BL 6 inch gun Mk II – VI

BL 6 inch gun Mk II – VI

| Ordnance BL 6-inch gun Mks II, III, IV, VI | |
|---|---|
| Type | Naval gun Coast defence gun |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1880 – 1905 |
| Used by | Royal Navy |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Royal Gun Factory (RGF) |
| Manufacturer | RGF and EOC |
| Variants | Mks II, III, IV, VI |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Mk II : 81 cwt or 89 cwt (4½ tons)[2] Mks III, IV, VI : 5 tons barrel & breech[3] |
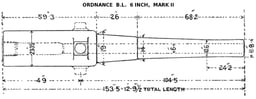
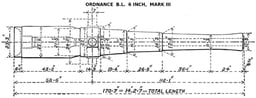
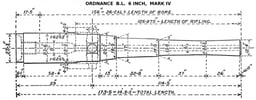
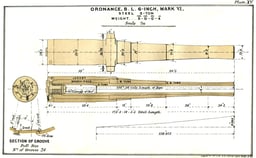
| Barrel length | Mk III : 153.2 inches (3,891 mm) (25.53 calibres) Mk IV, VI : 156 inches (3,962 mm) (26 calibres)[4] |
| Shell | 100 pounds (45.36 kg)[4] |
| Calibre | 6-inch (152.4 mm) |
| Breech | 3 motion interrupted screw. De Bange obturation. |
| Muzzle velocity | Mk III, IV, VI : 1,960 feet per second (597 m/s)[5] QFC guns : 1,913 feet per second (583 m/s)[6] BLC guns : 2,166 feet per second (660 m/s)[7] |
| Maximum firing range | 10,000 yards (9,100 m)[8] |
The BL 6-inch gun Marks II, III, IV and VI[1] were the second and subsequent generations of British 6-inch rifled breechloading naval guns, designed by the Royal Gun Factory in the 1880s following the first 6-inch breechloader, the relatively unsuccessful BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun designed by Elswick Ordnance. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants but from the mid-1890s onwards were adapted to use the new cordite propellant. They were superseded on new warships by the QF 6-inch gun from 1891.
| Ordnance BL 6-inch gun Mks II, III, IV, VI | |
|---|---|
| Type | Naval gun Coast defence gun |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1880 – 1905 |
| Used by | Royal Navy |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Royal Gun Factory (RGF) |
| Manufacturer | RGF and EOC |
| Variants | Mks II, III, IV, VI |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Mk II : 81 cwt or 89 cwt (4½ tons)[2] Mks III, IV, VI : 5 tons barrel & breech[3] |
| Barrel length | Mk III : 153.2 inches (3,891 mm) (25.53 calibres) Mk IV, VI : 156 inches (3,962 mm) (26 calibres)[4] |
| Shell | 100 pounds (45.36 kg)[4] |
| Calibre | 6-inch (152.4 mm) |
| Breech | 3 motion interrupted screw. De Bange obturation. |
| Muzzle velocity | Mk III, IV, VI : 1,960 feet per second (597 m/s)[5] QFC guns : 1,913 feet per second (583 m/s)[6] BLC guns : 2,166 feet per second (660 m/s)[7] |
| Maximum firing range | 10,000 yards (9,100 m)[8] |
Development history

Seen mounted on a sponson on third class cruiser HMS Cossack circa. 1900
These were Royal Gun Factory designs, although they were also manufactured by Elswick Ordnance.
Mark II
Mk II followed the early weakly made and less powerful Mark I 80-pounder and introduced a 100-pound projectile, which became standard for British 6-inch guns until 1930. It consisted of a much thicker steel barrel with wrought-iron jackets shrunk over it and as originally introduced weighed 81 cwt (9720 pounds). The gun proved to be too weakly constructed, and 5 steel chase hoops were added to strengthen it and the gun was shorted by 12 inches to rebalance it, resulting in a bore length of 144 inches (24 calibres) and final weight of 89 cwt (9968 pounds), or 4½ tons. These guns were relegated to non-firing drill use following a burst gun incident on HMS Cordelia in June 1891.[9]
Marks III, IV, VI
Mark III finally introduced an all-steel construction, with a steel barrel and steel breech-piece and hoops shrunk over it, weighing 89 cwt (4½ tons). However, as originally introduced Mk III was still limited to weak charges and low muzzle velocity, and most guns were strengthened by being chase-hooped to allow a full powder charge of 48 lb gunpowder and muzzle velocity of 1,960 feet per second. This brought the gun weight up to 100 cwt (5 tons).[10]
Mk IV incorporated the improvements to Mk III. Mk VI differed from Mk IV only in having slightly simplified construction.
Marks III, IV and VI became the most commonly deployed versions, and their widespread adoption would indicate they were considered successful. Marks III, IV and VI were interchangeable and had the same performance. They are generally referred to as "6-in 5-ton B.L.R." in contemporaneous publications such as Brassey's Naval Annual.
Guns equipped the following British warships :
Comus-class corvettes and Calypso-class corvettes, laid down 1878 : Mk II
Admiral-class battleships laid down 1880
Imperieuse-class cruisers laid down 1881
Colossus-class battleships of 1882
Leander-class cruisers of 1882
HMS Hotspur as re-gunned in 1883 : Mk II
Victoria-class battleships laid down 1885
Orlando-class cruiser laid down 1885
HMS Bellerophon as re-gunned in 1885
Mersey-class cruiser of 1885
Conqueror-class ironclad turret ships completed 1886–1888 : Mk II
Marathon-class cruisers laid down 1887
HMS Rupert as re-gunned in 1887
Archer-class cruiser, launched in 1888
Bacchante-class corvettes as re-gunned in the 1880s : Mk II
QFC conversion
From 1895 many ships' guns were converted to QF to use the same brass cartridge case and charge as the modern QF 6-inch guns. They were designated QFC for "QF Converted", and the new Mark designation began at I over the old gun Mark e.g. I/IV was the first version of Mk IV gun converted to QFC, II/VI was the second version of Mk VI gun converted.
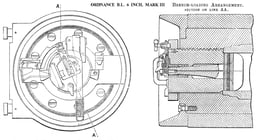
Coast defence gun

