started in 1833 by Albert Ellis and John V. Suydam. The borough of Green Bay, created in 1838, is the center of the present-day city. The borough combined the town of Astoria (a company town of the American Fur Company), with Navarino, platted by Daniel Whitney.[21] Before Wisconsin became a state in 1848, its commerce was based on the fur trade, which became dominated by John Jacob Astor's American Fur Company. After statehood, there was a shift away from fur trading toward lumbering. "For a short time in 1860s and 1870s, iron smelting in charcoal kilns rivaled the timber industry while the port handled increasing amounts of fuel, feed, and lumber. Today's major local industry had its start in 1865 when the first paper mill was built."[16]
By 1850 the town had a population of 1,923. The town was incorporated as the city of Green Bay in 1854. The Green Bay Area Public School District was founded in 1856.[16] Throughout the 1850s, word spread of America's cheap land and good soil, bringing in an influx of Belgian people, German, Scandinavian, Irish and Dutch immigrants, each adding to the culture. The greatest concentration of newcomers came from Belgium. They cleared the land to farm and build their homes.[16]
The railroad arrived in the 1860s. Chicago and Northwestern Railroad companies were formed, which allowed people and products to travel all over the state, increasing business and trade opportunities. The area was able to grow and enrich itself with the use of the river and the plentiful timber resources. This led to the paper industry becoming the major employer in Green Bay, and opened up the port for international trade.[12]
In 1934, President Franklin D. Roosevelt came to Green Bay to honor its tercentenary.[14] By 1950, the city had a population of 52,735. In 1964, the Town of Preble was consolidated with the city of Green Bay.[22]
Geography
Green Bay is in the northeastern part of Wisconsin at the mouth of the Fox River. Today, Interstate 43 meets Interstate 41 (also U.S. Route 41) in Green Bay, about 90 miles (140 km) north of Milwaukee.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 55.96 square miles (144.94 km2), of which, 45.47 square miles (117.77 km2) is land and 10.49 square miles (27.17 km2) is water.[23]
Climate
Green Bay has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfb),[24] with some moderation due to the city's proximity to Lake Michigan. Like other cities with this type of climate, there are four distinct seasons, often with severe or extreme variation between them in terms of temperature and precipitation. Green Bay experiences warm, humid, frequently hot summers and long, cold and snowy winters. The variance in temperature and precipitation between months is severe and often extreme. Tornadoes are rare in the Green Bay area, with the strongest being an F3 tornado that hit the community of Pittsfield on June 26, 1969.[25]
Monthly mean temperatures range from 16.6 °F (−8.6 °C) in January to 69.1 °F (20.6 °C) in July.[26] In July, the warmest month, the average high temperature is 81.2 °F (27.3 °C).[26] There are 6.1 days of 90 °F (32 °C)+ highs, 68 days where the high remains at or below freezing, and 19 days with sub-0 °F (−18 °C) lows annually. From December to February, even during thaws, the temperature rarely reaches 50 °F (10 °C). Extremes have ranged from −36 °F (−38 °C) on January 21, 1888 to 104 °F (40 °C) on July 13, 1936.
The wettest month in Green Bay is August, when 3.77 inches (95.8 mm) of precipitation falls, mostly in the form of rainfall from thunderstorms. The driest month in Green Bay is February, when the majority of precipitation falls as low moisture-content snow due to cold, dry air. On average, 1.01 inches (25.7 mm) of precipitation falls in February.
| Climate data for Green Bay, Wisconsin (Austin Straubel Int'l), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1886–present[1] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 56 (13) | 65 (18) | 82 (28) | 89 (32) | 99 (37) | 101 (38) | 104 (40) | 100 (38) | 97 (36) | 88 (31) | 74 (23) | 64 (18) | 104 (40) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 24.3 (−4.3) | 28.2 (−2.1) | 39.2 (4.0) | 53.9 (12.2) | 66.0 (18.9) | 75.3 (24.1) | 79.8 (26.6) | 77.7 (25.4) | 69.9 (21.1) | 56.6 (13.7) | 42.2 (5.7) | 28.5 (−1.9) | 53.5 (11.9) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 9.0 (−12.8) | 12.4 (−10.9) | 22.4 (−5.3) | 33.8 (1.0) | 44.0 (6.7) | 54.1 (12.3) | 58.4 (14.7) | 56.9 (13.8) | 48.5 (9.2) | 37.7 (3.2) | 26.9 (−2.8) | 14.4 (−9.8) | 34.9 (1.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −36 (−38) | −33 (−36) | −29 (−34) | 7 (−14) | 21 (−6) | 32 (0) | 40 (4) | 38 (3) | 24 (−4) | 8 (−13) | −12 (−24) | −27 (−33) | −36 (−38) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 1.13 (29) | 1.11 (28) | 1.85 (47) | 2.63 (67) | 2.93 (74) | 3.88 (99) | 3.50 (89) | 3.37 (86) | 3.04 (77) | 2.44 (62) | 2.13 (54) | 1.51 (38) | 29.52 (750) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 13.0 (33) | 9.9 (25) | 8.1 (21) | 2.9 (7.4) | 0.2 (0.51) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.2 (0.51) | 4.0 (10) | 13.1 (33) | 51.4 (131) |
