Danish Museum of Art & Design
Danish Museum of Art & Design

Designmuseum Danmark | |
 The facade towards Bredgade | |
| Established | 1907 |
|---|---|
| Location | 68 Bredgade Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Coordinates | 55°41′10.95″N 12°35′36.06″E [9] |
| Director | Anne-Louise Sommer |
| Website | Official website [10] |

Ticket-pin

The courtyard in front of the museum by night
The Danish Museum of Art & Design (formerly, Danish Museum of Decorative Art; Danish: Kunstindustrimuseet) is a museum in Copenhagen for Danish and international design and crafts. It features works of famous Danish designers like Arne Jacobsen, Jacob Jensen and Kaare Klint, who was one of the two architects who remodeled the former Frederiks Hospital (built 1752–57) into a museum in the 1920s. The exhibition also features a variety of Chinese and German porcelain.
The museum houses the biggest library for design in Scandinavia. It also hosts a fully annotated and illustrated database of all furniture made in Denmark from 1900 to 2000, originally compiled by Reese and Marilyn Palley and later donated to and further developed by the museum.
Designmuseum Danmark | |
 The facade towards Bredgade | |
| Established | 1907 |
|---|---|
| Location | 68 Bredgade Copenhagen, Denmark |
| Coordinates | 55°41′10.95″N 12°35′36.06″E [9] |
| Director | Anne-Louise Sommer |
| Website | Official website [10] |
History
The museum was founded in 1890 at the initiative of, among others, Industriforeningen. A purpose-built building designed by Vilhelm Klein and located next to Industriforeningen's premises on City Hall Square was completed in 1894 and opened to the public the following year. The exhibitions were housed in separate galleries, each dedicated to a particular field such as porcelain, faience, silver, furniture, glass and textiles. This arrangement reflected the primary aim of the museum which was to serve as a source of inspiration for craftsmen and manufacturers by highlighting the very best in craftsmenship and design from different ages.[1]
In 1926 the museum moved to its current building, the defunct Frederick's Hospital from 1757, a gift from the banker Emil Glückstadt. The architects Kaare Klint and Ivar Bentsen had undertaken the necessary alterations and furnishings.[1]
Collections
Library and archives
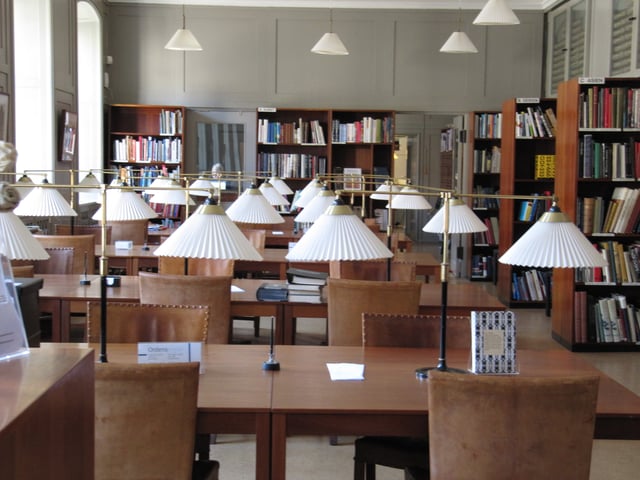

The Kaare Klint-designed reading room
The museum is home to the largest library in Scandinavia dedicated to decorative arts and industrial design.[2] Open to the general public, the library is at once a museum library, research library, and Danish central library within its field. Opening hours are Tuesday–Friday from 11–17. The library contains more than 1,000 journals. The latest issues of the 75 journals and magazines which the museum subscribes to can be read in the library's reading room.[3]
The reading room of the library hosts public lectures on design-related topics which draw upon the collections in both the museum and the library.[4]
The Danish Design Archive and the Poster Collection are located on the museum's first floor.
Auditorium
The museum has a small auditorium on the first floor seating 120 people. It is rented out for lectures, concerts, receptions and other events.[5]
Cultural references
In the first Olsen Gang film, Bredgade 68 is where the Olsen Gang steals the golden statue.[6]
See also
David Collection
Danish Design Centre
Danish design
Danish modern
List of museums in Denmark