Mk IV or VI gun on disappearing mounting under construction at the Royal Carriage Factory, Woolwich, 1890s

A Mark II and a Mark IV (a Mk VII is mounted, behind), awaiting restoration at the Bermuda Maritime Museum, in the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda.
Mk IV and VI guns were widely used in coast defence around the British Empire, both on hydro-pneumatic disappearing mountings and Vavasseur slides (inclined slides that absorbed recoil).
A small number of Mk IV and VI guns had their old 3-motion breeches replaced by modern single-motion types and the chamber lengthened to accept a more powerful cartridge, and became the BLC (breech-loading converted) coast defence gun in 1902. They attained a maximum range of 12,000 yards (11,000 m) using a 20 lb (9.1 kg) 15 oz cordite cartridge. They were replaced by the modern 6-inch (150 mm) Mk VII as they became available, and were declared obsolete in 1922.[11]
BLC Siege gun
Mk IV and VI BLC guns were also fitted out with wagons in 1902 to allow them to be transported as semi-mobile siege guns – the gun and siege platform were transported as separate loads, the siege platform was assembled at the firing site and the gun mounted on it. When World War I broke out in 1914, 2 batteries of these BLC siege guns were equipped with primitive wheeled gun carriages with traction engine wheels and sent to France as heavy field guns. They were towed by steam traction engines. They had limited recoil buffers and required chocks in front and behind the wheels when firing. These guns had a maximum range of 14,200 yards. They were soon replaced in action as guns in 1915 by the more modern 6-inch Mk VII[12] and were then converted into 8-inch howitzers.
World War I conversion to 8-inch howitzer
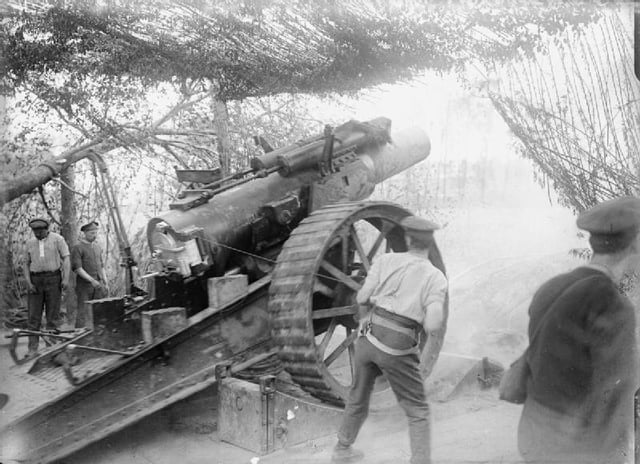

As converted to 8-inch howitzer
Britain was desperately short of heavy field artillery at the beginning of World War I, and in 1915 old BL 6-inch naval guns were shortened and bored-out to produce BL 8-inch howitzers as follows :[13]
12 BLC guns Mk I/IV became 8-inch howitzer Mk I
6 BL Mk IV and VI guns became 8-inch Howitzer Mk II
6 BL MK IV and VI guns, but adapted for different carriage, became 8-inch howitzer Mk III
8 BLC Mk I/VI adapted for Mk IV carriage became 8-inch howitzer Mk IV
Mk V
Mk V was a longer (30-calibres, 183.5 inch bore) unrelated Elswick Ordnance export gun.
Image gallery
See also
List of naval guns
Weapons of comparable role, performance and era
6"/30 caliber gun approximate US equivalent