| Average precipitation days(≥ 0.01 in) | 9.9 | 8.4 | 10.6 | 11.1 | 11.4 | 10.3 | 10.4 | 10.4 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 10.0 | 10.3 | 123.0 |
| Average snowy days(≥ 0.1 in) | 9.6 | 7.8 | 6.9 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 9.2 | 40.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74.0 | 73.5 | 72.8 | 67.0 | 65.9 | 68.9 | 71.3 | 75.1 | 76.5 | 74.4 | 76.9 | 77.3 | 72.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 146.7 | 159.8 | 198.6 | 222.1 | 285.1 | 302.8 | 314.5 | 278.7 | 205.2 | 158.0 | 107.4 | 112.3 | 2,491.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 51 | 55 | 54 | 55 | 62 | 65 | 67 | 64 | 55 | 46 | 37 | 41 | 56 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[26][27][28] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 2,276 | — | |
| 1870 | 4,698 | 106.4% | |
| 1880 | 7,476 | 59.1% | |
| 1890 | 9,069 | 21.3% | |
| 1900 | 23,748 | 161.9% | |
| 1910 | 25,216 | 6.2% | |
| 1920 | 31,643 | 25.5% | |
| 1930 | 37,407 | 18.2% | |
| 1940 | 46,205 | 23.5% | |
| 1950 | 52,735 | 14.1% | |
| 1960 | 62,952 | 19.4% | |
| 1970 | 87,829 | 39.5% | |
| 1980 | 87,947 | 0.1% | |
| 1990 | 96,466 | 9.7% | |
| 2000 | 102,313 | 6.1% | |
| 2010 | 104,057 | 1.7% | |
| Est. 2018 | 104,879 | [6] | 0.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[29] 2013 Estimate[30] | |||
2010 census
As of the census[5] of 2010, there were 104,057 people, 42,244 households, and 24,699 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,288.5 inhabitants per square mile (883.6/km2). There were 45,241 housing units at an average density of 995.0 per square mile (384.2/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 77.9% White, 3.5% African American, 4.1% Native American, 4.0% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 7.2% from other races, and 3.1% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 13.4% of the population.
There were 42,244 households of which 31.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 40.4% were married couples living together, 12.5% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.6% had a male householder with no wife present, and 41.5% were non-families. 32.4% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.39 and the average family size was 3.06.
The median age in the city was 33.7 years. 24.7% of residents were under the age of 18; 11.7% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 27.7% were from 25 to 44; 24.5% were from 45 to 64; and 11.3% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 49.4% male and 50.6% female.
2000 census
As of the census of 2000,[7] there were 102,313 people, 41,591 households, and 24,663 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,332.1 people per square mile (900.5/km2). There were 43,123 housing units at an average density of 982.9 per square mile (379.5/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 85.86% White, 1.38% African American, 3.28% Native American, 3.76% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 3.72% from other races, and 1.97% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 7.13% of the population.
There were 41,591 households of which 30.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 44.1% were married couples living together, 10.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.7% were non-families. About 31.6% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.40 and the average family size was 3.06.
In the city, the age distribution of the population shows 25.4% under the age of 18, 11.6% from 18 to 24, 31.7% from 25 to 44, 19.5% from 45 to 64, and 11.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33 years. For every 100 females, there were 97.2 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.8 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $38,820, and the median income for a family was $48,678. Males had a median income of $33,246 versus $23,825 for females. The per capita income for the city was $19,269. About 7.4% of families and 10.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 12.7% of those under the age of 18 and 9.2% of those 65 and older.
Government
Green Bay is governed by a mayor and a city council. The mayor is elected in a citywide vote. The city council consists of 12 members each elected from districts.
Mayors

