Gnome-Rhône 14N
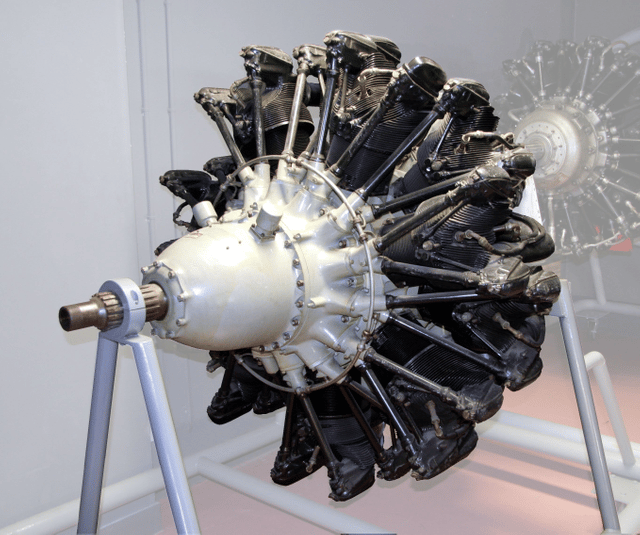
Gnome-Rhône 14N

| Gnome-Rhône 14N | |
|---|---|
| Type | Radial engine |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Gnome et Rhône |
| First run | 1937 |
| Major applications | Bloch MB.150 Messerschmitt Me 323 Amiot 351 Lioré et Olivier LeO 45 |
| Developed from | Gnome-Rhône Mistral Major |
| Developed into | Gnome-Rhône 14M |
The Gnome-Rhône 14N was a 14-cylinder two-row air-cooled radial engine designed and manufactured by Gnome-Rhône. A development of the pre-war Gnome-Rhône 14K, the 14N was used on several French and German aircraft of World War II.
| Gnome-Rhône 14N | |
|---|---|
| Type | Radial engine |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Gnome et Rhône |
| First run | 1937 |
| Major applications | Bloch MB.150 Messerschmitt Me 323 Amiot 351 Lioré et Olivier LeO 45 |
| Developed from | Gnome-Rhône Mistral Major |
| Developed into | Gnome-Rhône 14M |
Design and development
Facing criticisms over the 14K's reliability, Gnome-Rhône undertook a major upgrade of its 14-cylinder design, using different materials for the pistons and valves, and enlarging cooling surfaces by 39%.
The new 14N was introduced in 1937 and was quickly adopted on several aircraft models. In 1939, minor improvements allowed Gnome-Rhône to increase the compression ratio from 6.1:1 to 6.8:1, which resulted in increased power for wartime production aircraft.
The 14N was further developed into the Gnome-Rhône 14R featuring a 2-stage supercharger, but this type was not widely used until after World War II as production of improved engines was prohibited by the terms of the armistice with Germany.
Postwar the 14R was developed into a 28 cylinder high capacity engine as the Gnome-Rhône 28T-1 , essentially two 14R-24 engines back to back driving co-axial contra-rotating propeller shafts.[1]
Variants
- 14N-2LH rotation, 770 kW (1,050 PS)14N-3RH rotation version of -214N-10LH rotation, 670 kW (910 PS)14N-11RH rotation version of -1014N-16LH rotation, 688 kW (935 PS)14N-17RH rotation version of -1614N-20LH rotation, 835 kW (1,135 PS)14N-21RH rotation version of -2014N-44LH rotation, 770 kW (1,050 PS)14N-45RH rotation version of -4414N-48LH rotation, 870 kW (1,180 PS)14N-49RH rotation version of -4814N-50LH rotation, 1,000 kW (1,400 PS)14N-54LH rotation, 920 kW (1,250 PS)14N-55RH rotation version of -5414N-58LH rotation, 870 kW (1,180 PS)14N-59RH rotation version of -58
Applications
Amiot 351
Amiot 354
Bloch MB.131
Bloch MB.151
Bloch MB.152
Bloch MB.155
Bloch MB.170
Bloch MB.174
Bloch MB.175
Bloch MB.220
Breguet 891R Mars (2 × 14R)
Farman F.222
Latécoère 611
Sud-Est SE.161 Languedoc
Messerschmitt Me 323
Koolhoven F.K.58
PZL P.24
PZL.43 Karaś
SNCAO CAO.700 (2X 14N-48 + 2x 14N-49)
Specifications (14N-48)
Data from Aircraft engines of the World 1945[2]
General characteristics
Type: Fourteen-cylinder two-row air-cooled piston engine
Bore: 146 mm (5.75 in)
Stroke: 165 mm (6.50 in)
Displacement: 38.67 l (2,360 cu in)
Length: 1,480 mm (58.27 in)
Diameter: 1,290 mm (50.79 in)
Dry weight: 620 kg (1,370 lb)
Components
Valvetrain: Two inlet and two exhaust overhead valves per cylinder
Supercharger: Single-stage single-speed centrifugal type supercharger
Fuel system: Stromberg carburetor
Fuel type: 87 octane rating gasoline
Oil system: Pressure fed at 480 kPa (70 psi)
Cooling system: Air-cooled
Reduction gear: 0.5:1 planetary reduction gearing
Performance
Power output:
Take-off: 870 kW (1,180 PS) at 2,650 rpm
Military: 780 kW (1,060 PS) at 2,400 rpm at 3,900 m (12,800 ft)
Cruise: 630 kW (850 PS) at 2,100 rpm at 3,900 m (12,800 ft)
Specific power: 22.45 kW/l (0.49 hp/in³)
Compression ratio: 6.8:1
Power-to-weight ratio: 1.4 kW/kg (0.85 hp/lb)
See also
Pratt & Whitney R-1830 a comparable engine sometimes fitted as an alternative to the 14N on French designs
BMW 801
Bristol Hercules
Bristol Taurus
Fiat A.74
Mitsubishi Kinsei
Nakajima Sakae
Piaggio P.XIX
Shvetsov ASh-82
Tumansky M-88
Wright R-2600