City Hall

W. C. E. Thomas, first mayor of Green Bay

Chicago and North Western Railway Passenger Depot (Green Bay)

Austin Straubel International Airport

Brown County Courthouse.

Weidner Center, part of UW–Green Bay

Cathedral of Saint Francis Xavier

Lambeau Field
W. C. E. Thomas 1854
Francis X. Desnoyers 1855
H. E. Eastman 1856, 1857
Burley Follett 1858, 1863
Nathan Goodell 1859, 1864
E. H. Ellis 1860
Henry S. Baird 1861, 1862
M. P. Lindsley 1865
Charles D. Robinson 1866, 1872
James S. Marshall 1868
Anton Klaus 1868-1870
Alonzo Kimball 1871, 1873
Dr. C. E. Crane 1874-1875; 1877-1879
F. S. Ellis 1876
J. C. Neville 1880
W. J. Abrams 1881, 1883-1884
J. H. M. Wigman 1882
Charles Hartung 1885-1887
Arthur C. Neville 1888-1889
James H. Elmore 1890-1895
Frank B. Desnoyers 1896-1898
Simon J. Murphy Jr. 1899-1901
J. H. Tayler 1902-1903
Robert E. Minahan 1904−1907
Winford Abrams 1908−1916
Elmer S. Hall 1916−1920
Wenzel Wiesner 1921−1927
James H. McGillan 1927−1929
John V. Diener 1929−1937
John S. Farrell 1937−1938
Alex Biemeret 1938−1945
Dominic Olejniczak 1945−1955
Otto Rachals 1955−1959
Roman Denissen 1959−1965
Donald Tilleman 1965−1972
Harris Burgoyne 1972−1973
Thomas Atkinson 1973−1975
Michael Monfils 1975−1979
Samuel J. Halloin 1979−1995
Paul Jadin 1995−2003
Jim Schmitt 2003−2019
Eric Genrich 2019−
Green Bay is represented by Mike Gallagher (R) in the United States House of Representatives, and by Ron Johnson (R) and Tammy Baldwin (D) in the United States Senate. André Jacque (R), Robert Cowles (R), and Dave Hansen (D) represent Green Bay in the Wisconsin State Senate, and David Steffen (R), John Macco (R), and Staush Gruszynski (D) represent Green Bay in the Wisconsin State Assembly.
Law enforcement
The Green Bay Police Department was established in on August 27, 1857, when the Green Bay Police Corps was established, and Henry Baird was named Chief of Police. The Green Bay Police Department provides many specialized services such as a Dive Team, Harbor Patrol, Motorcycle Patrol, and a S.W.A.T. Team.
Since the establishment of the Green Bay Police Department, one officer has died in the line of duty.[31]
Infrastructure
Transportation
Railroads
From 1896 to 1993 the city was the headquarters of the Green Bay and Western Railroad. In 1993, the line was purchased by the Wisconsin Central. In 2001, the WC was merged into the Canadian National Railway. The Chicago and North Western Railway also served Green Bay and its depot still stands. Green Bay was last served with a regular passenger train, the CNW's Peninsula 400, in 1971. The CNW sold its trackage from Green Bay south to Sheboygan in 1987 to the Fox River Valley Railroad, which became part of the WC in 1993. Green Bay also saw passenger service from the Milwaukee Road's Chippewa-Hiawatha, which ran from Chicago into the upper peninsula of Michigan. Green Bay is also served by the Escanaba and Lake Superior Railroad.
Airport
Green Bay is served by Green Bay–Austin Straubel International Airport, located in Ashwaubenon just west of the city.
Highways
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/66/I-43.svg/25px-I-43.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/66/I-43.svg/38px-I-43.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/66/I-43.svg/50px-I-43.svg.png 2x|I-43.svg|h25|w25]] I-43 Northbound terminates at the northwestern side of Green Bay. Southbound continues to Manitowoc and Milwaukee.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/58/I-41.svg/25px-I-41.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/58/I-41.svg/38px-I-41.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/58/I-41.svg/50px-I-41.svg.png 2x|I-41.svg|h25|w25]] I-41 Northbound terminates at the northwestern side of Green Bay. Southbound continues to Appleton and Milwaukee.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/US_41.svg/25px-US_41.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/US_41.svg/38px-US_41.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/US_41.svg/50px-US_41.svg.png 2x|US 41.svg|h25|w25]] US 41 travels towards Marinette, and south concurrently with I-41.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6d/US_141.svg/25px-US_141.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6d/US_141.svg/38px-US_141.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6d/US_141.svg/50px-US_141.svg.png 2x|US 141.svg|h20|w25]] US 141 begins east of Green Bay in Bellevue, and continues north towards Crivitz.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/13/WIS_29.svg/25px-WIS_29.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/13/WIS_29.svg/38px-WIS_29.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/13/WIS_29.svg/50px-WIS_29.svg.png 2x|WIS 29.svg|h25|w25]] WIS 29 travels east towards Kewaunee, and west towards Shawano and Wausau.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d5/WIS_32.svg/25px-WIS_32.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d5/WIS_32.svg/38px-WIS_32.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d5/WIS_32.svg/50px-WIS_32.svg.png 2x|WIS 32.svg|h25|w25]] WIS 32 travels north towards Pulaski, and south towards Chilton and Milwaukee.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/61/WIS_54.svg/25px-WIS_54.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/61/WIS_54.svg/38px-WIS_54.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/61/WIS_54.svg/50px-WIS_54.svg.png 2x|WIS 54.svg|h25|w25]] WIS 54 travels east to Algoma, and west towards Seymour.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/WIS_57.svg/25px-WIS_57.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/WIS_57.svg/38px-WIS_57.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/WIS_57.svg/50px-WIS_57.svg.png 2x|WIS 57.svg|h25|w25]] WIS 57 travels north towards Sturgeon Bay, and south towards Milwaukee.
[[INLINE_IMAGE|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/WIS_172.svg/25px-WIS_172.svg.png|//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/WIS_172.svg/38px-WIS_172.svg.png 1.5x, //upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/WIS_172.svg/50px-WIS_172.svg.png 2x|WIS 172.svg|h25|w25]] WIS 172 begins at I-43 and travels west to Hobart.
Local transit
Green Bay Metro provides mass transit bus service throughout Green Bay and the surrounding suburbs.
Jefferson Lines, Indian Trails, and Lamers Bus Lines provide intercity transportation from the central Green Bay Metro station which is downtown.
Water
Utilities
Electricity
Green Bay is served by Wisconsin Public Service Corporation, which operates the J. P. Pulliam Generating Station within the city.[33]
Water
Water service is provided to the city by the Green Bay Water Utility.[34]
Sewer service is provided by the Green Bay Metropolitan Sewerage District, also known as NEW Water.[35]
Health care
Green Bay is the headquarters of Bellin Health and Prevea Health, regional health care providers.[36]
Green Bay is home to four hospitals: Aurora Baycare Medical Center, Bellin Hospital, St. Mary's Hospital Medical Center, and St. Vincent Hospital.
Green Bay is also home to the Milo C. Huempfner VA Outpatient Clinic, and Bellin Psychiatric Center and Willow Creek Behavioral Health, the city's two psychiatric hospitals.[37]
Education
Green Bay is served by the Green Bay Area Public School District. It operates twenty-five elementary schools, two K-8 schools, four middle schools, four high schools, and one alternative school in the city and surrounding area. Two of the city's high schools, East High School and West High School, have Wisconsin's longest consecutively-played high school football rivalry, played since 1905. Private schools in Green Bay include Notre Dame de la Baie Academy, Northeastern Wisconsin Lutheran High School, and Bay City Baptist School.
Higher education
Green Bay area colleges and universities:
Public libraries
The Brown County Library (BCL) Central Branch is downtown in downtown Green Bay and has served as the county public library since 1968. The Central Branch is the headquarters for the BCL system, which encompasses all public libraries in Brown County, including eight branch libraries and a bookmobile that regularly visits locations throughout the county. In 1994, the Brown County Library was named Wisconsin Library of the Year.[42]
Religion
In 2000, the American Religion Data Archive reported Green Bay to be predominantly Catholic (71.5%), with Lutherans composing an additional 16.4%. The remaining 12% is almost entirely made-up of other Protestant denominations.[43]
Christ the King Lutheran Church is a church of the Evangelical Lutheran Synod in Green Bay.[49]
The city is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Green Bay. The Cathedral of Saint Francis Xavier in Green Bay is the mother church of the Diocese which is in the province of the Archdiocese of Milwaukee. The Saint Joseph Oratory is in Green Bay. St. Mary of the Angels Church and Monastery is also located in the city.
The Islamic Society of Wisconsin, Green Bay serves the Islamic community. The Green Bay Area Unitarian Universalist Fellowship is in the city. Congregation Cnesses Israel Temple, serving the area's Jewish population, is on the city's east side.
Sports

The Resch Center
| Club | Sport | Founded | Current League | Stadium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Bay Packers | Football | 1919[50] | National Football League | Lambeau Field |
| Green Bay Blizzard | Indoor Football | 2003 | Indoor Football League | Resch Center |
| Green Bay Phoenix (University of Wisconsin-Green Bay) | 15 Varsity teams | 1965 | Horizon League | Resch Center, Kress Events Center, Aldo Santaga Stadium |
| St. Norbert Green Knights (St. Norbert College) | 18 Varsity teams | 1898 | Midwest Conference and Northern Collegiate Hockey Association | Schneider Stadium, Mel Nicks Sports Complex, Schuldes Center, Cornerstone Community Ice Center |
| Green Bay Booyah | Summer College baseball | 2007 | Northwoods League | Capital Credit Union Park |
| Green Bay Gamblers | Junior Ice hockey | 1994 | United States Hockey League | Resch Center |
| Green Bay Voyageurs FC | Soccer | 2018 | USL League Two | Capital Credit Union Park |
Other major sporting events in Green Bay include the Bellin Run and the Cellcom Green Bay Marathon.
Arts and culture
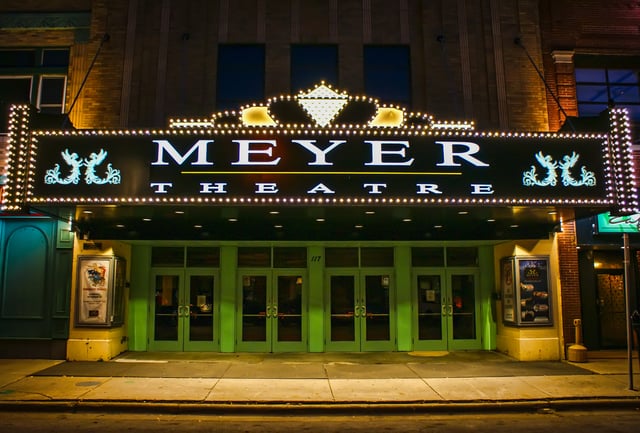

The Meyer Theatre
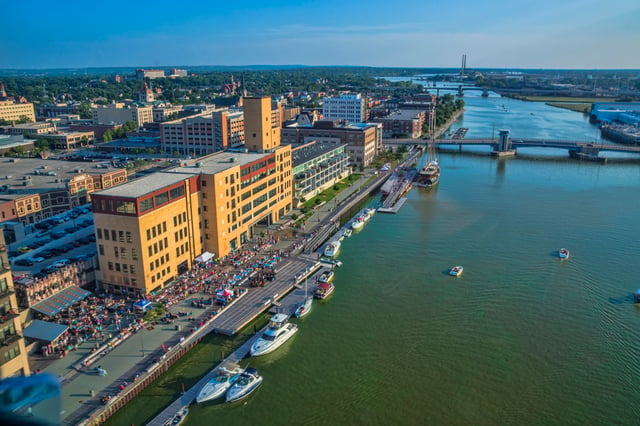

Downtown Green Bay CityDeck along the Fox River
The Meyer Theatre and the Hotel Northland are on the National Register of Historic Places. The Northland was once the largest hotel in Wisconsin.[51]
Daddy D Productions perform at Riverside Ballroom and Let Me Be Frank Productions perform at the Meyer Theatre.[52] The Civic Symphony of Green Bay performs at the Meyer Theatre, its home venue. The former Green Bay Symphony Orchestra disbanded after their 2014–2015 season, after performing for over 100 years, citing financial difficulties.[53]
Performance venues in Green Bay include: Lambeau Field, Resch Center, Weidner Center, the Meyer Theatre, and The Tarlton Theatre.
The Art Garage and the Automotive Gallery are art galleries in the downtown area.[52]
Museums in the city include the Neville Public Museum and the Hazelwood Historic House Museum.[52]
Every summer, the downtown area plays host to ArtStreet, an art festival featuring studio displays, demonstrations, and live entertainment.[54] Dine on the Deck is an event that allows patrons to dine on the CityDeck and features dishes from local restaurants.[55] Taste on Broadway has live entertainment and dishes served by local restaurants who compete for awards.[56] The Broadway Neighborhood association hosts a farmer's market every Wednesday from May to October.
Media and internet

WBAY-TV studio.
Television stations in Green Bay are WBAY (2), (ABC); WFRV (5), (CBS); WLUK (11), (FOX); WCWF (14), (CW); WGBA (26), (NBC); WACY (32), (MNT); and WPNE (38), a PBS affiliate. Green Bay is served by the Green Bay Press-Gazette and The Press Times[57][58], a new locally-published weekly newspaper introduced on March 1, 2019. Another local newspaper, the Green Bay News-Chronicle, ceased publication in 2005.
The free public Wi-Fi system in the downtown Green Bay Broadway District went into operation in 2007.[59]
Economy
Industry
Green Bay is known as the "Toilet Paper Capital of the World" because of the prevalence of the paper industry in the city.[60] Northern Paper Company, Fort Howard Paper Company, and Hoberg Paper Company were among Green Bay's first paper companies. Northern Paper Company offered the first splinter-free toilet paper in the early 1930s.[61] The presence of the paper industry helped Green Bay avoid the worst effects of the Great Depression.[62] Today, major paper producers include Georgia-Pacific,[63] Procter & Gamble,[64] and Steen-Macek Paper Company.[65]
Among the earliest packing companies in Green Bay were Acme Packing Company and Indian Packing Company, the namesake of the Green Bay Packers.[66] Today, major meatpackers in the city include JBS S.A. (formerly Packerland Packing)[67] and American Foods Group.
Largest employers
As of 2017, the largest employers in the city were:[68]
| Employer | of Employees | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Humana | 3,133 |
| 2 | Bellin Health | 2,892 |
| 3 | Oneida Nation of Wisconsin | 2,752 |
| 4 | Schneider National | 2,628 |
| 5 | Aurora BayCare Medical Center | 2,305 |
| 6 | Georgia-Pacific | 2,875 |
| 7 | UnitedHealth Group | 1,730 |
| 8 | Green Bay Packaging | 1,575 |
| 9 | St. Vincent Hospital | 1,563 |
| 10 | American Foods Group | 1,520 |
Other major employers include Associated Banc-Corp, Green Bay Area Public School District, Shopko, JBS USA, Expert Global Solutions, Walmart, Procter & Gamble, Schreiber Foods, the Green Bay Packers, Nature's Way, HJ Martin and Son, and Nicolet National Bank.[69]
Points of interest
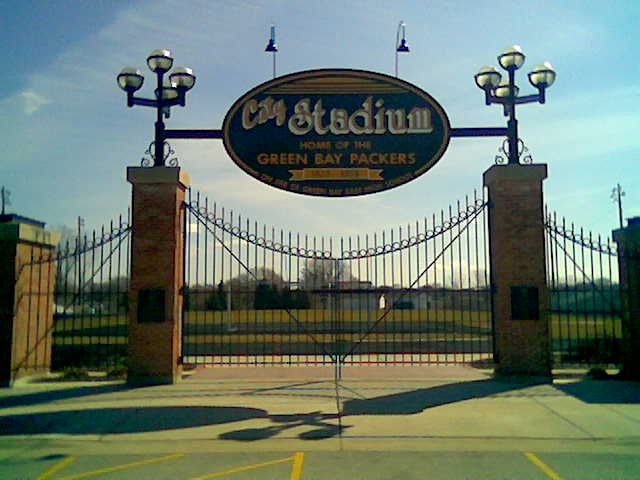

Modern-day Old City Stadium
Bay Beach Amusement Park
Bay Beach Wildlife Sanctuary
City Stadium, former home of the Packers
Cofrin Memorial Arboretum
Fox River State Recreational Trail
Green Bay Botanical Garden
Heritage Hill State Park
Joannes Stadium
The Broadway District
Lambeau Field, home of the Green Bay Packers
Meyer Theatre
National Railroad Museum in the Ashwaubenon suburb
Neville Public Museum of Brown County
Northeast Wisconsin Technical College
NEW Zoo
Packers Heritage Trail
Resch Center, home of the Green Bay Blizzard and Green Bay Gamblers
Weidner Center
Shopping
Green Bay has one enclosed shopping mall, East Town Mall, located within the city. The Bay Park Square shopping mall is located in the suburb of Ashwaubenon. The city was home to the first Shopko discount department store, it closed on April 22, 2019.[70]
















